

Asbestos-Containing Material
Asbestos-coating-contamination differs from organic residues because it forms dense, fibrous layers on metal surfaces during industrial exposure. Layer builds up tightly and resists initial breakdown, so laser cleaning faces unique challenges in penetration. Before ablation, contamination embeds into substrate pores and creates uneven patterns across regions. Process applies pulsed energy, and heat causes fibers to fragment without scattering widely. During removal, material exhibits brittleness specific to its inorganic nature, so complete detachment requires controlled pulses to avoid residue re-adhesion. After treatment, surface shows improved uniformity because fragments disperse easily in air. Observations indicate that regional humidity influences formation thickness, and cleaning achieves better results on coated steels than alloys. Challenges arise from fiber durability, so intervals in laser passes prevent overheating. Contamination removal proves effective in applications like shipyard maintenance.
Ikmanda Roswati, Ph.D. from Indonesia
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
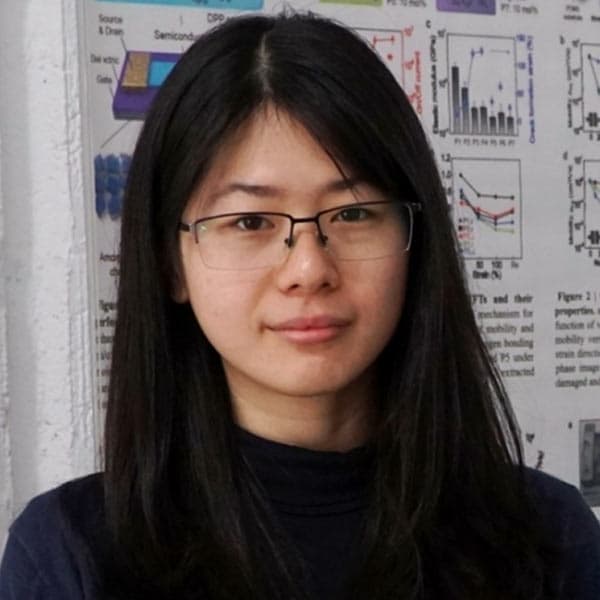
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
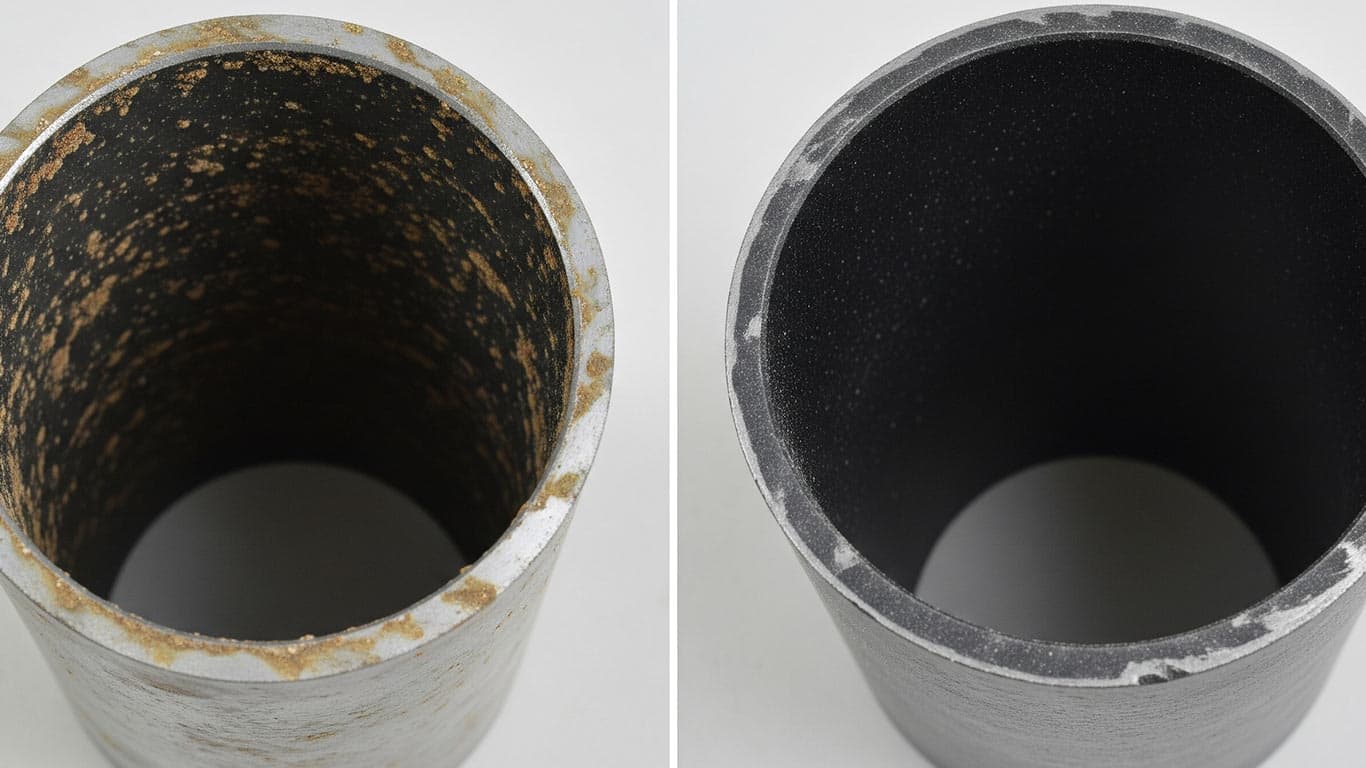

Epoxy Resin Composites
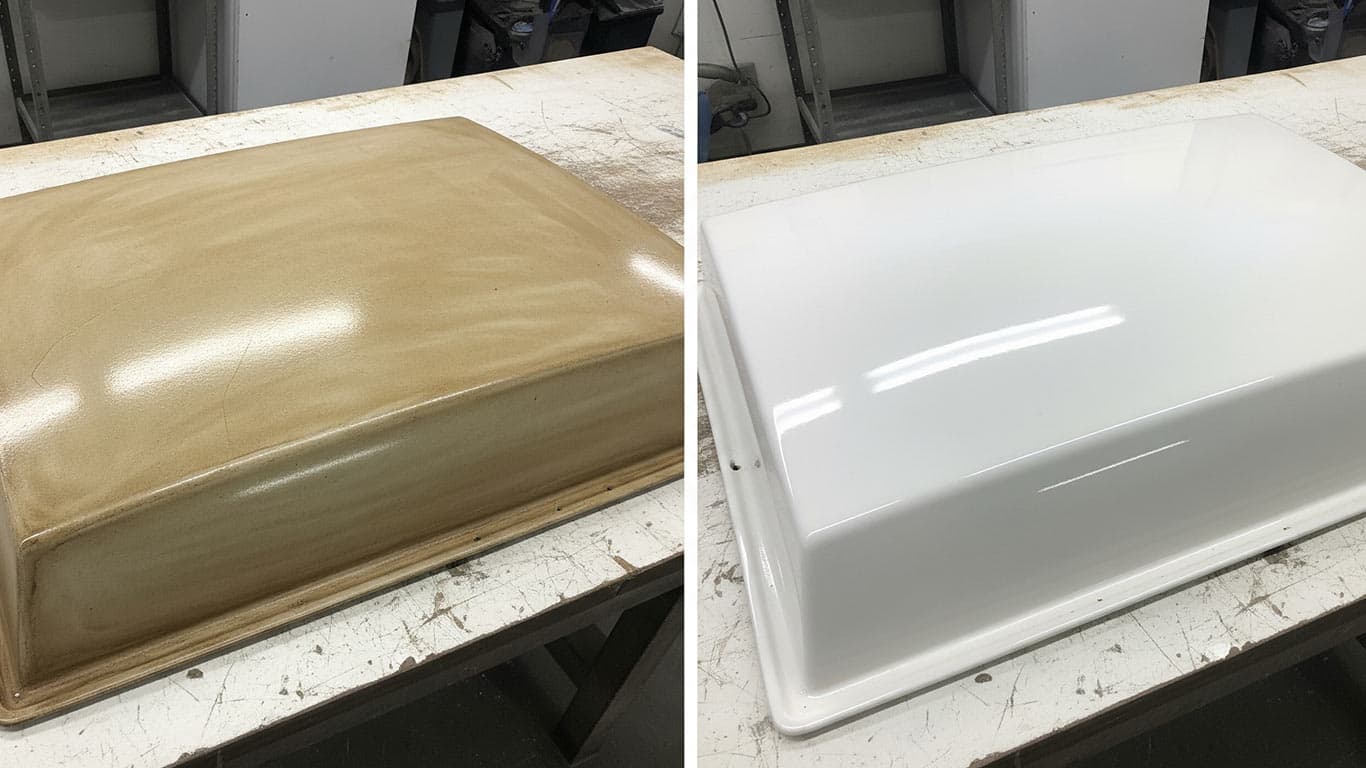

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
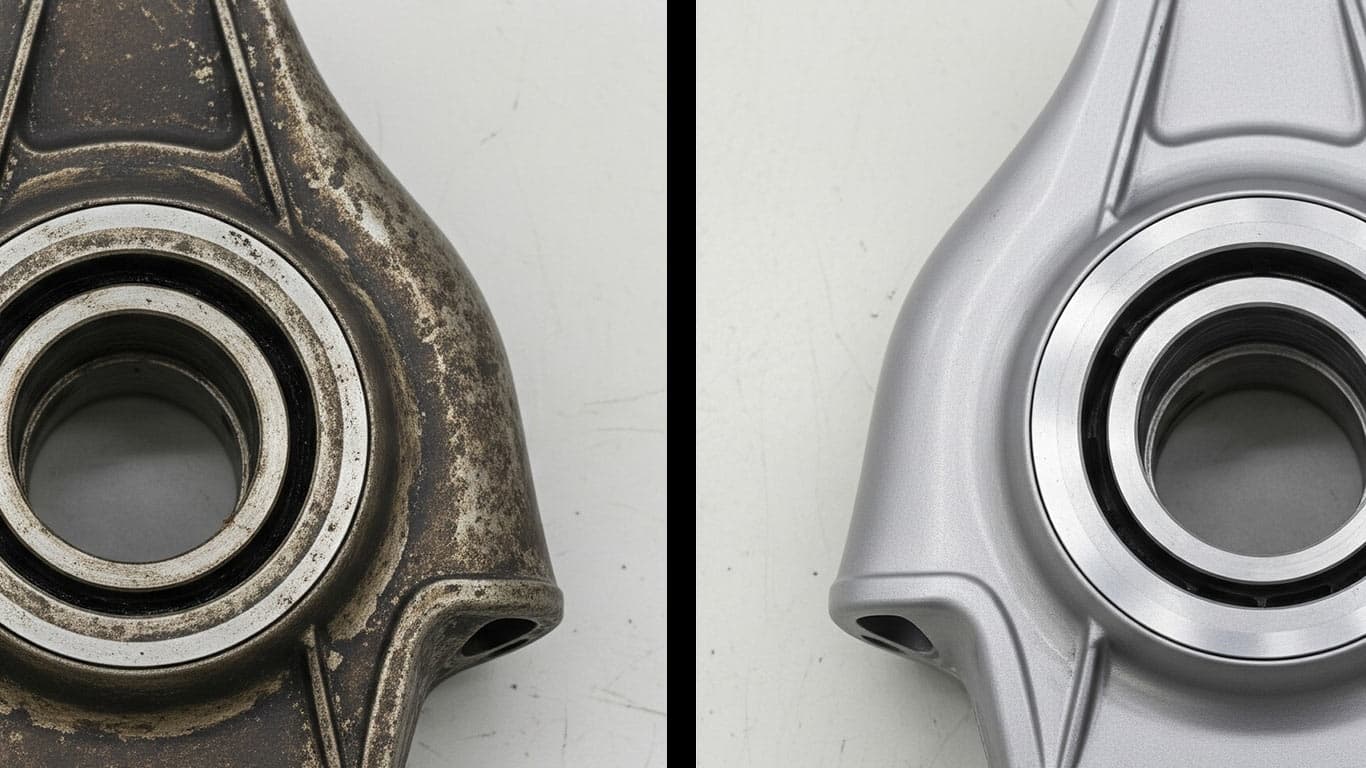

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
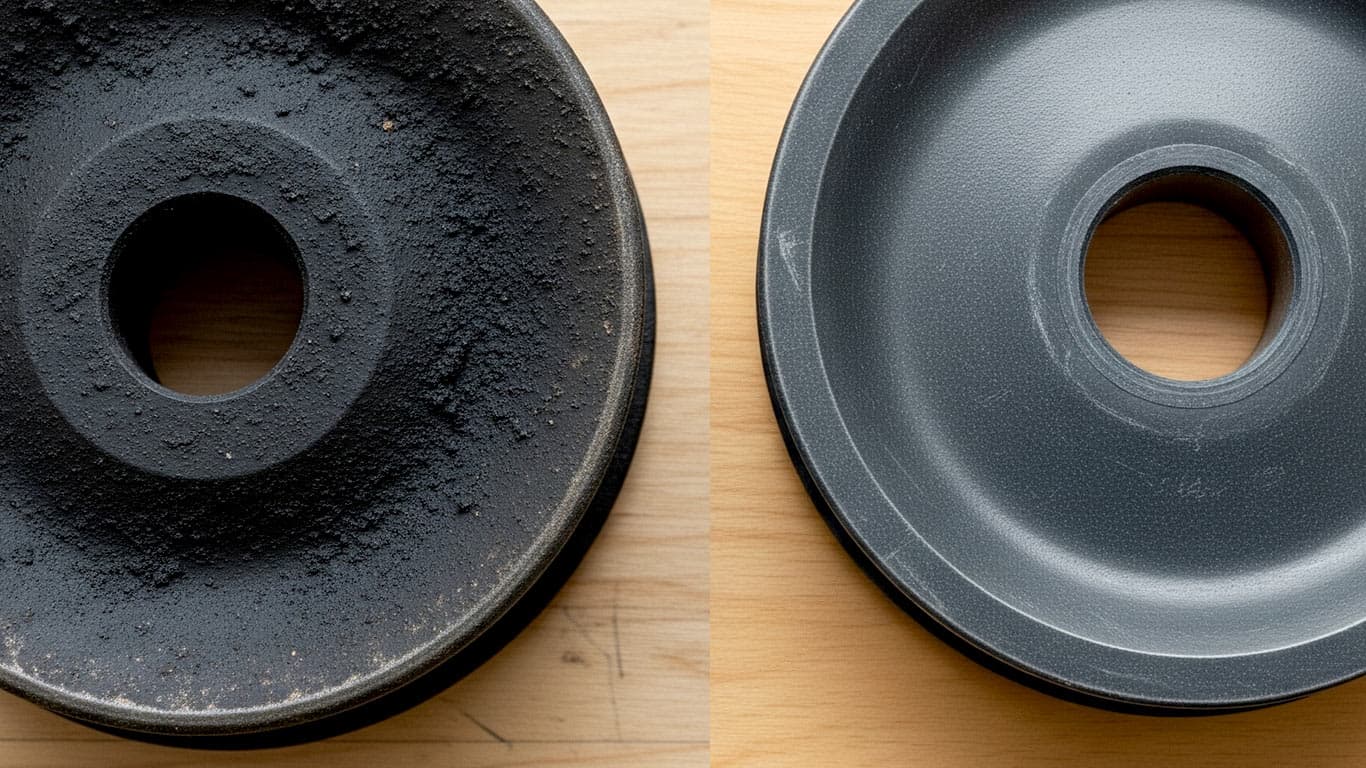

Phenolic Resin Composites
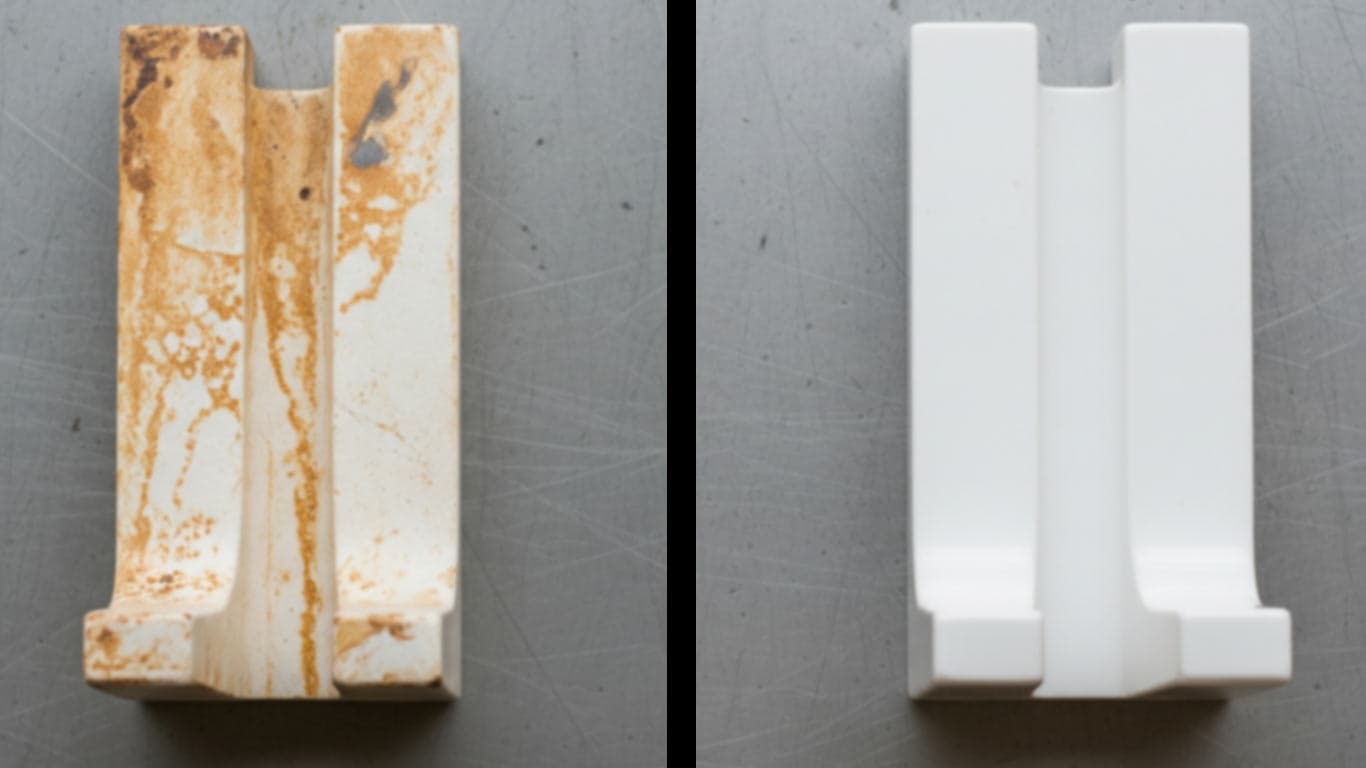

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
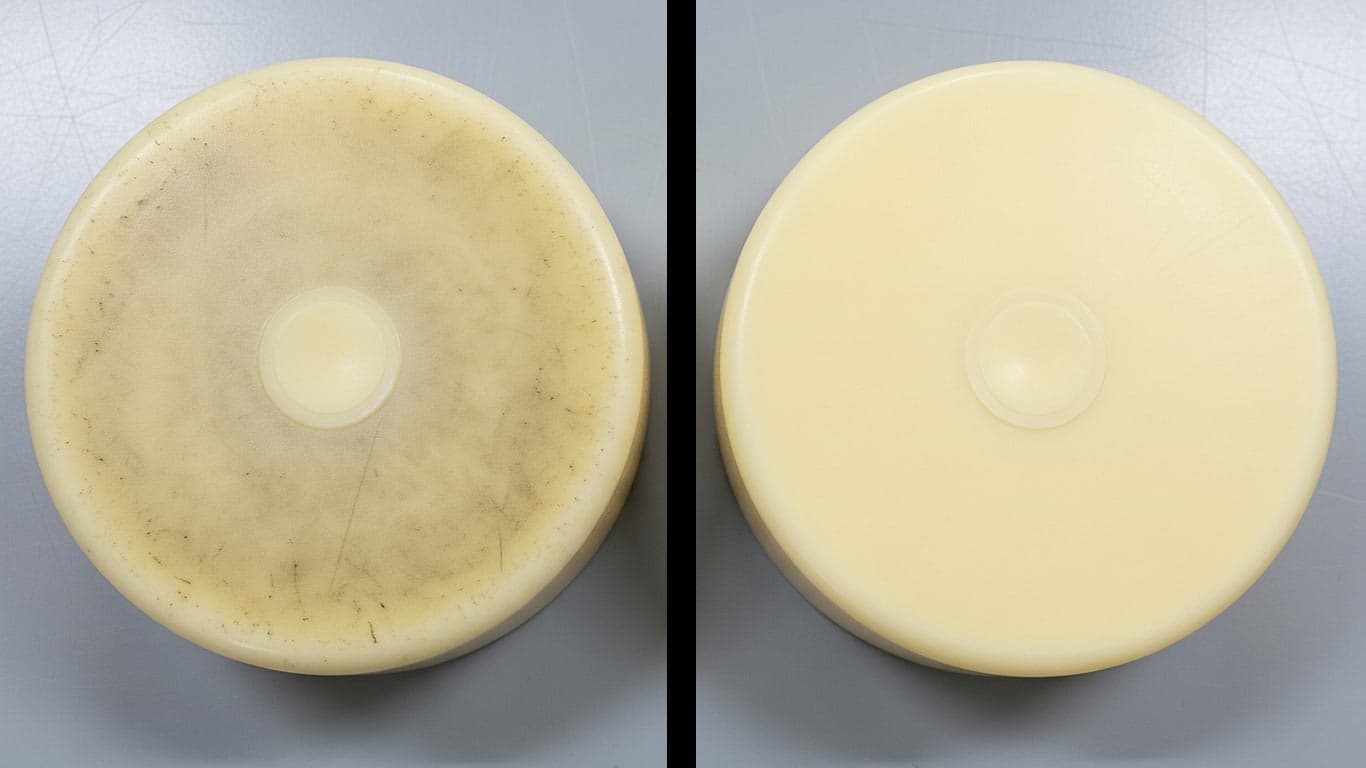

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Asbestos-Containing Material Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more


