


Ceramic Heat Barrier Coating
Ceramic-coating contamination, it manifests through unique formation patterns that depend from environmental exposure, particularly in industrial settings. This inorganic layer, which builds tenaciously on heat-resistant surfaces, exhibits regional variations influenced from humidity and particulates. The contamination, it persists with a dense adherence to ceramic substrates, that demonstrates material-specific behaviors under laser cleaning.
Removal challenges arise distinctly, as the coating resists ablation due to its durable composition. It seems that laser pulses, they struggle against this persistence, leading to incomplete detachment on metals versus ceramics. The process yields partial success, where surface smoothness improves selectively. Shows effectiveness in targeted applications, yet demands optimized parameters for thorough elimination.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
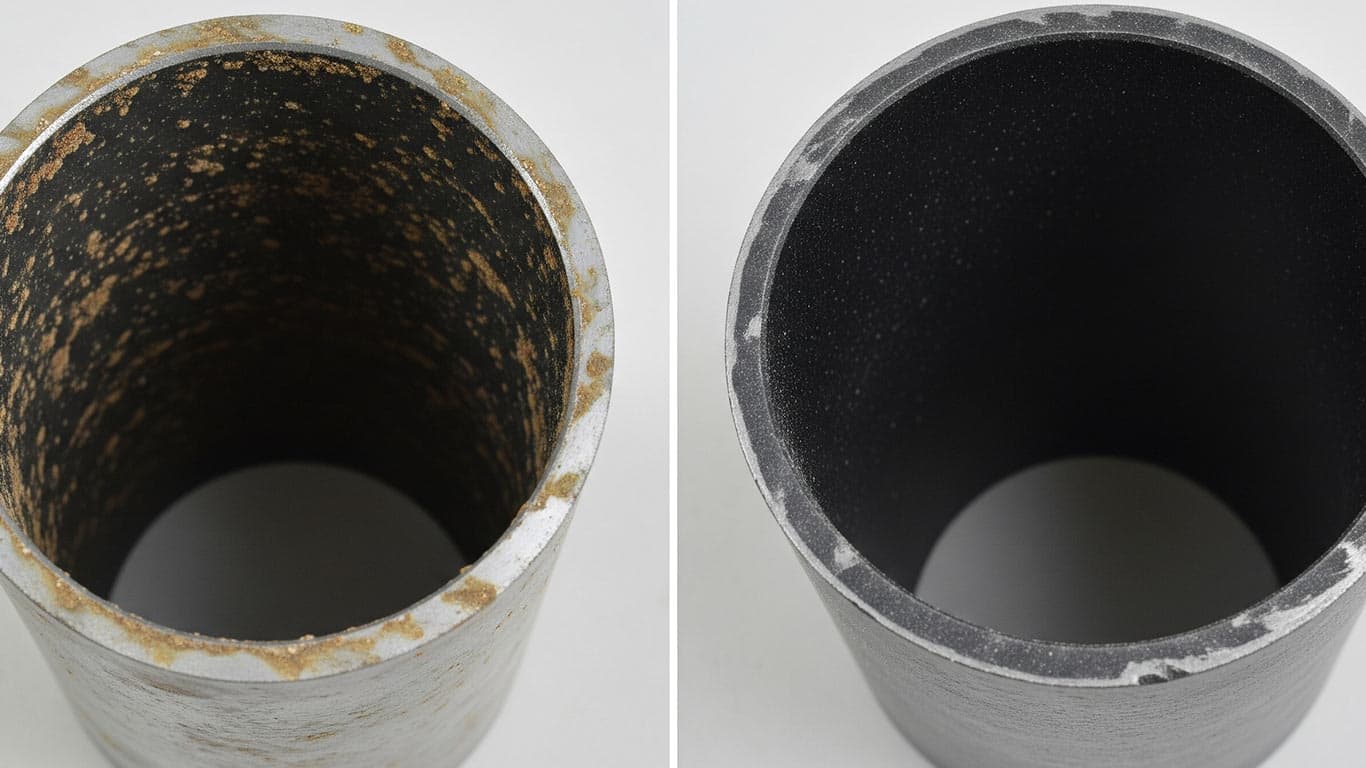

Epoxy Resin Composites
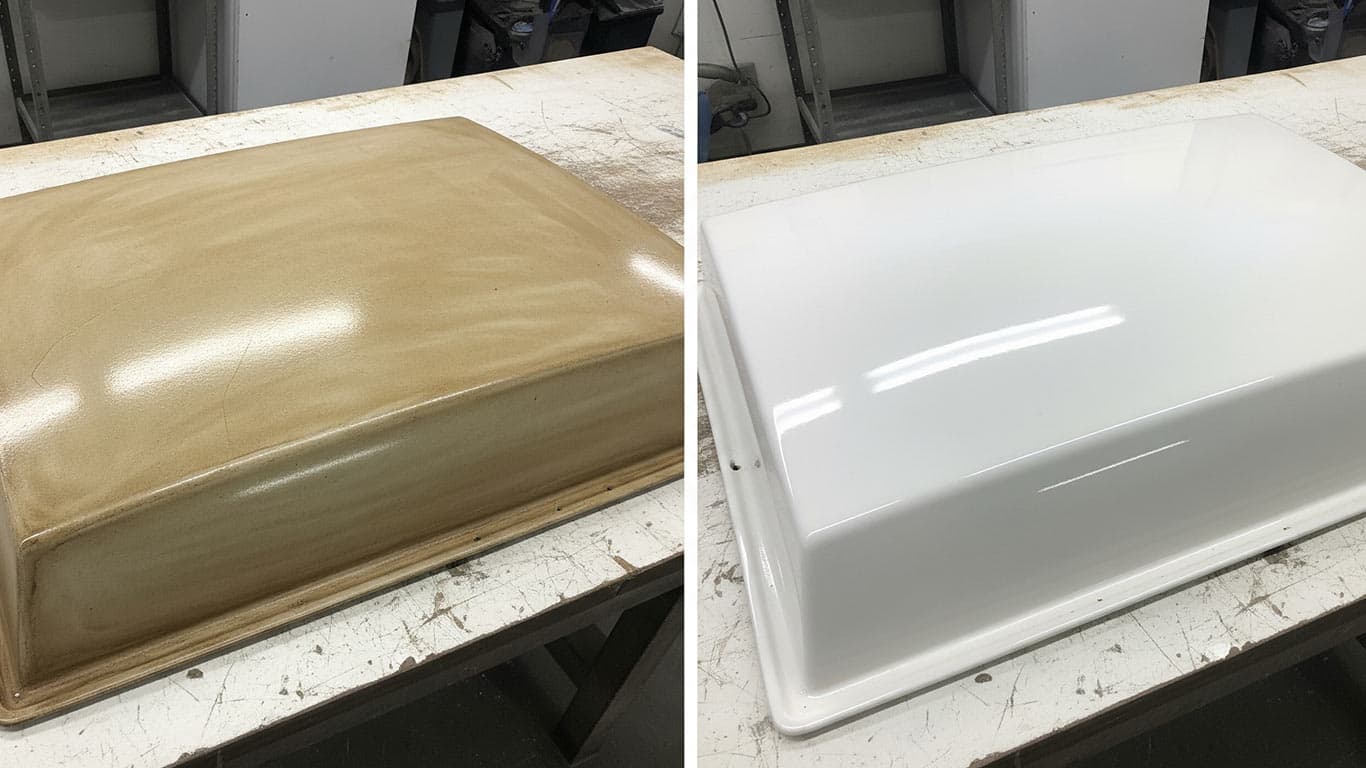

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
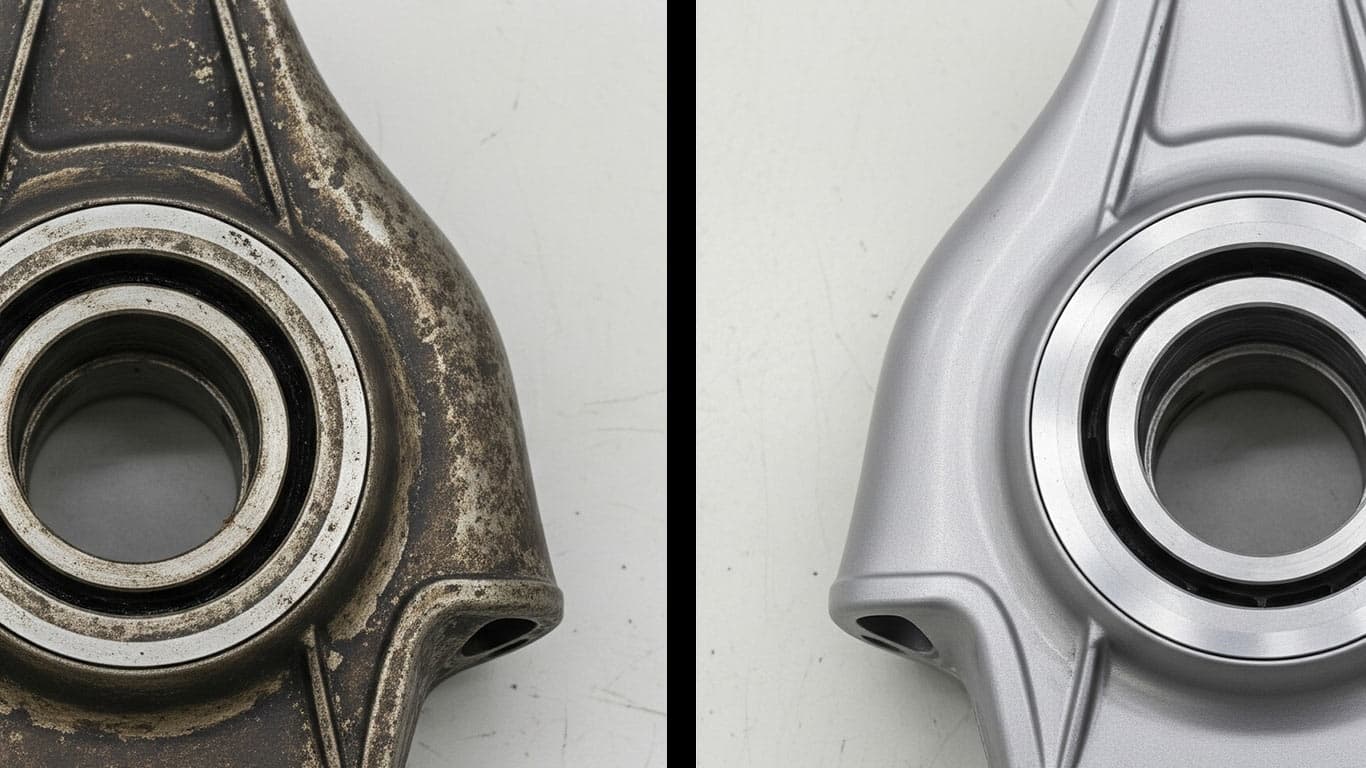

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
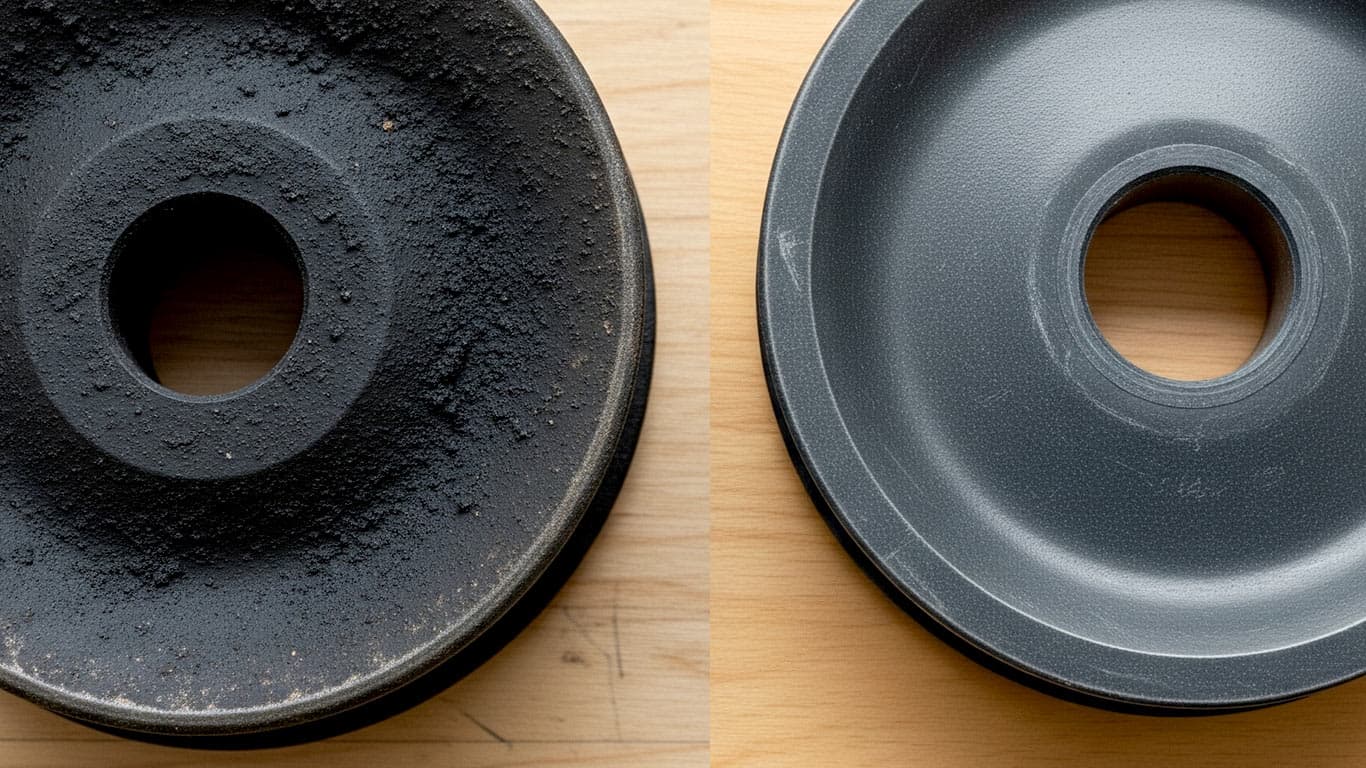

Phenolic Resin Composites
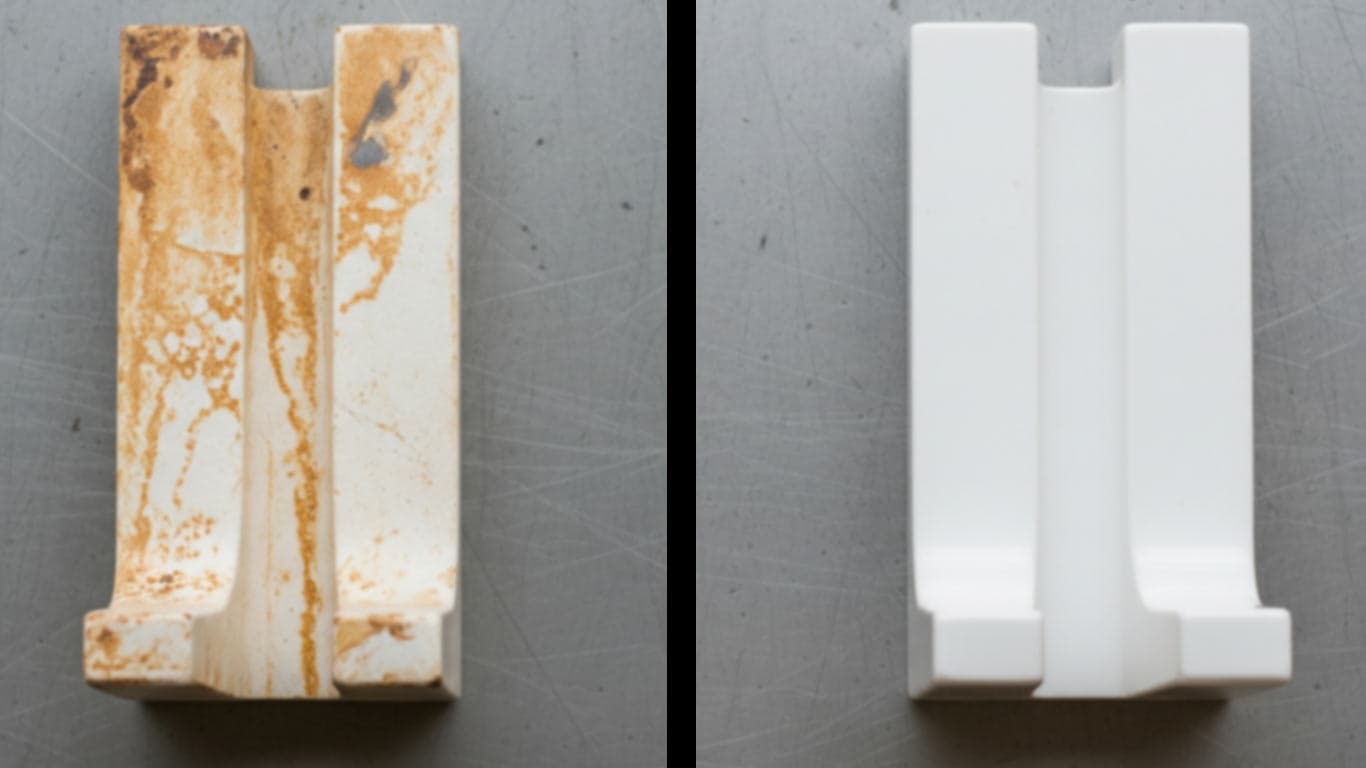

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
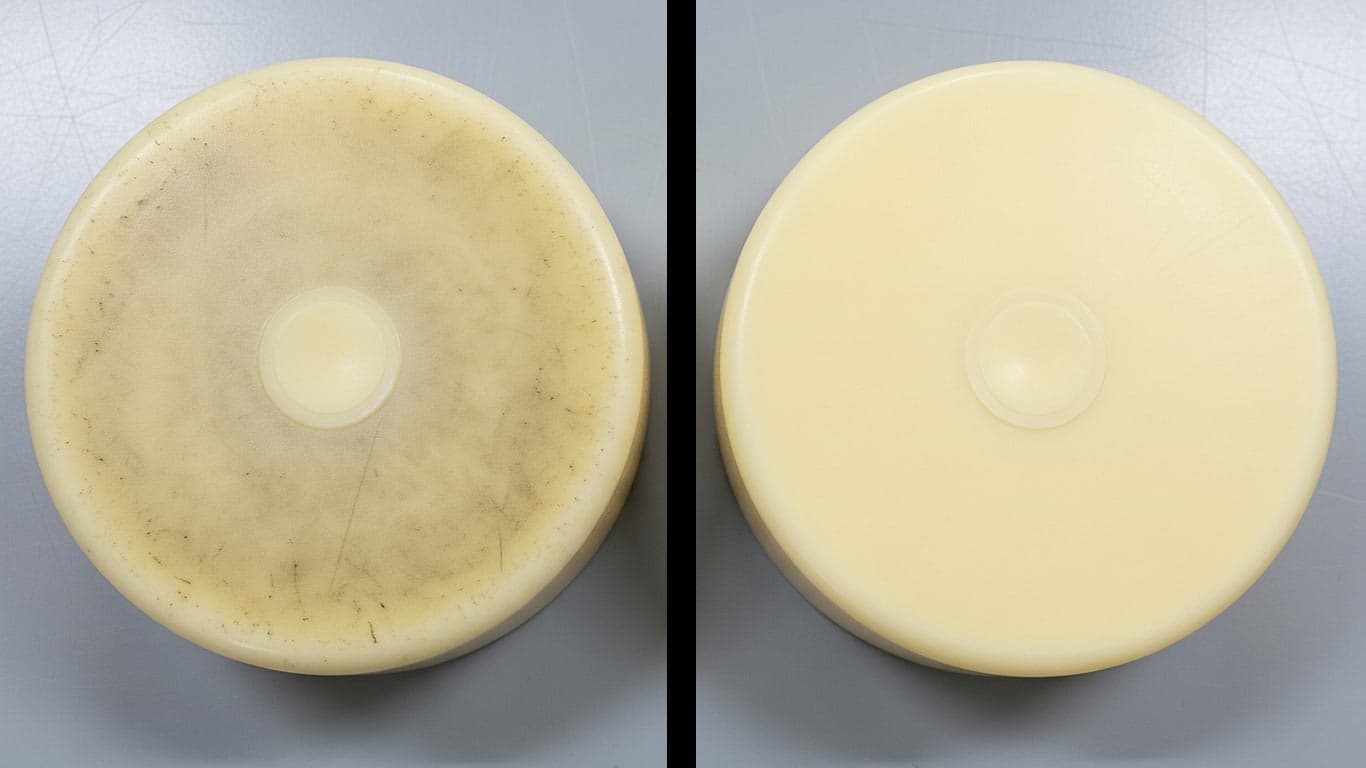

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Ceramic Heat Barrier Coating Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more


