


Lead-Based Paint Removal
Lead-paint contamination forms as durable inorganic coating on old surfaces. Before cleaning, layer adheres tightly to substrates like wood or metal, so removal demands care. Process exhibits unique patterns because paint flakes and bonds unevenly during aging. Exposure to weather causes cracking, and buildup occurs in layers over time.
In laser applications, treatment removes contamination effectively, yet challenges arise from toxicity. Heat vaporizes lead easily, so fumes develop during ablation. On porous materials, residue lingers because absorption happens deeply. Surface shows irregularity after partial removal. Results indicate that intervals prevent substrate damage, and scanning reveals uniformity post-treatment. Contamination behaves differently on smooth metals, where peeling occurs faster.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
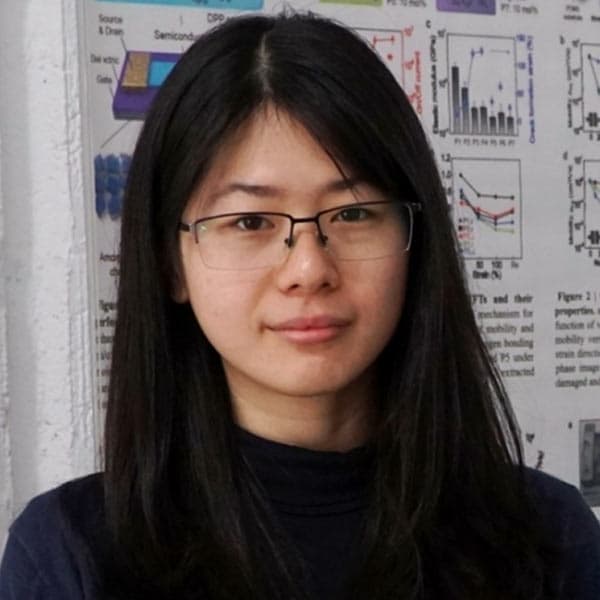
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper

Epoxy Resin Composites

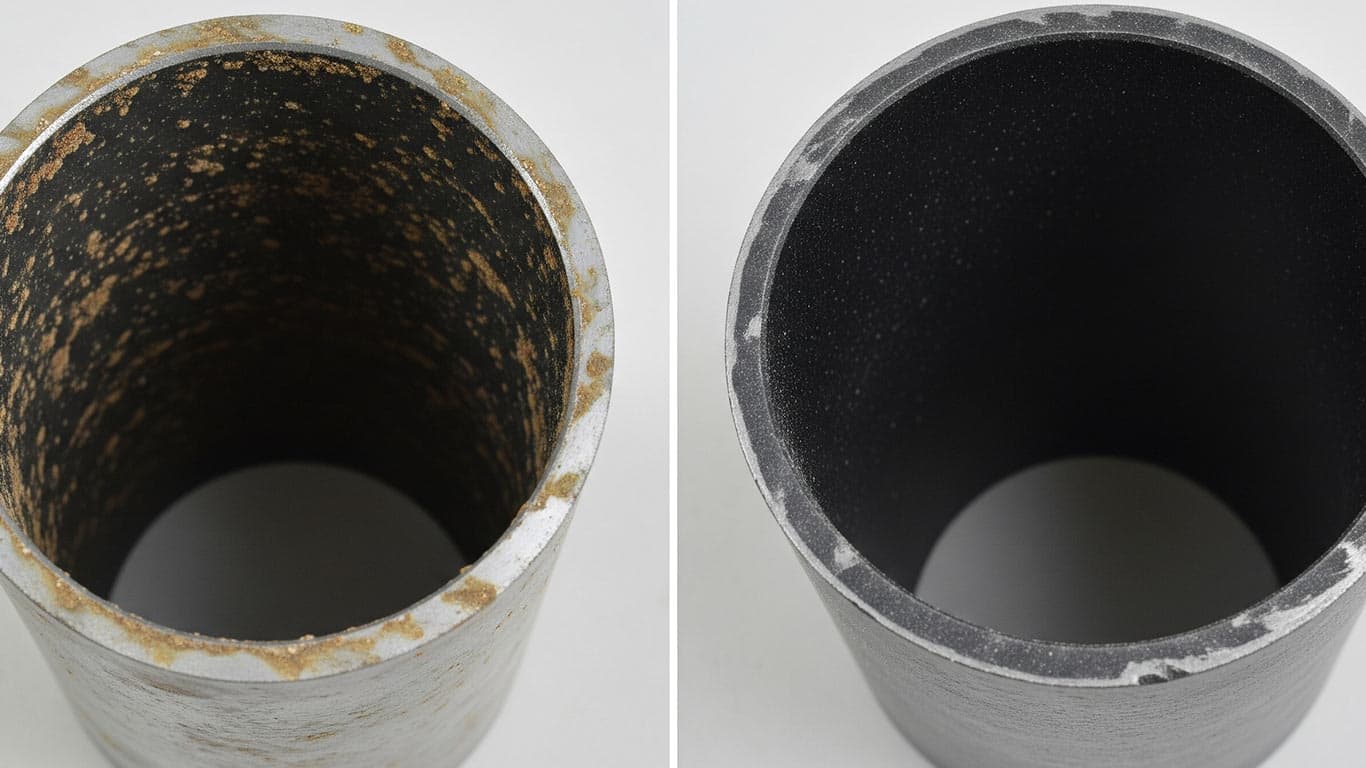
Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
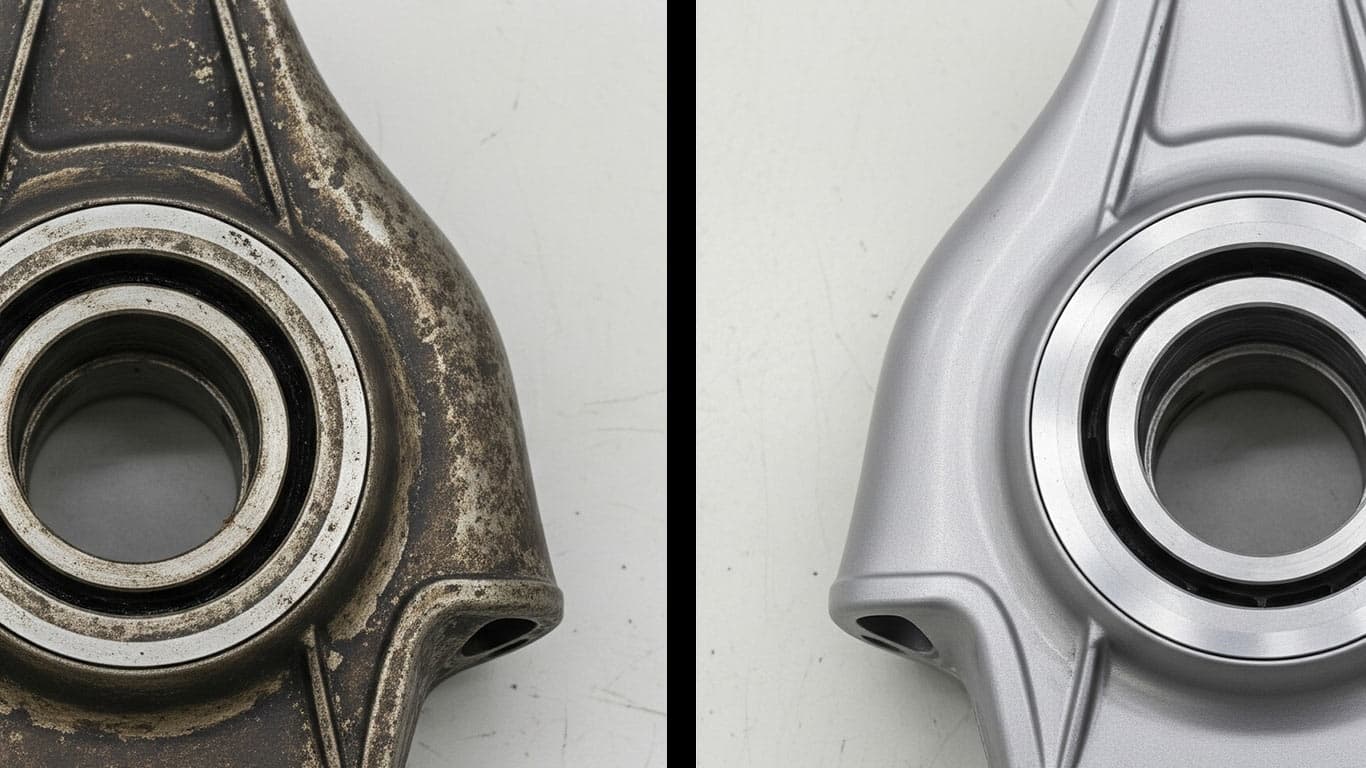

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
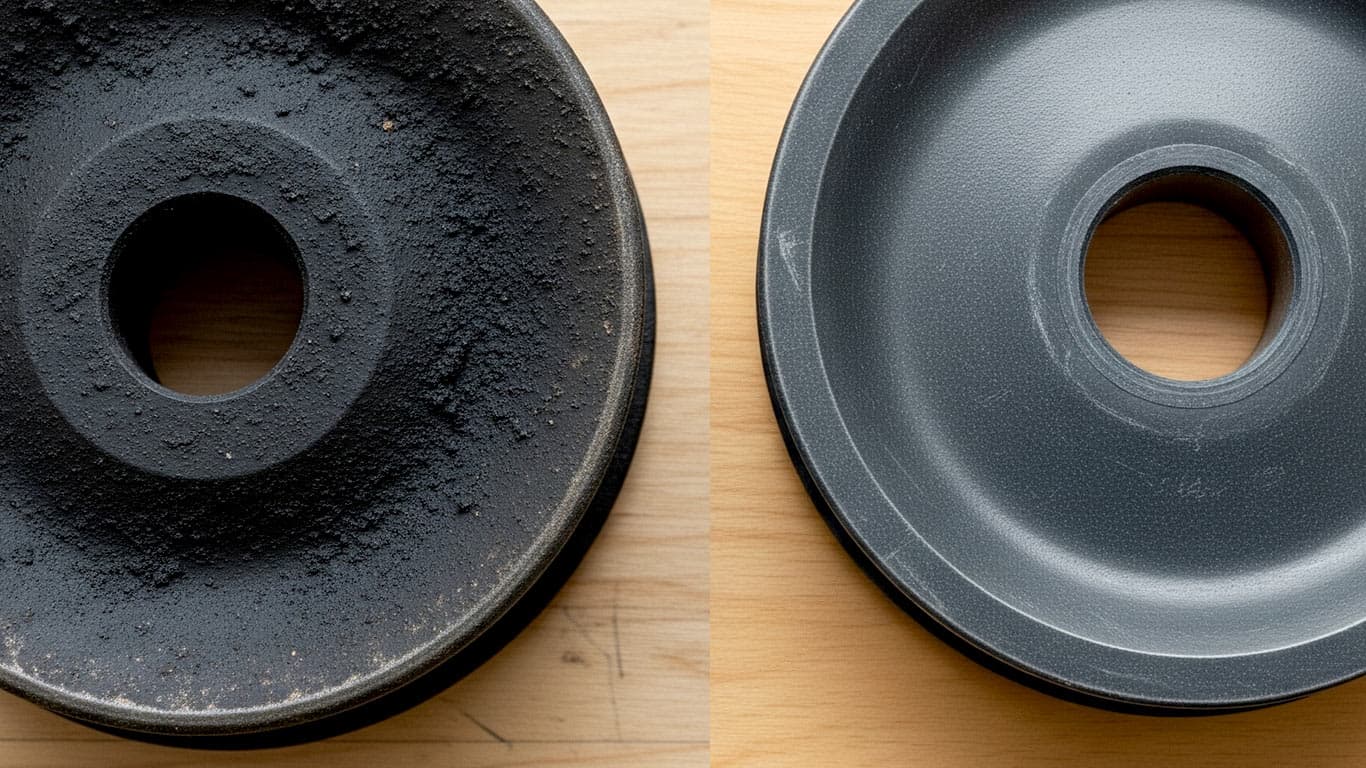

Phenolic Resin Composites
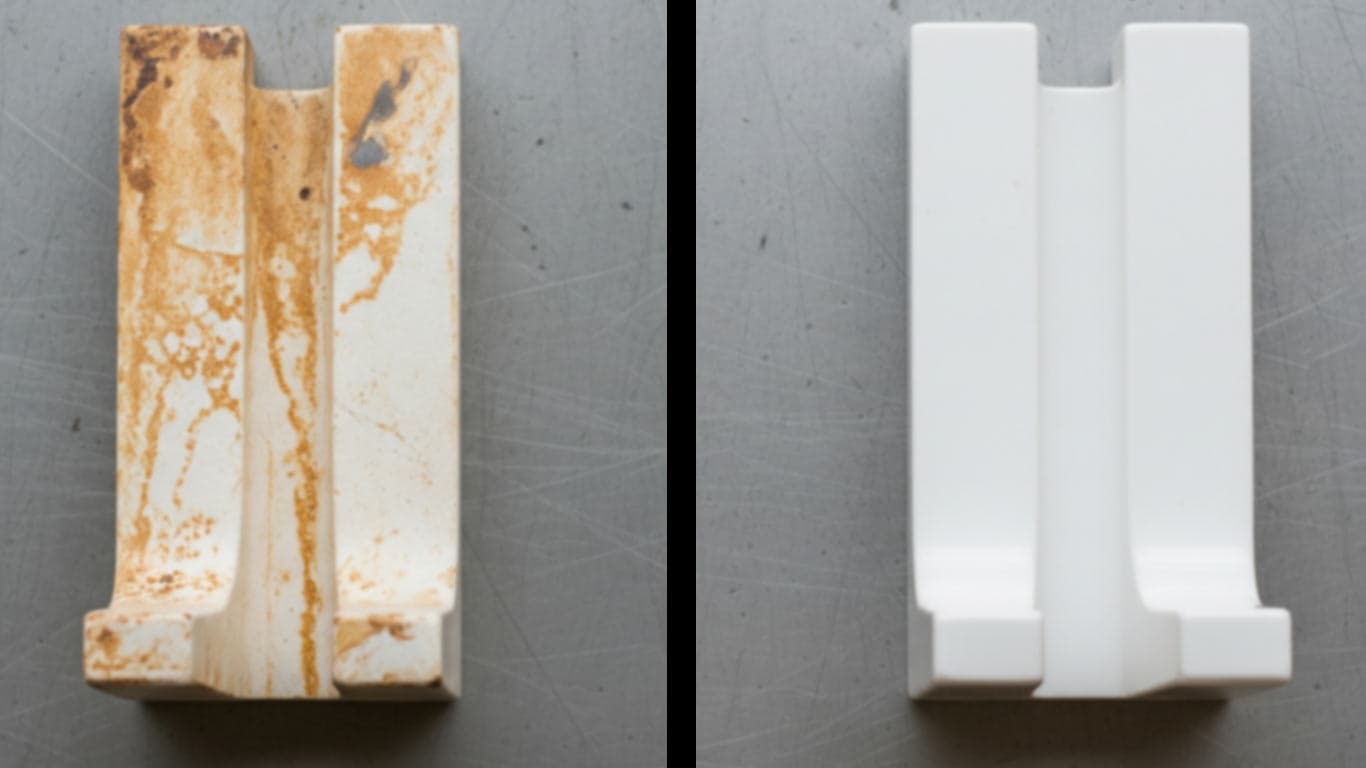

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
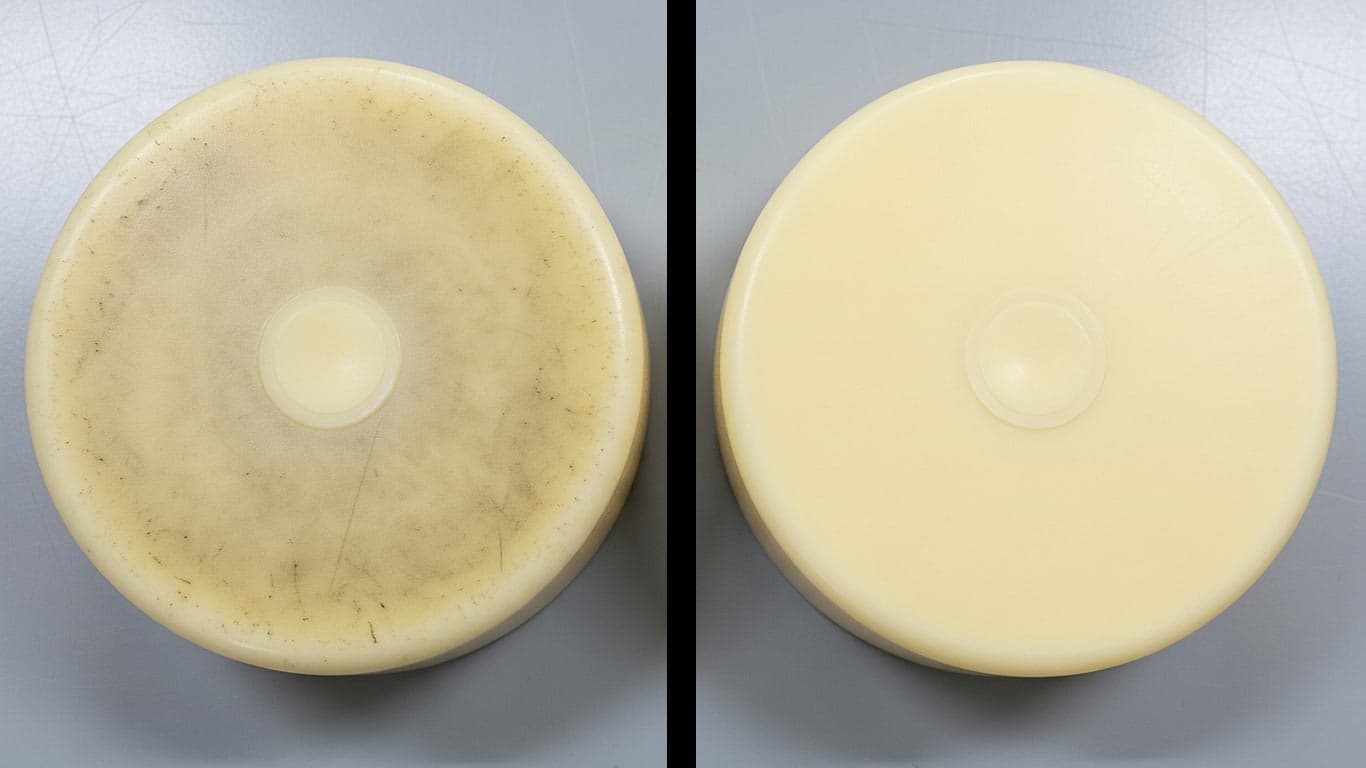

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Lead-Based Paint Removal Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more



