


Epoxy Resin Deposits
Epoxy residue differs from inorganic contaminants so laser cleaning faces unique challenges. Formation occurs during adhesive curing and leaves sticky layers on metal surfaces. These layers bond tightly because of polymer chains. Removal demands precise pulses to avoid substrate damage. After exposure, residue hardens unevenly on composites and resists ablation. So, multi-pass treatments apply for complete elimination. Surface exhibits residue patches during inspections. Buildup forms irregularly on polymers because heat alters epoxy flow. Cleaning achieves better results on metals yet struggles with flexible materials. Process removes organic films effectively in observations.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Bronze
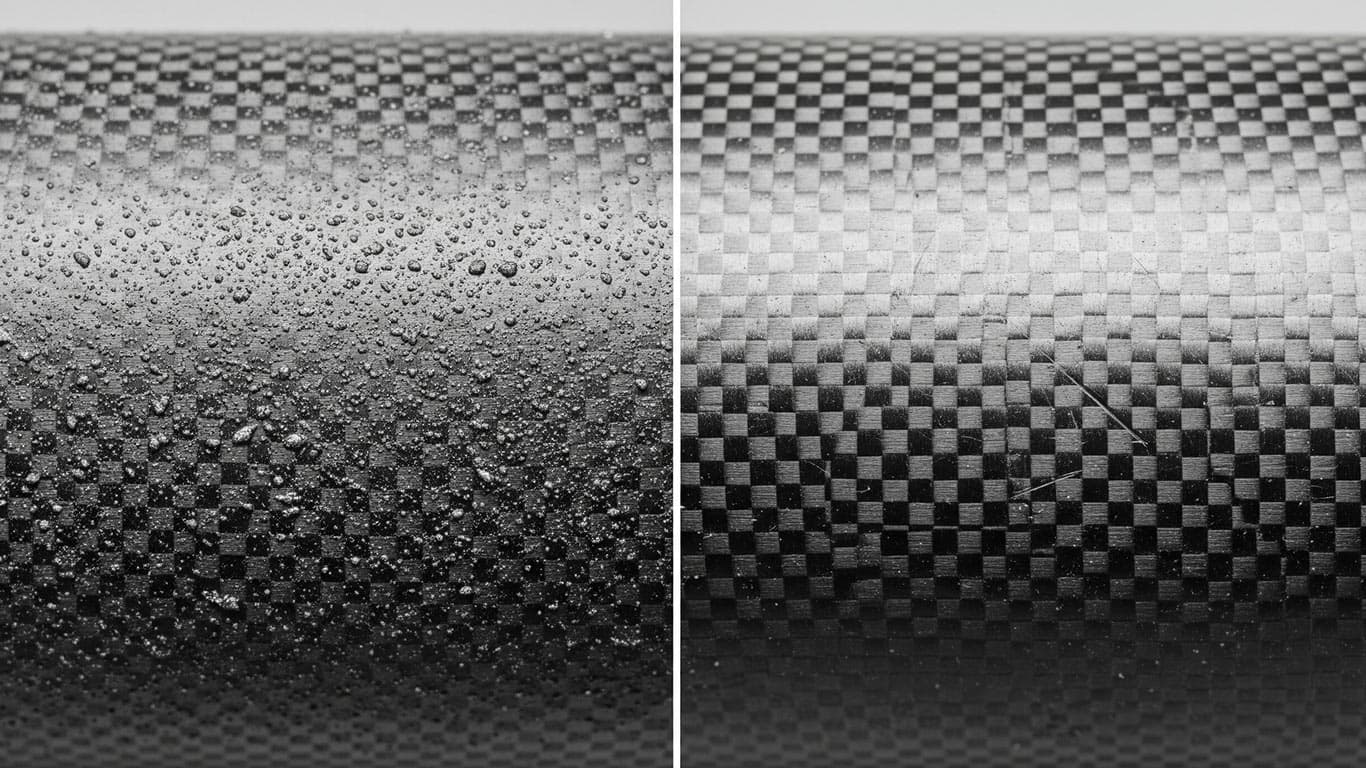
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Copper
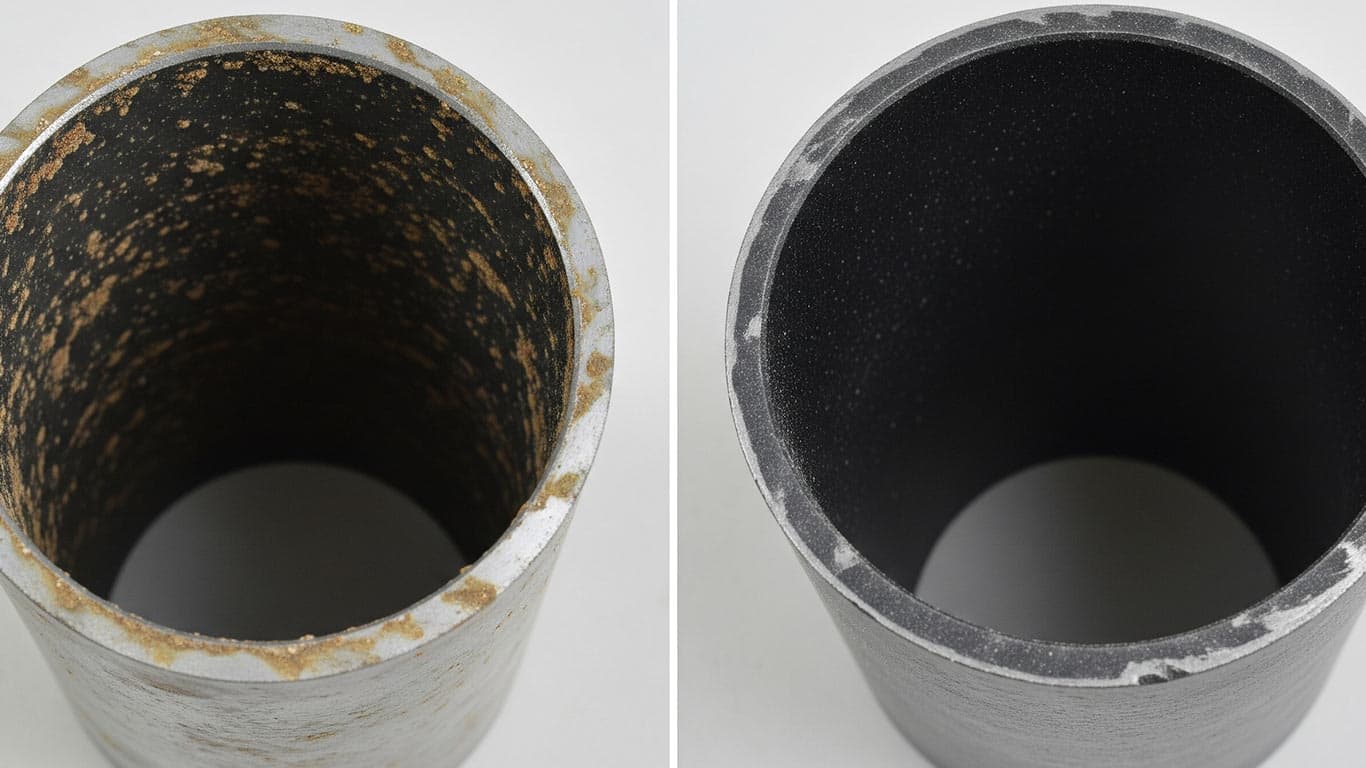

Epoxy Resin Composites
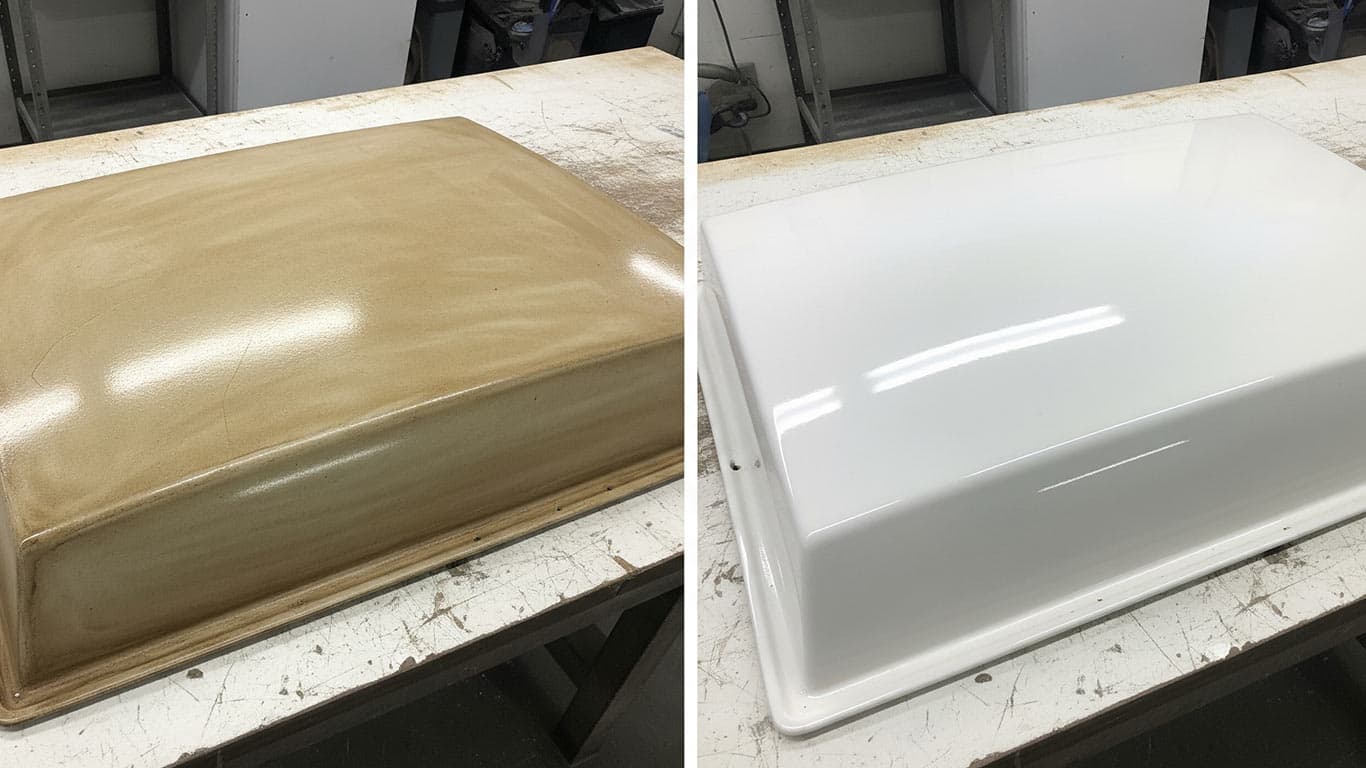

Fiberglass

Iron

Magnesium
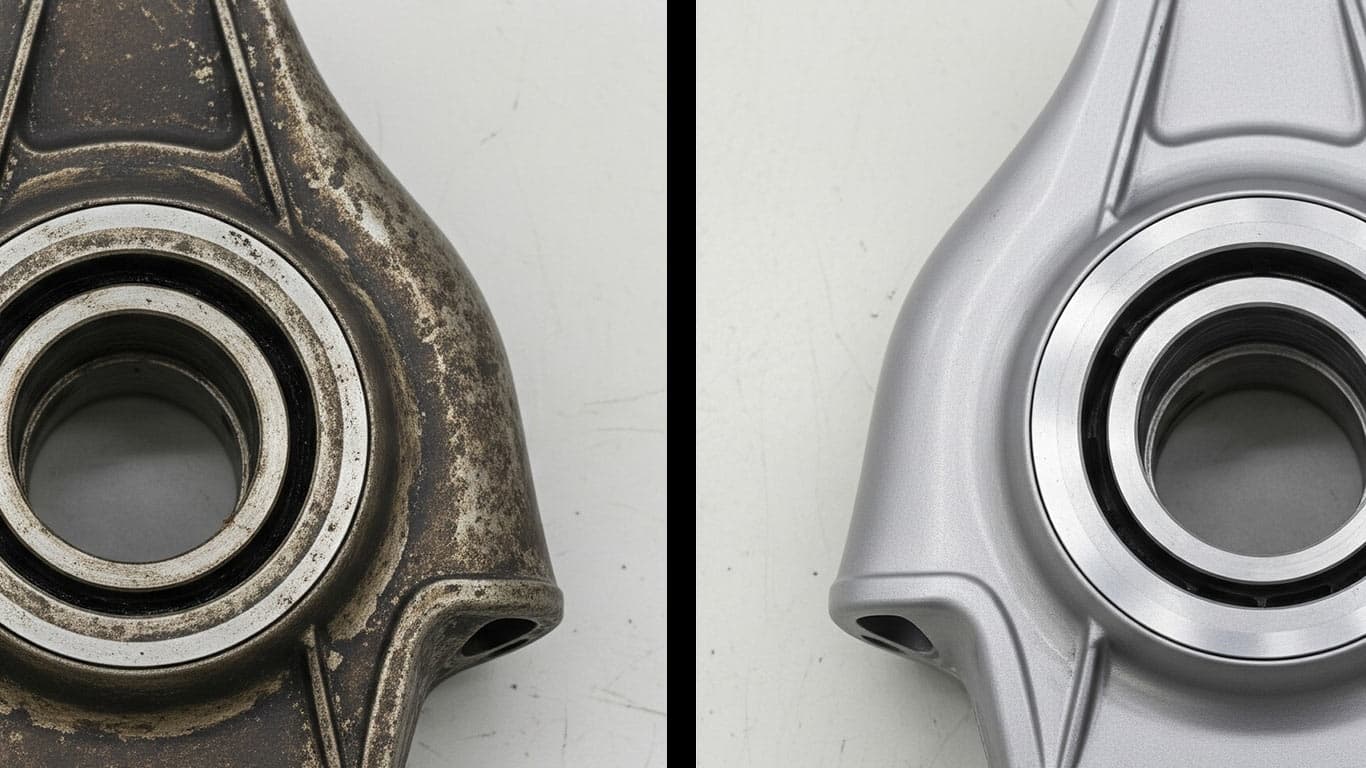

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
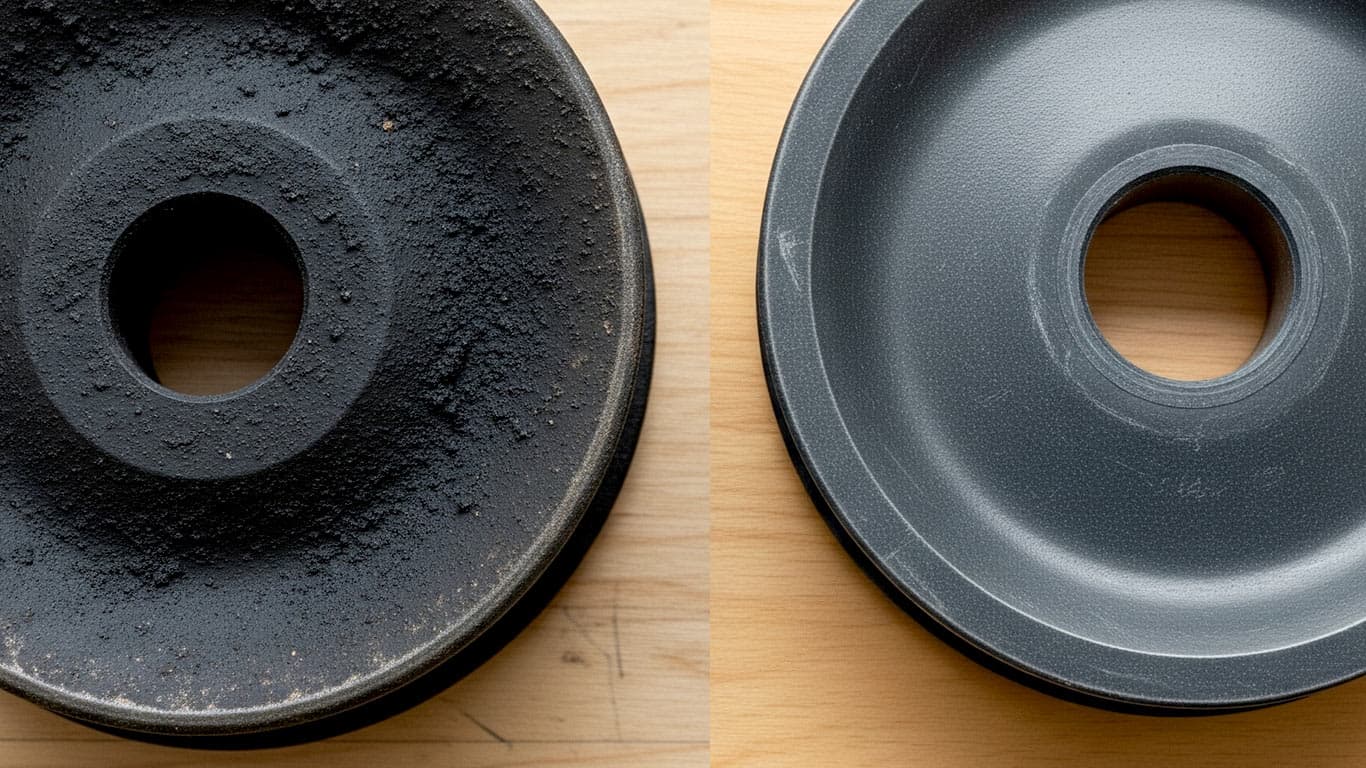

Phenolic Resin Composites
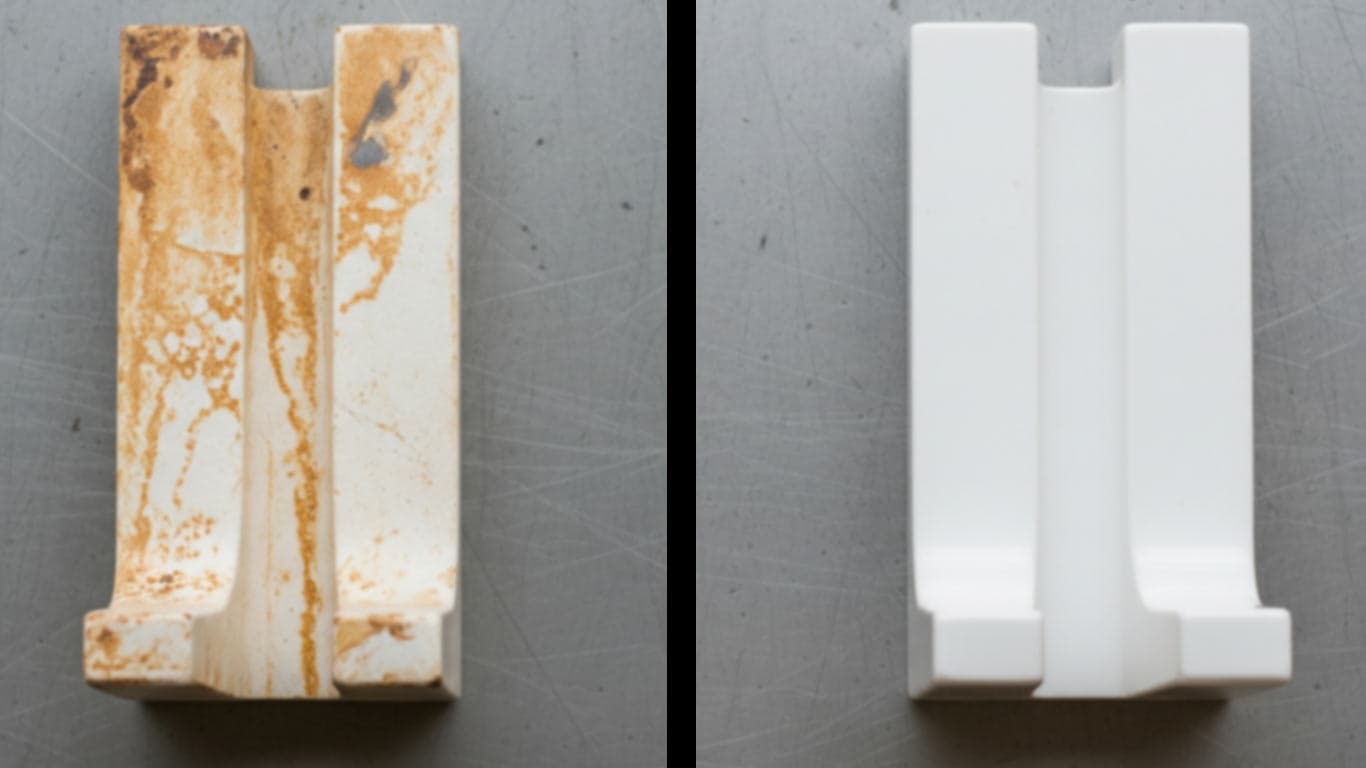

Polyester Resin Composites

Stainless Steel

Steel

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
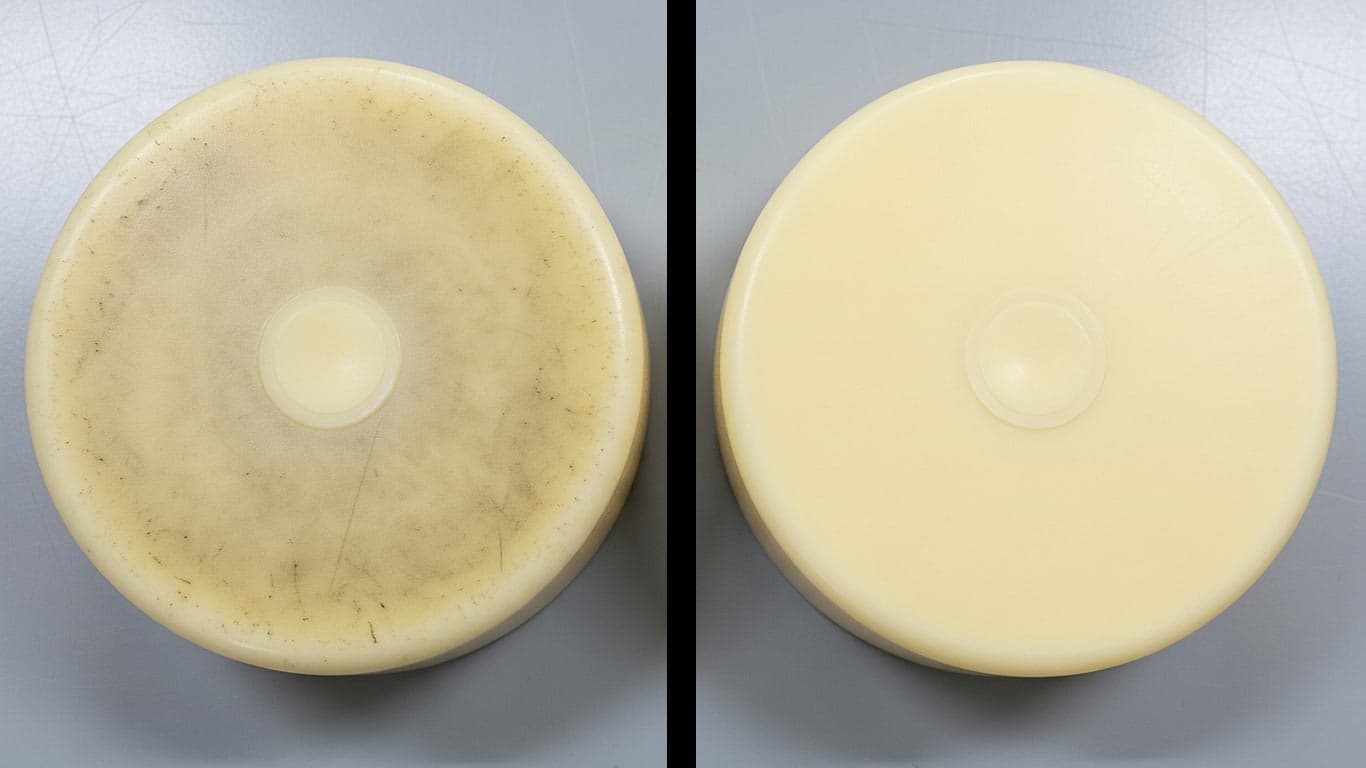

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Epoxy Resin Deposits Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more





