


Powder Coating Buildup
Powder-coating contamination, it forms through electrostatic adhesion and baking, thus creates dense inorganic layers on metal substrates. This contamination, it traps particles during application and exhibits irregular patterns from uneven powder distribution. Formation patterns, they show clustered deposits and thus resist uniform coverage. In laser cleaning applications, removal challenges arise, surface integrity demands precise energy control to avoid delamination. Material-specific behaviors, powder coating on steel bonds tightly and withstands heat, while on aluminum it shows fragility under pulse exposure. After treatment, contamination layers detach selectively, yet residues still persist in crevices. Cleaning process, it enhances surface durability and restores adhesion properties. Evidence from observations confirms, laser parameters adjust and yield clean finishes without substrate damage.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
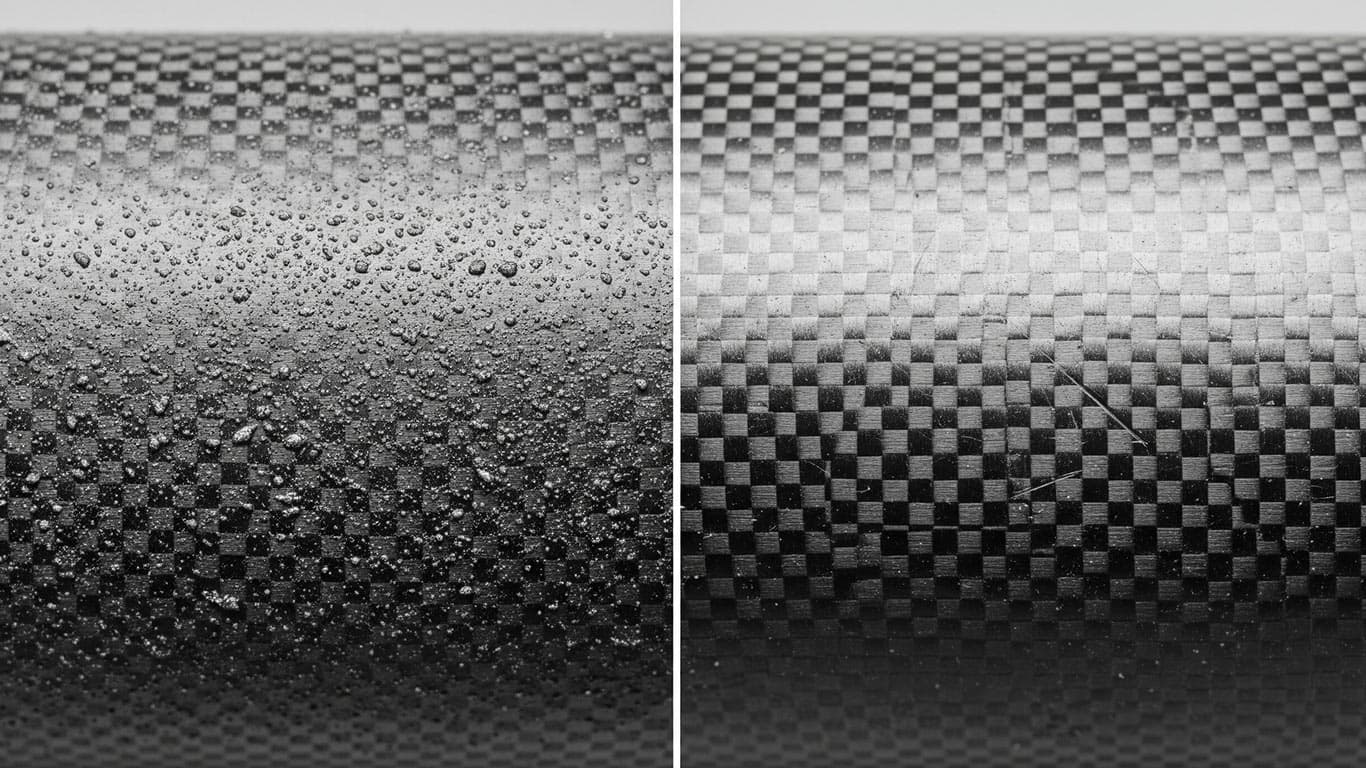
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
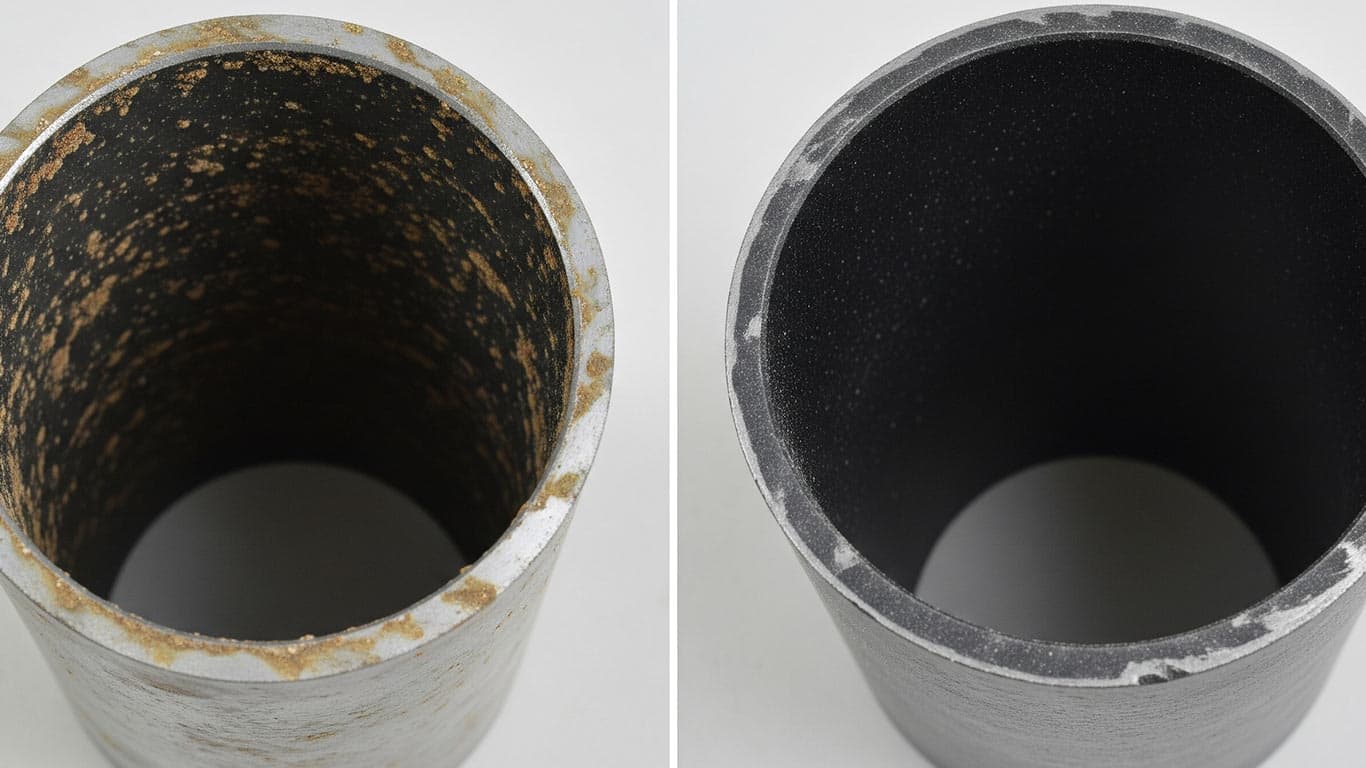

Epoxy Resin Composites
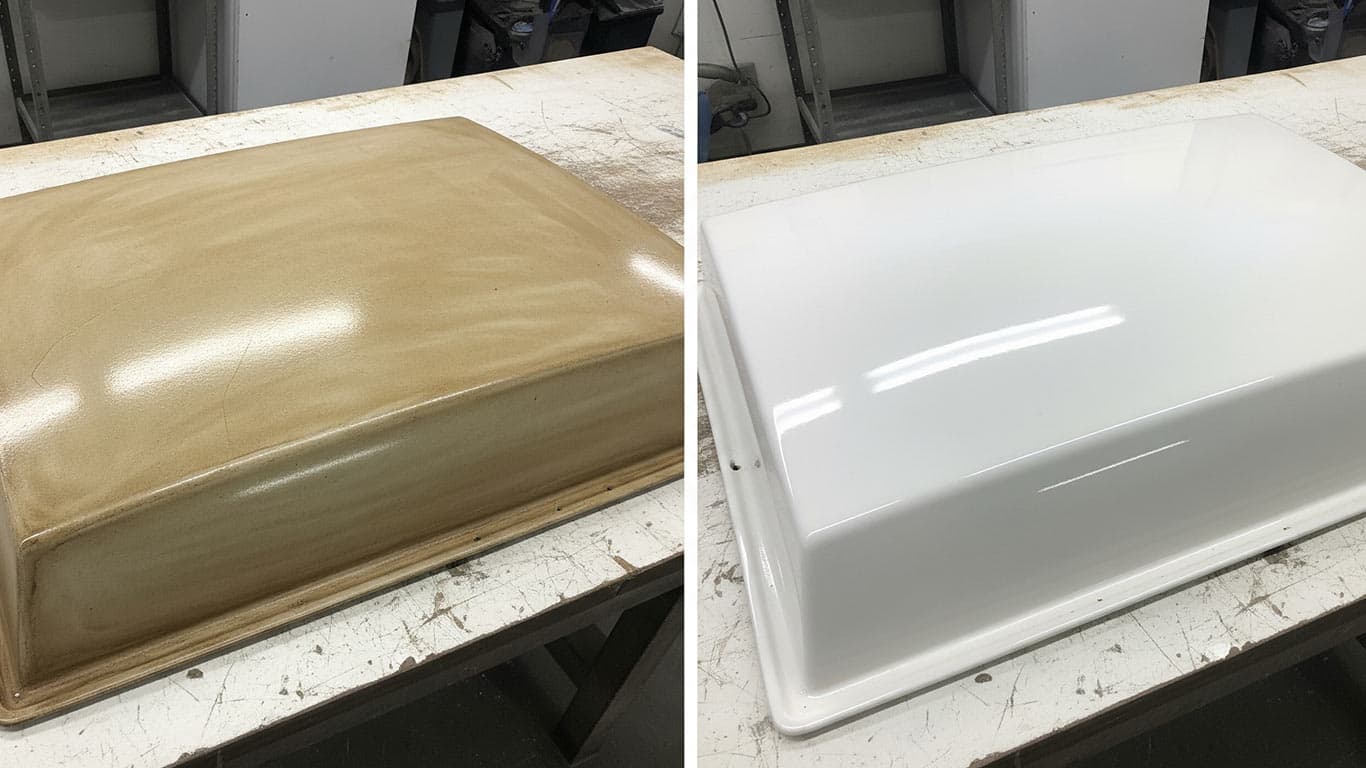

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
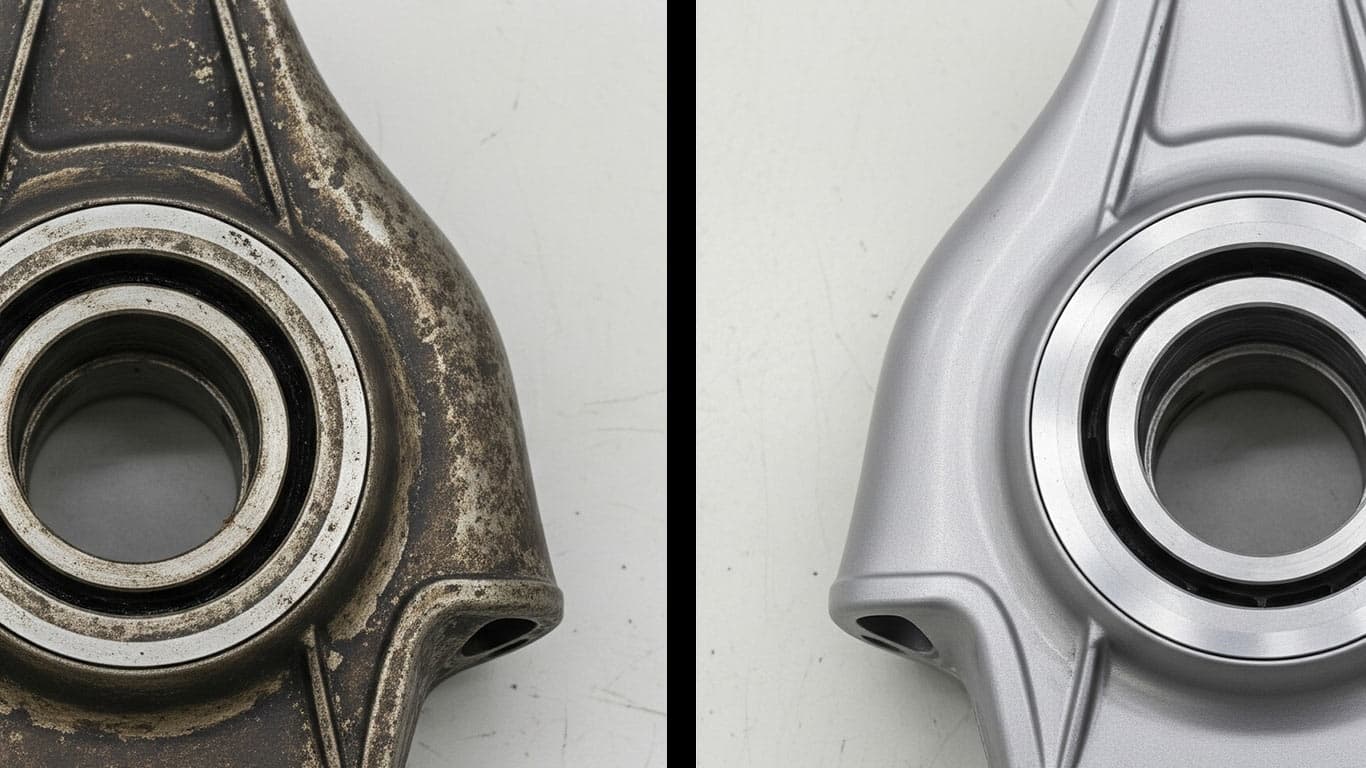

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
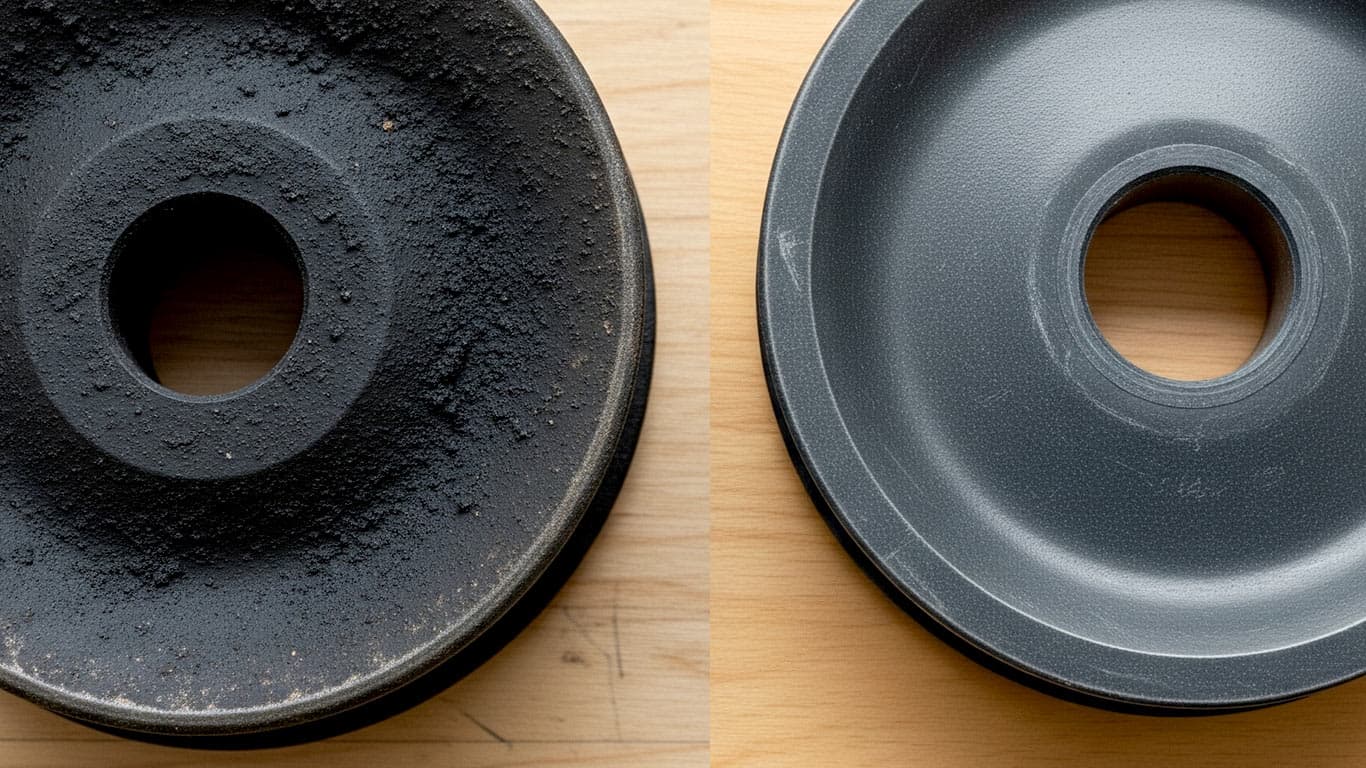

Phenolic Resin Composites
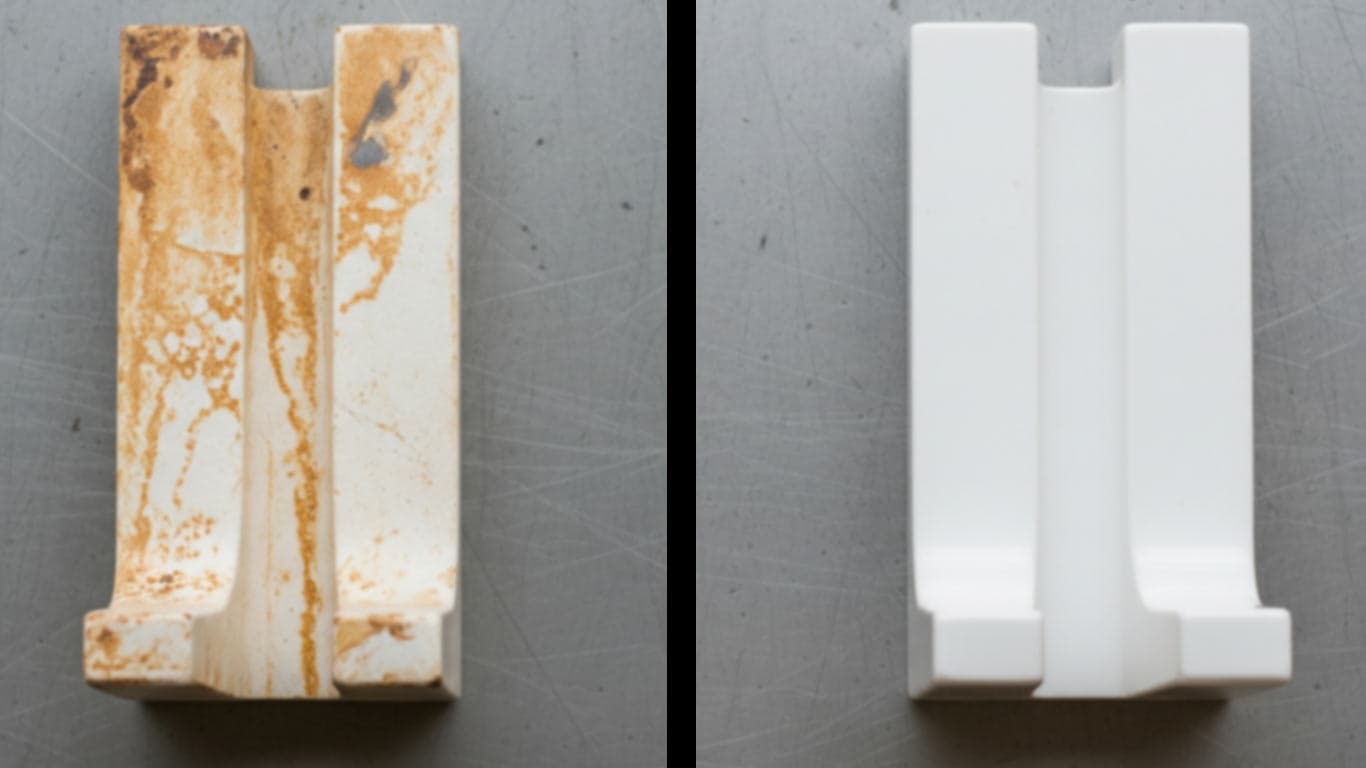

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
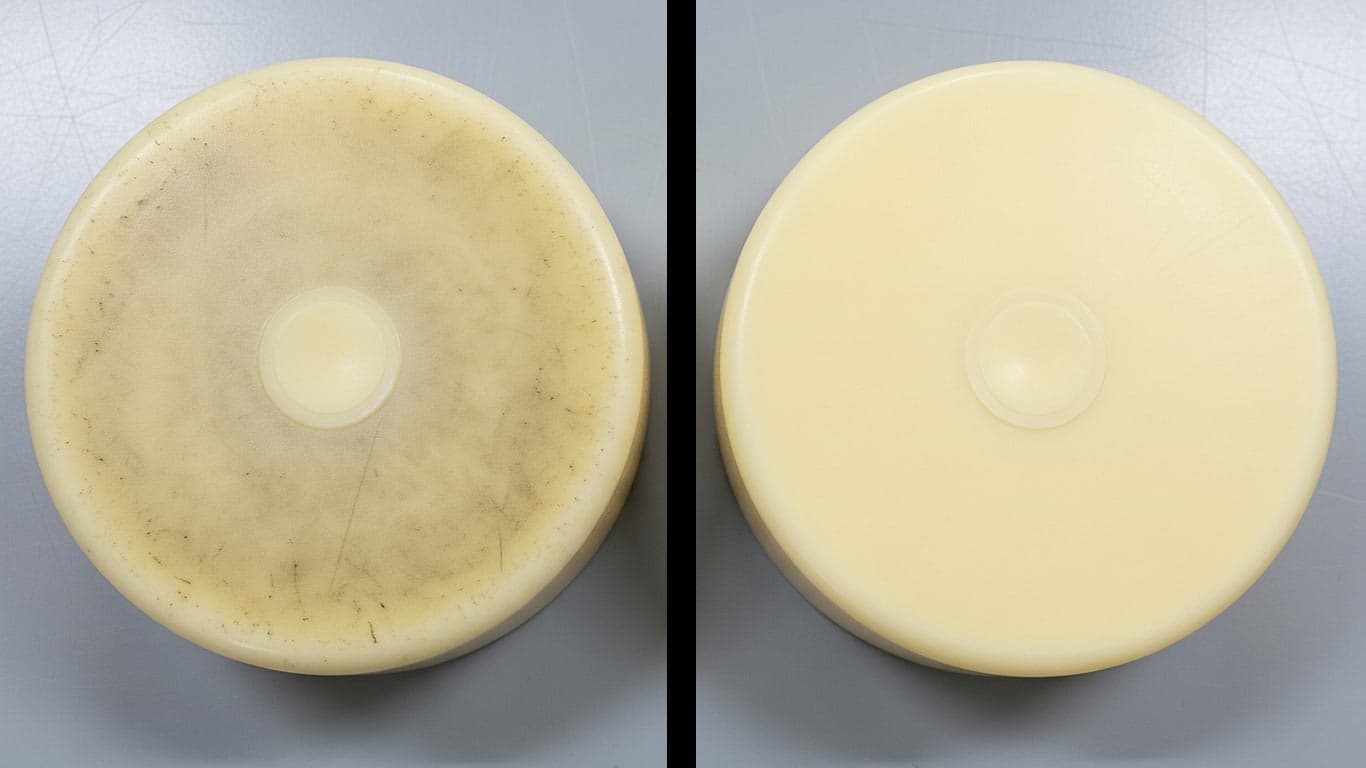

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Powder Coating Buildup Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more




