
FDA
FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 - Laser Product Performance Standards

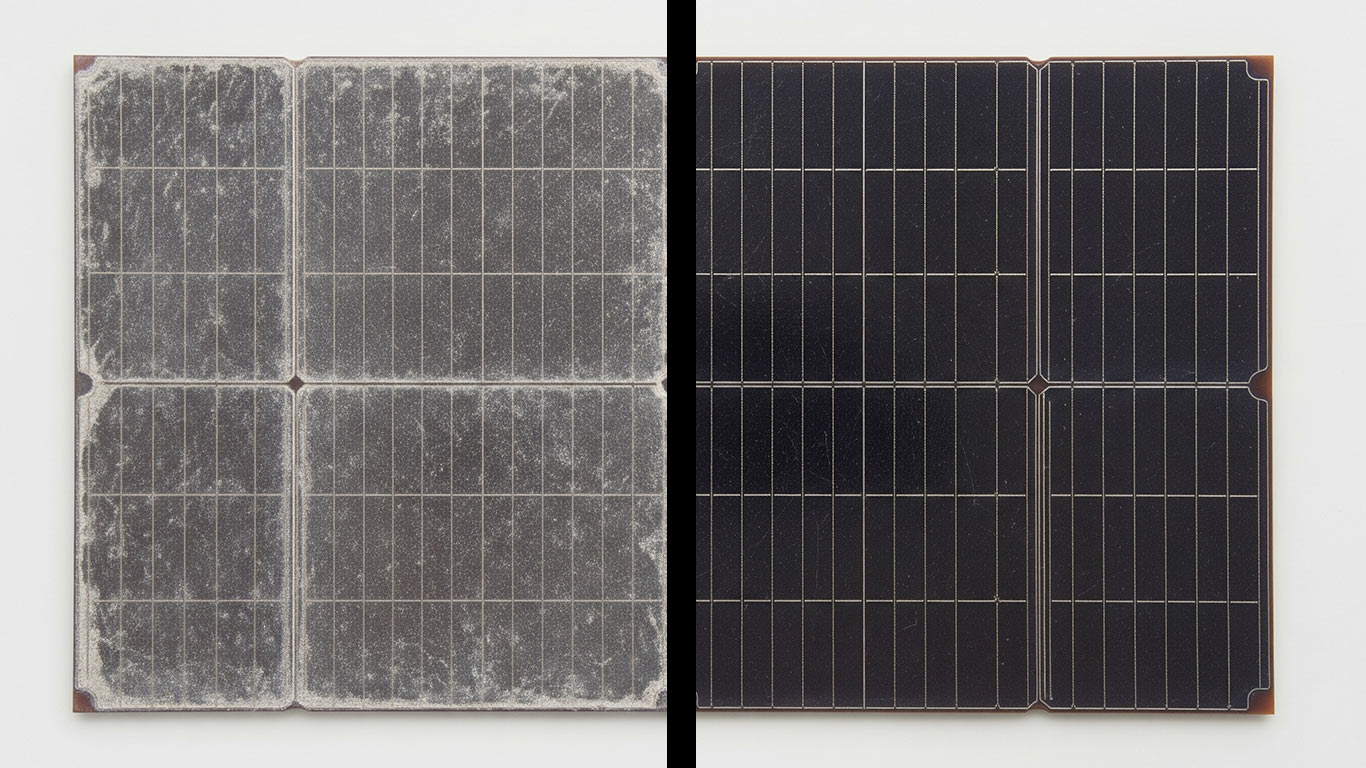

For laser cleaning Gallium Arsenide, begin with low power to protect its delicate semiconductor structure from damage, then slowly raise the power to strip away contaminants while keeping high electron mobility intact for solid electronics reliability
Under the microscope at high magnification, we see the gallium arsenide surface covered in scattered dark spots and uneven patches. These contaminants cling tightly, creating rough textures that obscure the material's natural shine. We've found this buildup often hides fine details, making the whole area look dull and irregular.
After laser treatment, the same surface appears smooth and uniformly bright across the view. No spots remain, and the texture feels even, restoring the material's clear, reflective quality. In our experience, this

FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 - Laser Product Performance Standards

ANSI Z136.1 - Safe Use of Lasers

IEC 60825 - Safety of Laser Products

OSHA 29 CFR 1926.95 - Personal Protective Equipment
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more