

Titanium Nitride
In our experience, the main challenge for titanium nitride in high-wear applications stems from routine abrasion and exposure to tough conditions, but its exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance offer enduring protection for tools and components while sustaining peak performance.
Laser Material Interaction
Material Characteristics
Compressive Strength
Fracture Toughness
Electrical Resistivity
Corrosion Resistance
Tensile Strength
Porosity
Oxidation Resistance
Youngs Modulus
Flexural Strength
Density
Hardness
Titanium Nitride 500-1000x surface magnification
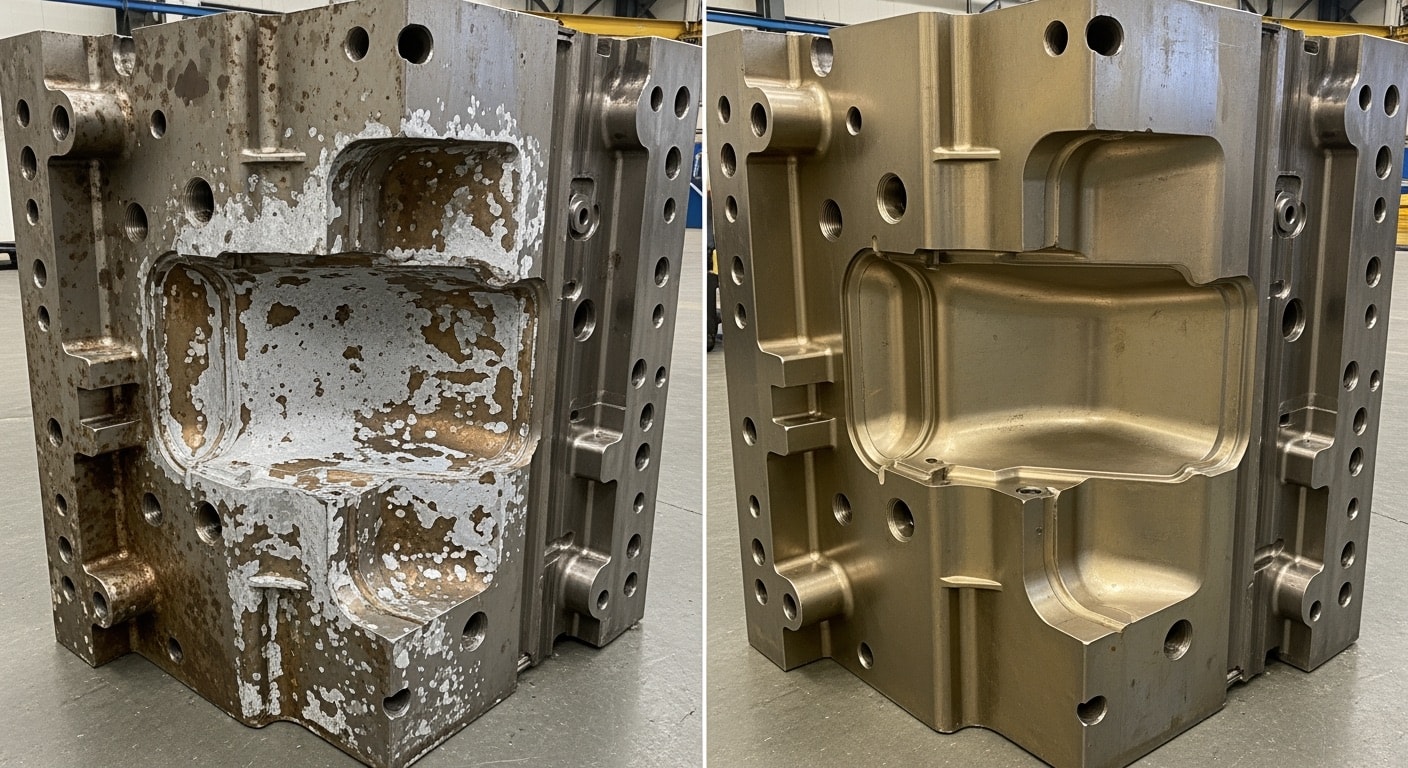
Before Treatment
I've seen contaminated Titanium Nitride surfaces up close at high magnification, and they always show thick layers of grime clinging tightly to the base. Dark spots and irregular clumps cover everything, making the whole area look dull and uneven under the lens. Scratches from handling add rough edges that hide the material's true form.
After Treatment
After laser treatment, the same surface transforms into a clear, even field with no trace of those clinging residues. Fine, uniform patterns emerge across the view, giving a
Industry Applications
Cutting Tools
Medical Devices
Automotive
Aerospace
Decorative Coatings
Wear-Resistant Applications
Semiconductor
Tool Manufacturing
FAQs for laser cleaning Titanium Nitride
How can I avoid damaging Titanium Nitride coatings during laser cleaning?
- When laser cleaning Titanium Nitride, you'll want to start with lower power settings compared to softer metals like aluminum, since this hard ceramic coating resists heat better but can crack under sudden thermal shock. Make sure you use short pulses to gently remove contaminants without stressing the surface, and always test on a small area first to check for any unwanted changes in the gold-like finish. Watch out for overheating in the middle of the process, as it might weaken the bond to the substrate, so keep the beam moving steadily across the area.
What settings work best for cleaning Titanium Nitride on tools?
- If you're cleaning Titanium Nitride on cutting tools, begin with a focused beam to target dirt and residue precisely, unlike with reflective metals where energy scatters more easily. You must adjust the wavelength to one that absorbs well into this durable coating, ensuring efficient removal without abrading the tough layer beneath. This approach brings
Common Contaminants


Algae and Lichen Growth

Heat Treatment Scale

Aerospace Sealant Residue

Organic Biofilm Deposits

Carbon Soot Deposits

Ceramic Heat Barrier Coating

Chemical Stains / Acid Etching

Machining Coolant Residue

Diamond-Like Carbon Removal

Epoxy Resin Deposits

Exhaust System Deposits

Fertilizer Salt Deposits

Graffiti and Spray Paint

Graphite Deposit Traces

Industrial Oil / Grease Buildup

Printing Ink Residue

Insect Impact Residue

Laser Marking Discoloration

Limescale Deposits

Mercury Spill Residue

Hard Water Mineral Scale

Paint Residue / Coating Failure

Pesticide Chemical Residue

Thermal Spray Coating

Degraded Polymer Deposits

Pollen Accumulation

Surface Radioactive Contamination

Rubber Compound Residue

Salt and Chloride Deposits

Mineral Scale / Hard Water Deposits
Silicone Sealant Buildup

Surgical Ink Markings

Tree Sap and Resin

Water Staining and Marks

Wax Coating Buildup
Titanium Nitride Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more

