


PVD Coating Defects
PVD coating contamination, it manifests as thin inorganic layers, dependent from deposition environments. These contaminants, they exhibit unique formation patterns, like irregular clustering on metallic substrates, which leads to tenacious adhesion. In laser cleaning applications, the removal challenges arise, particularly on aluminum surfaces, where the contamination persists under short pulses. It seems that on steel, behaviors differ, showing easier delamination yet risking substrate etching. The process yields distinct outcomes, influenced from wavelength selection, that demonstrates material-specific responses. Layers detach selectively, avoiding damage to the underlying coating. Shows effectiveness in preserving integrity.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
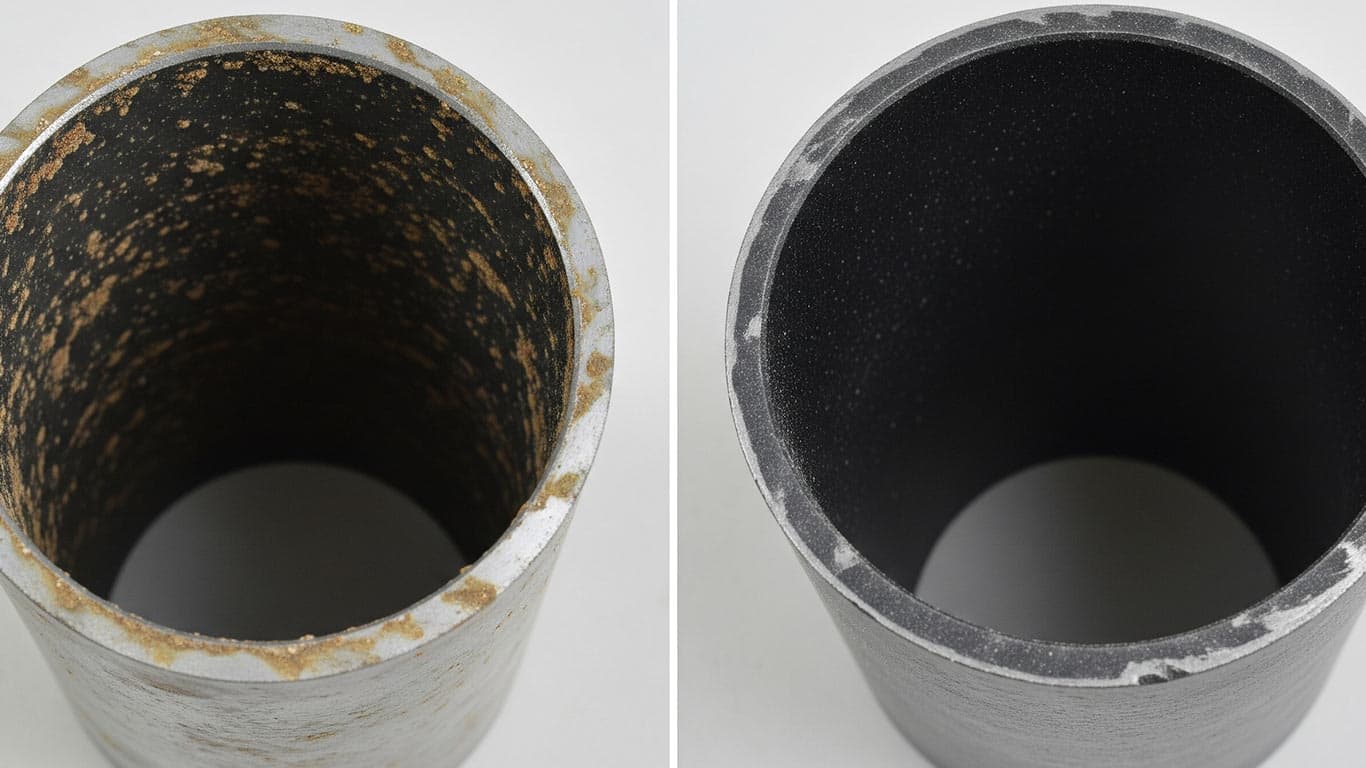

Epoxy Resin Composites
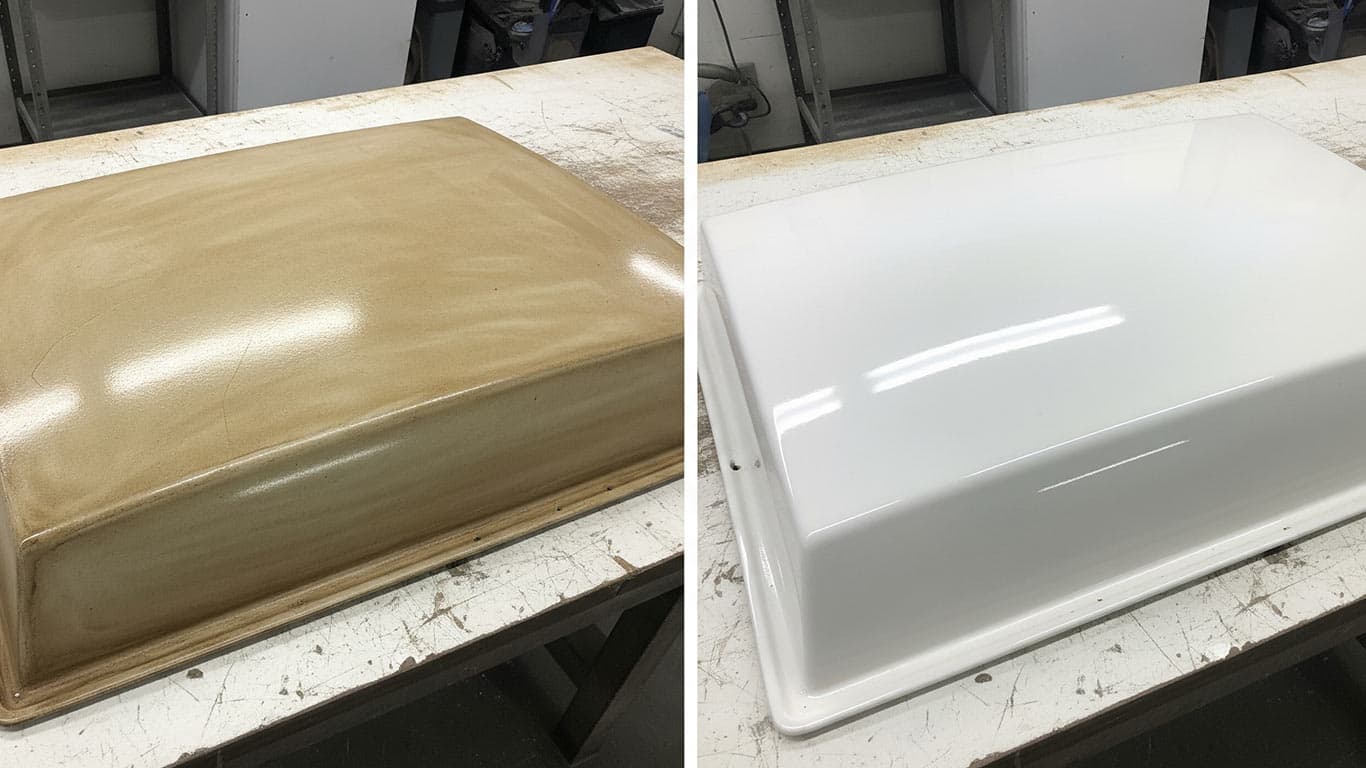

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
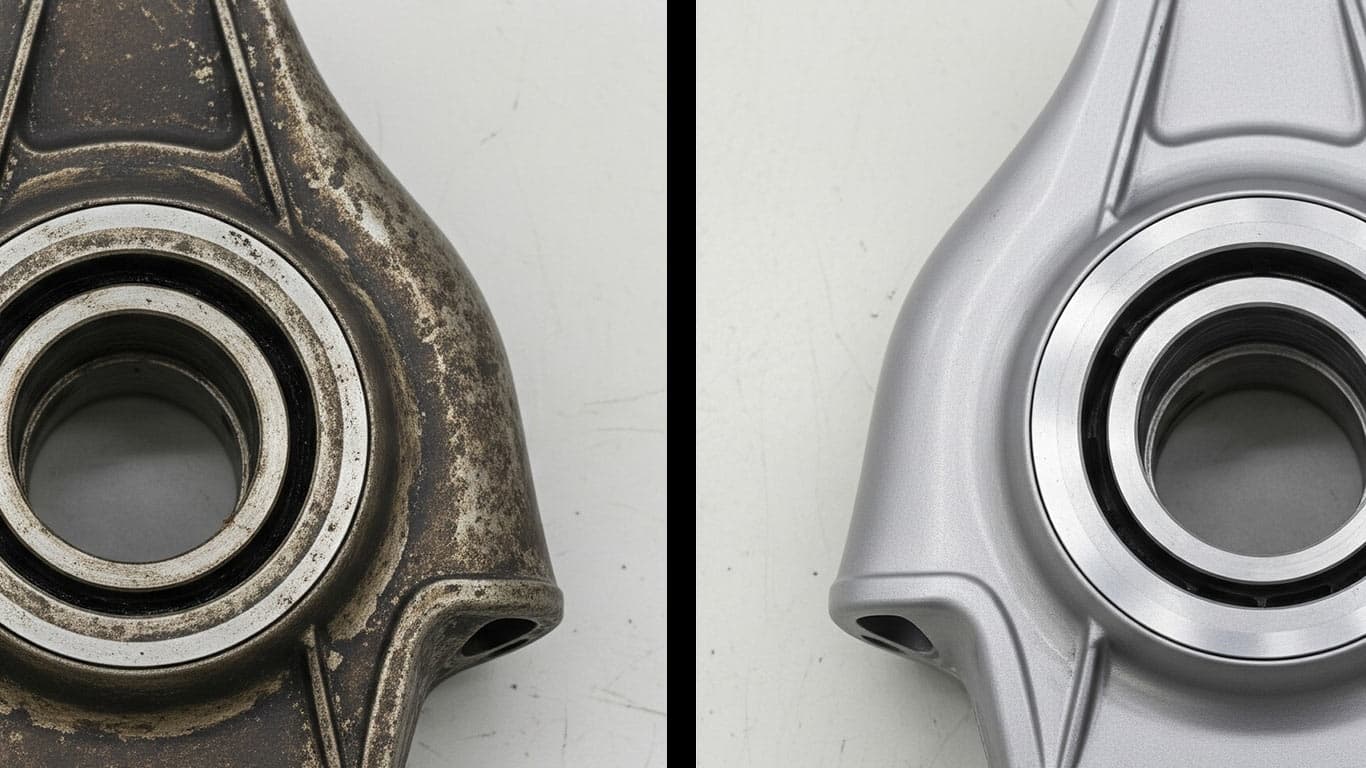

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
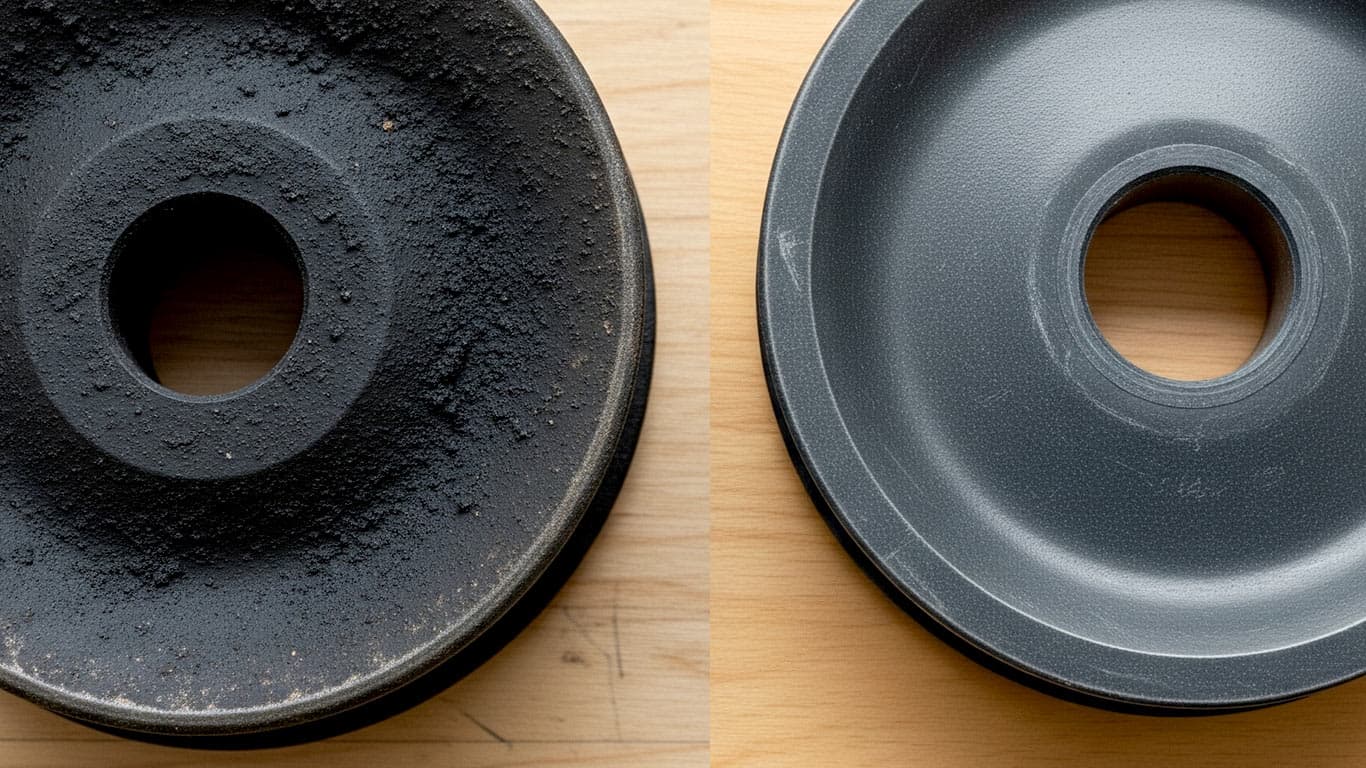

Phenolic Resin Composites
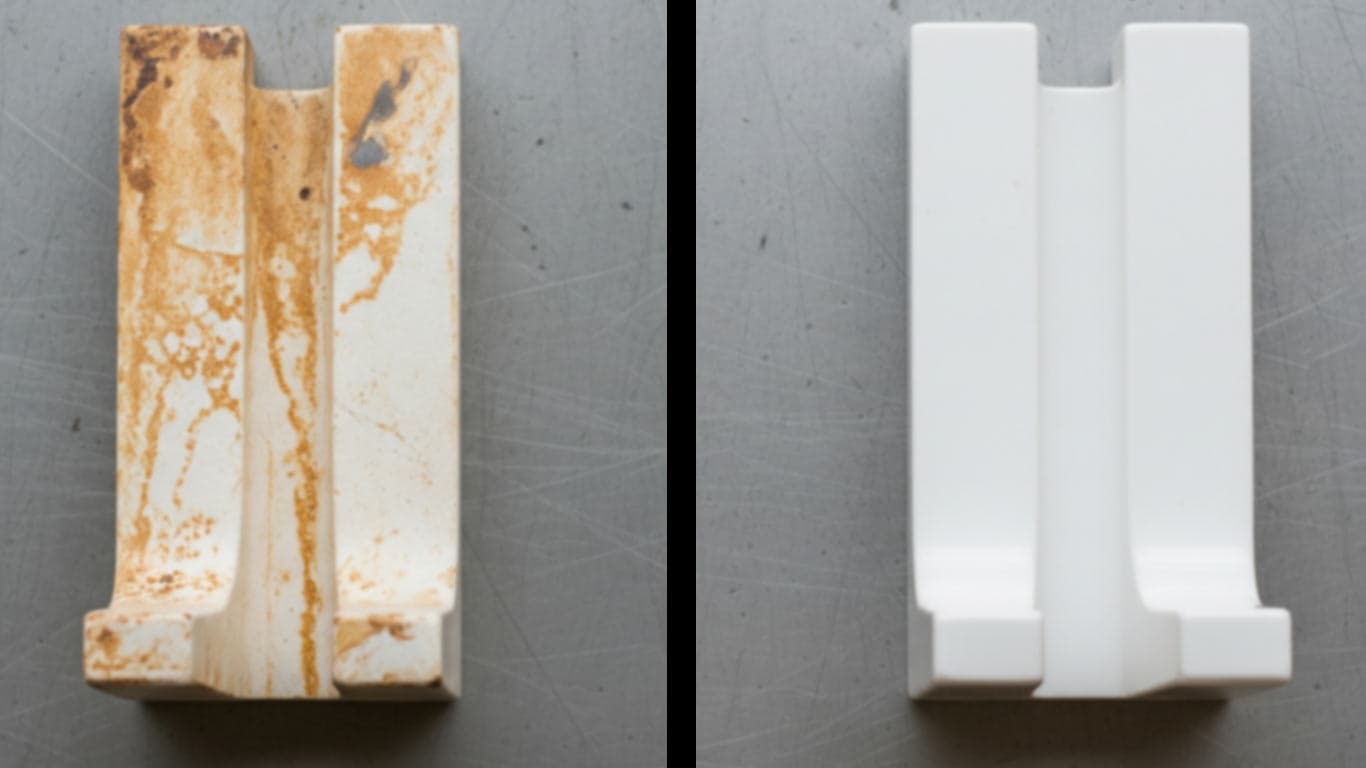

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
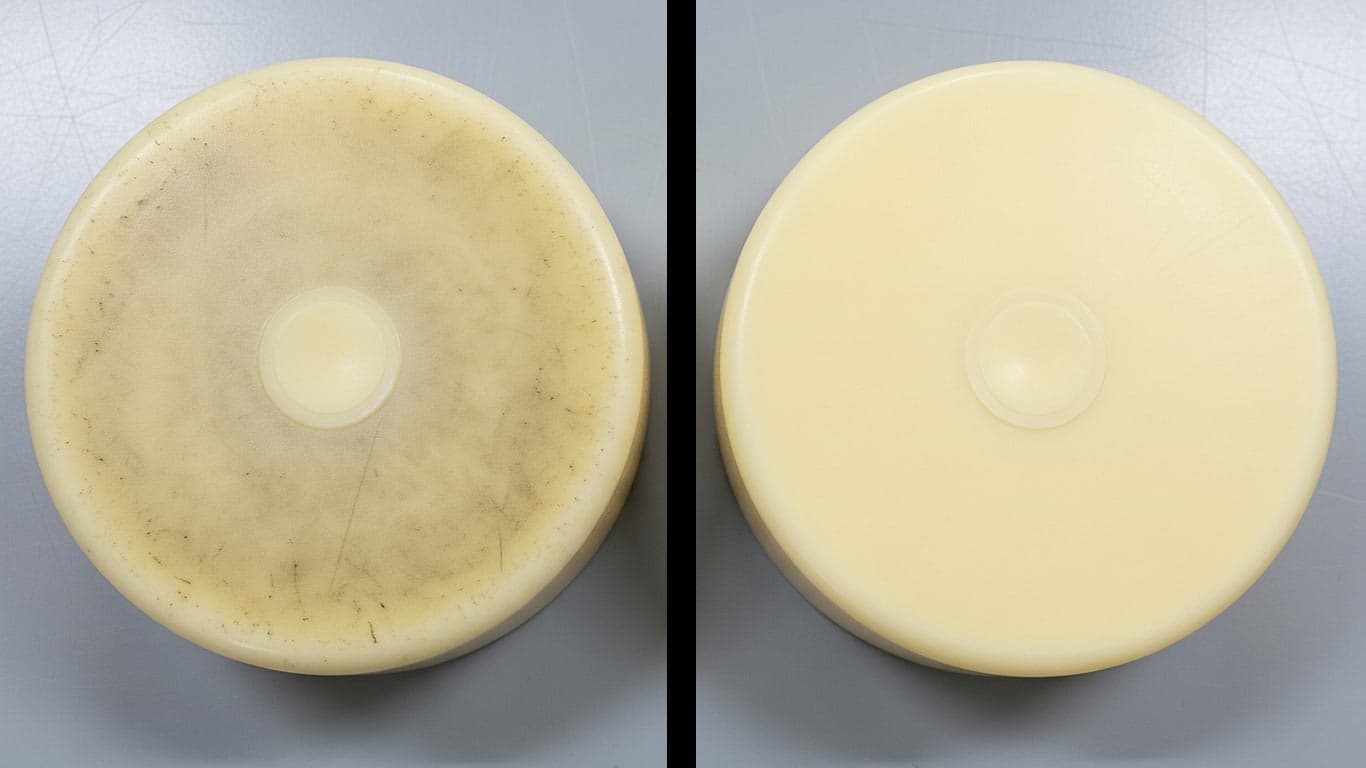

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
PVD Coating Defects Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more



