
FDA
FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 - Laser Product Performance Standards

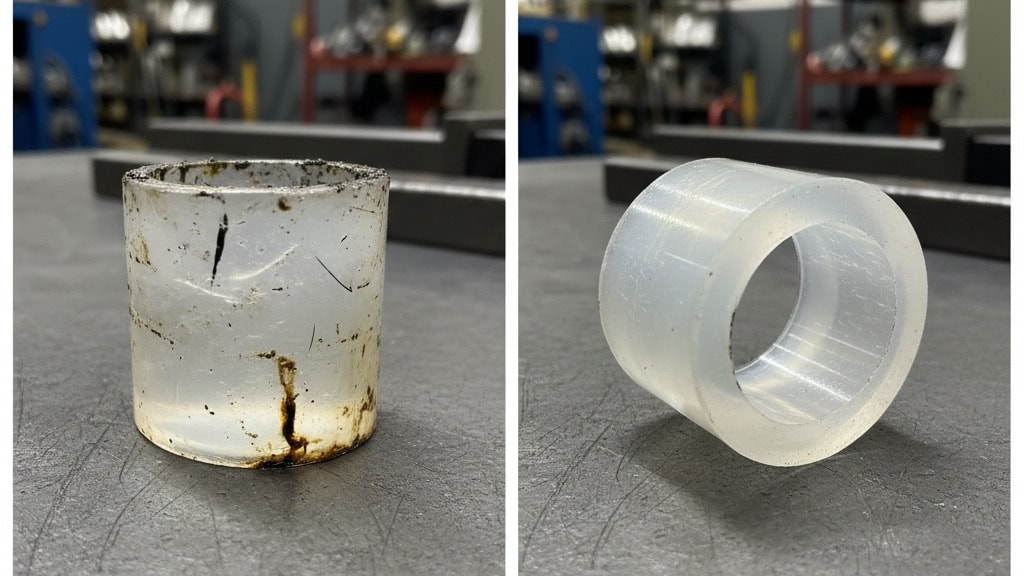

PET exhibits non-porous and smooth characteristics, so laser cleaning removes contaminants effectively from surfaces without damaging underlying structure.
When you examine the contaminated PET surface up close, you spot irregular patches of grime and tiny debris scattered everywhere. Dust particles cling tightly to the uneven texture, making the whole area look dull and cluttered. This buildup hides the material's natural smoothness beneath layers of residue.
After laser treatment, you notice the PET surface turns remarkably even and clear overall. The grime vanishes completely, leaving behind a polished finish without any visible spots. Now the texture appears uniform and bright, ready for practical
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more