


PCB Oil Contamination
Contamination on PCBs forms during soldering process and handling. Residues like flux and oils stick to copper traces and boards. After exposure, layer builds unevenly because board topography traps particles. So, patterns show clusters around joints.
Removal challenges arise from sensitivity of electronics. Laser cleaning targets residues selectively, but heat affects underlying materials. On FR4 substrate, process removes buildup without damaging insulation. Metal parts exhibit stronger adhesion, so higher energy risks etching.
In applications, treatment achieves clean surfaces effectively. Buildup is observed in crevices, and cleaning applies short pulses to avoid warping. Results are obtained from scans showing uniform finish after process. Surface exhibits reduced residue during inspections.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Bronze
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
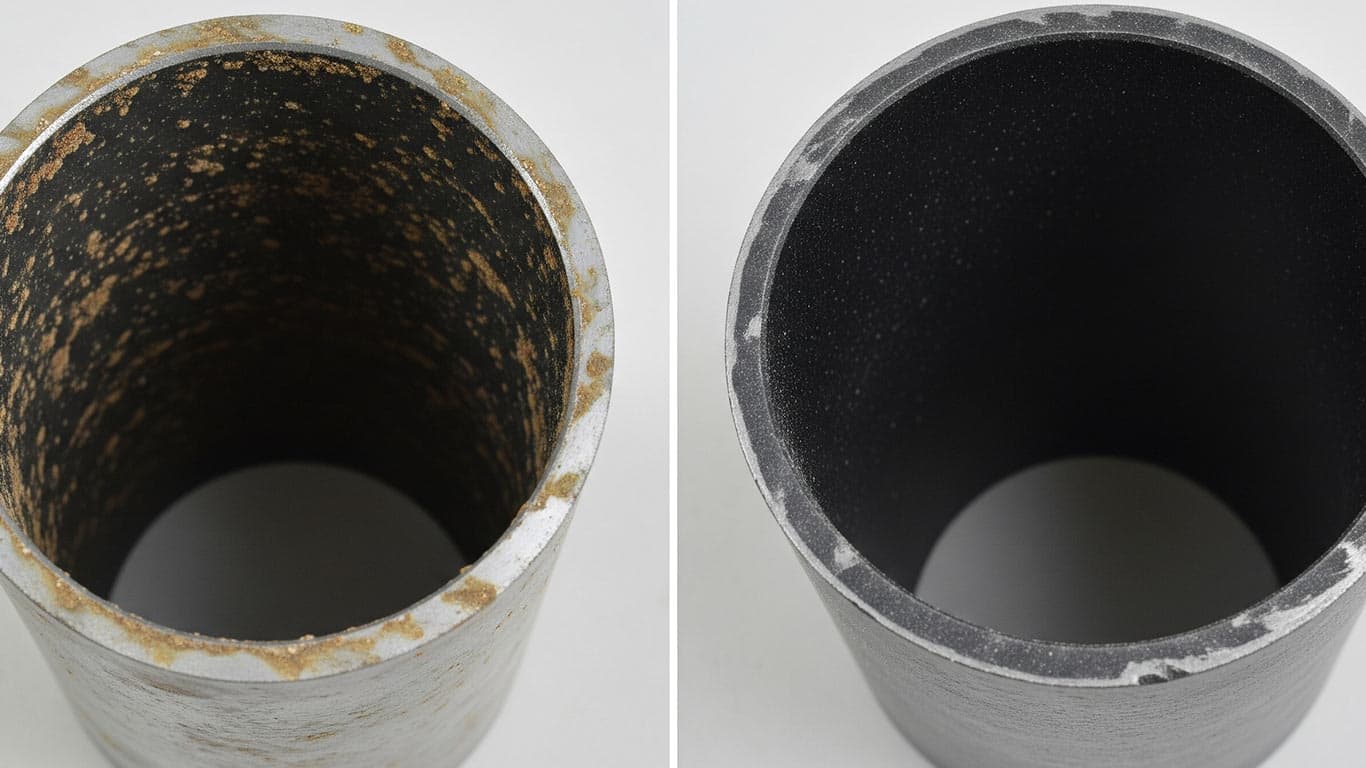

Epoxy Resin Composites
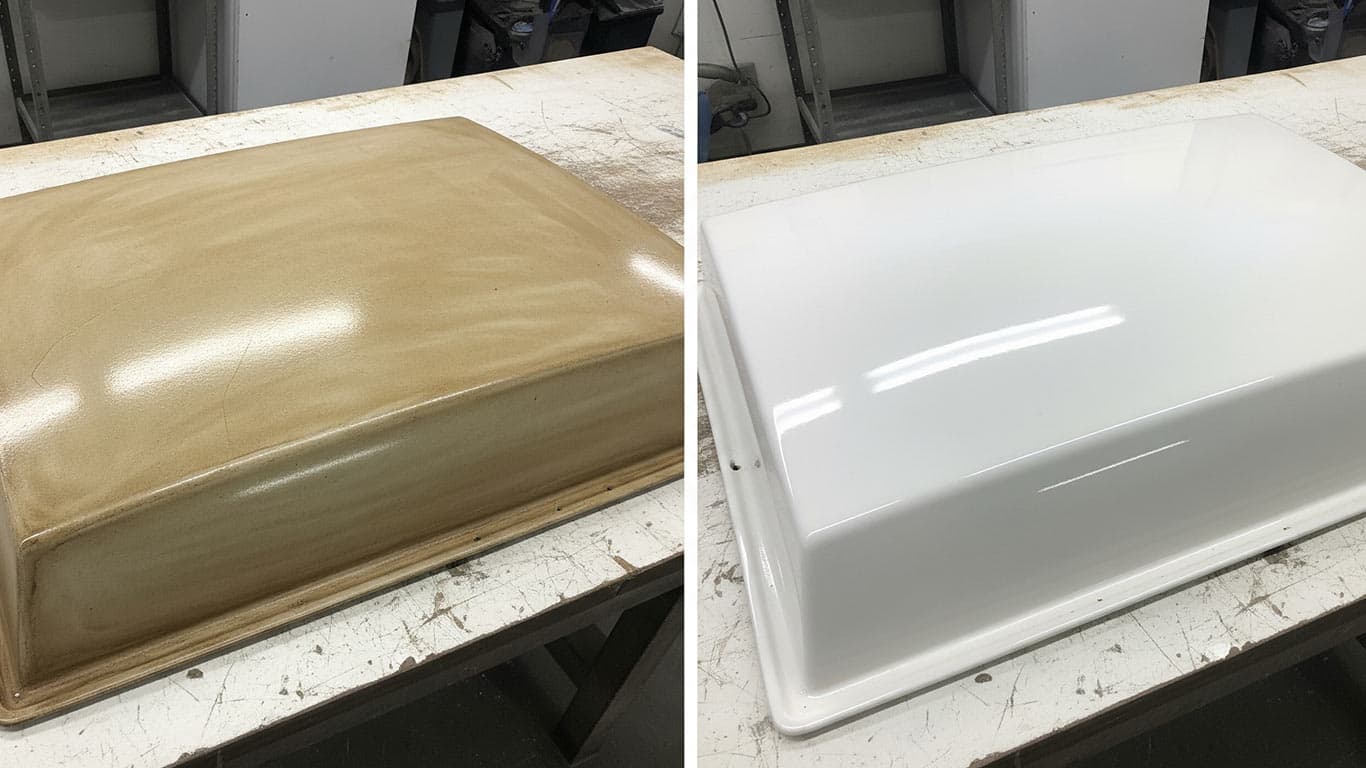

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
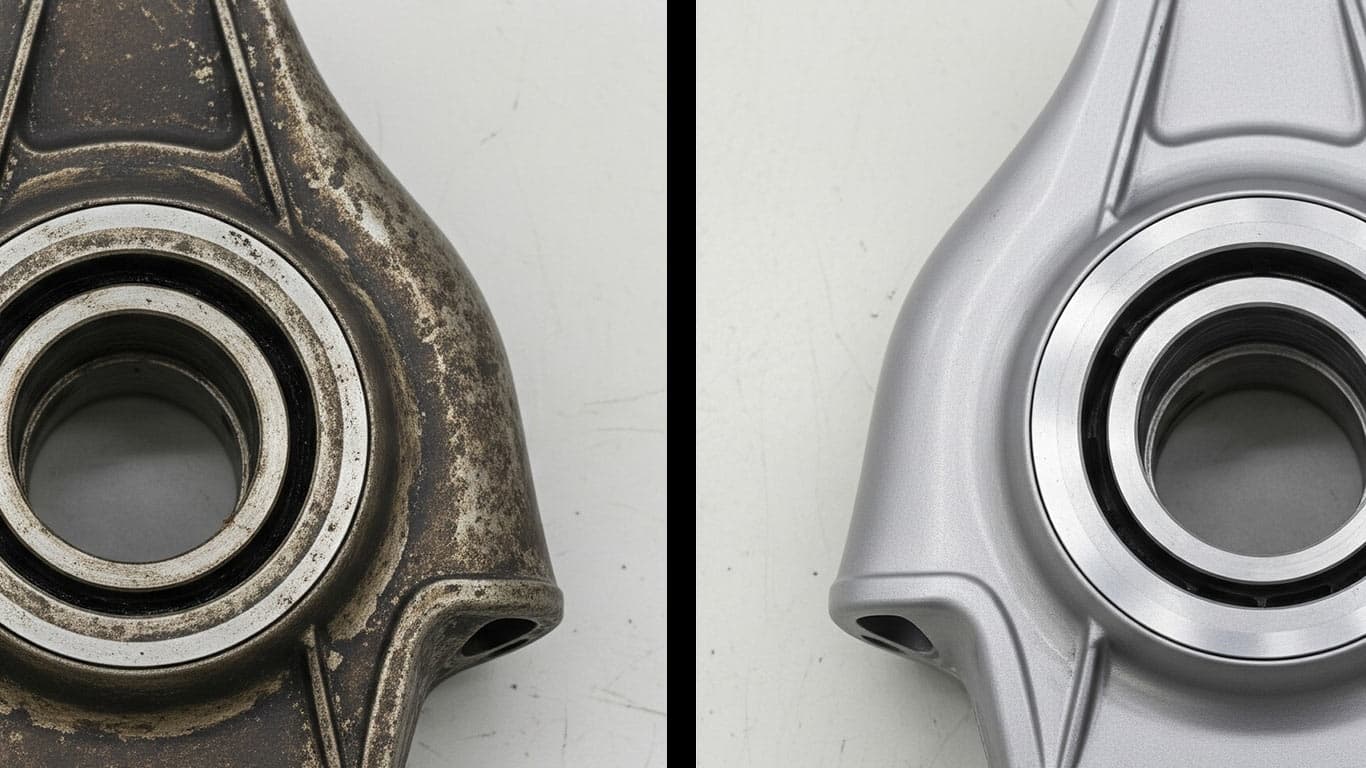

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
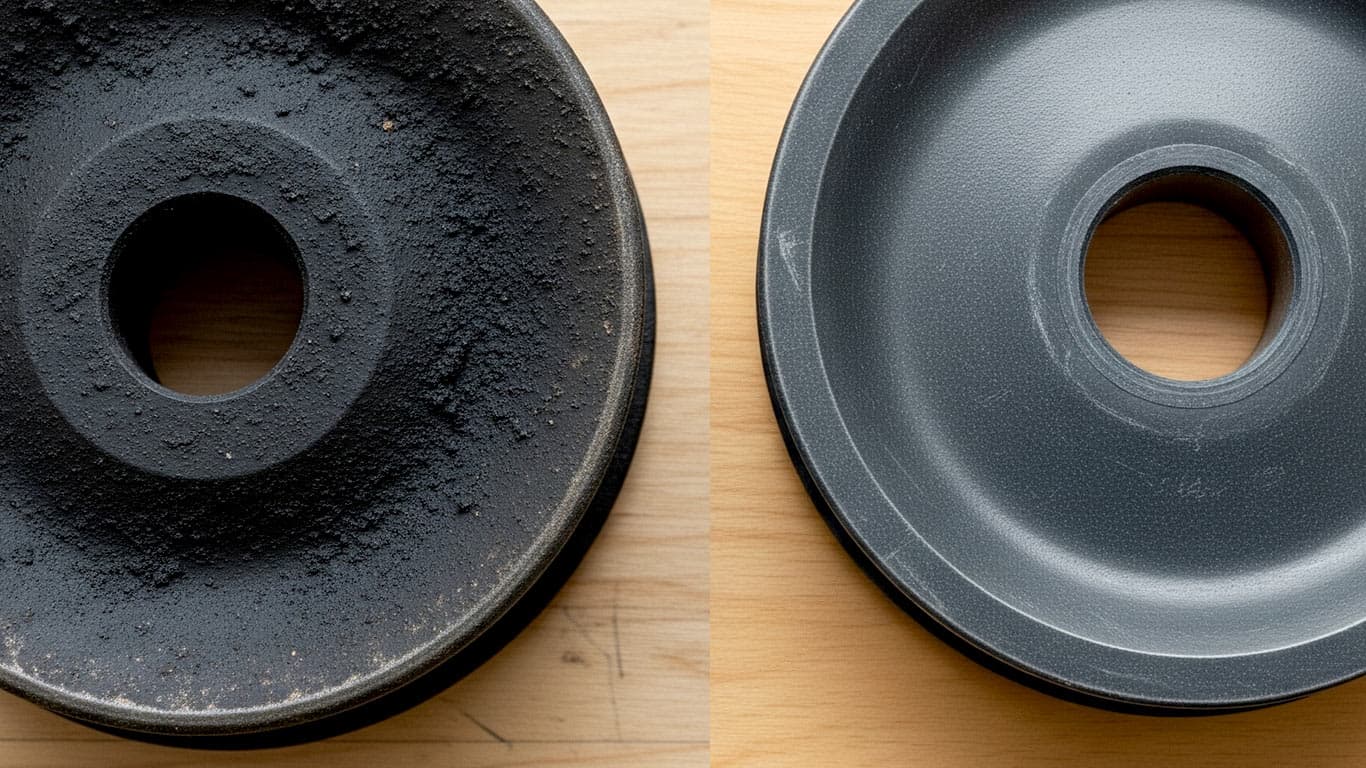

Phenolic Resin Composites
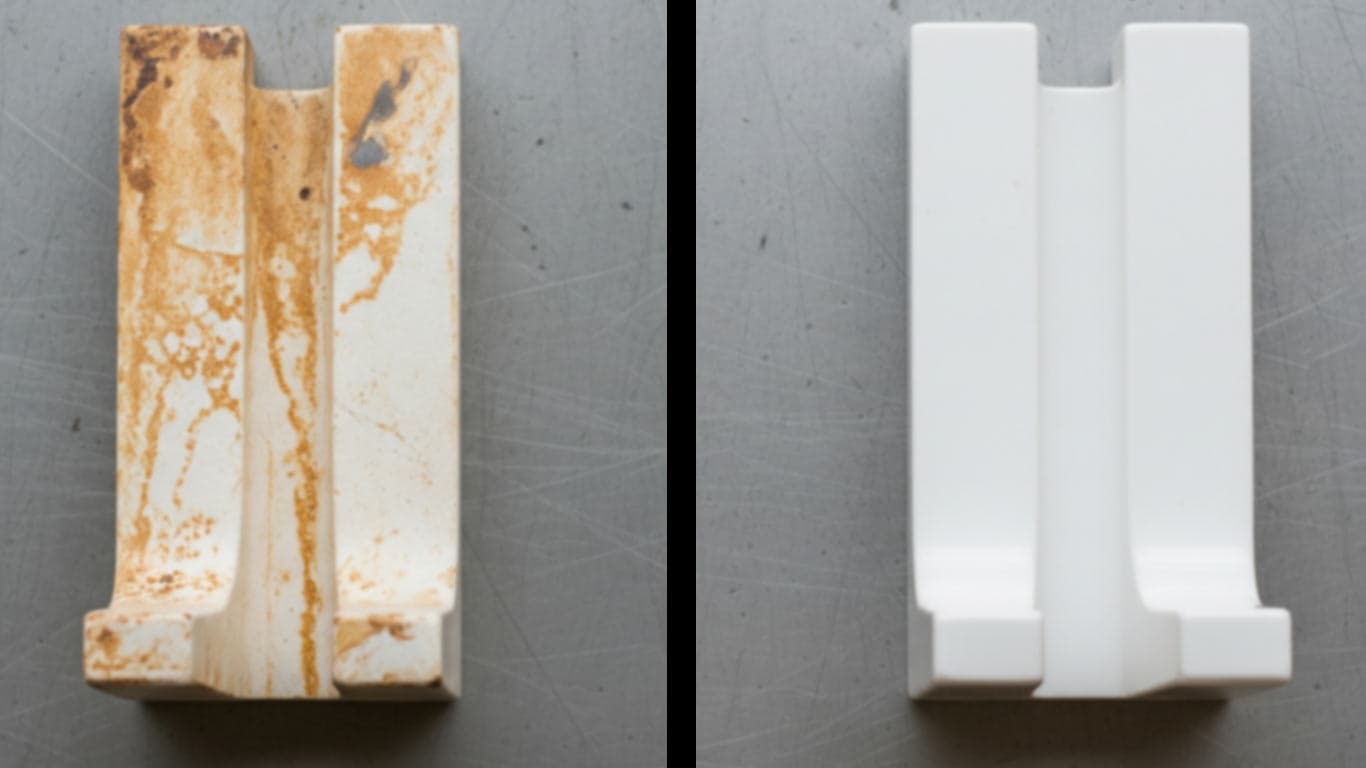

Polyester Resin Composites

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
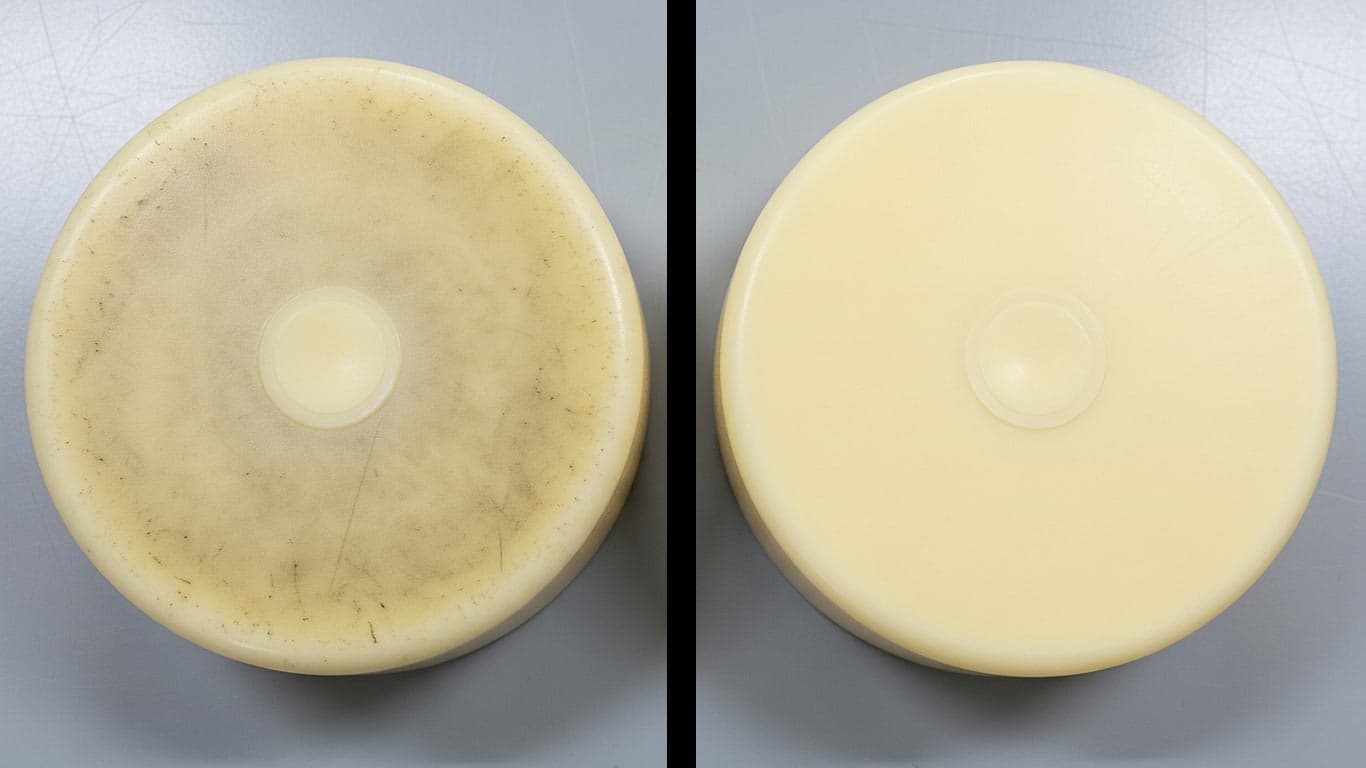

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
PCB Oil Contamination Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more





