


Brass Coating Removal
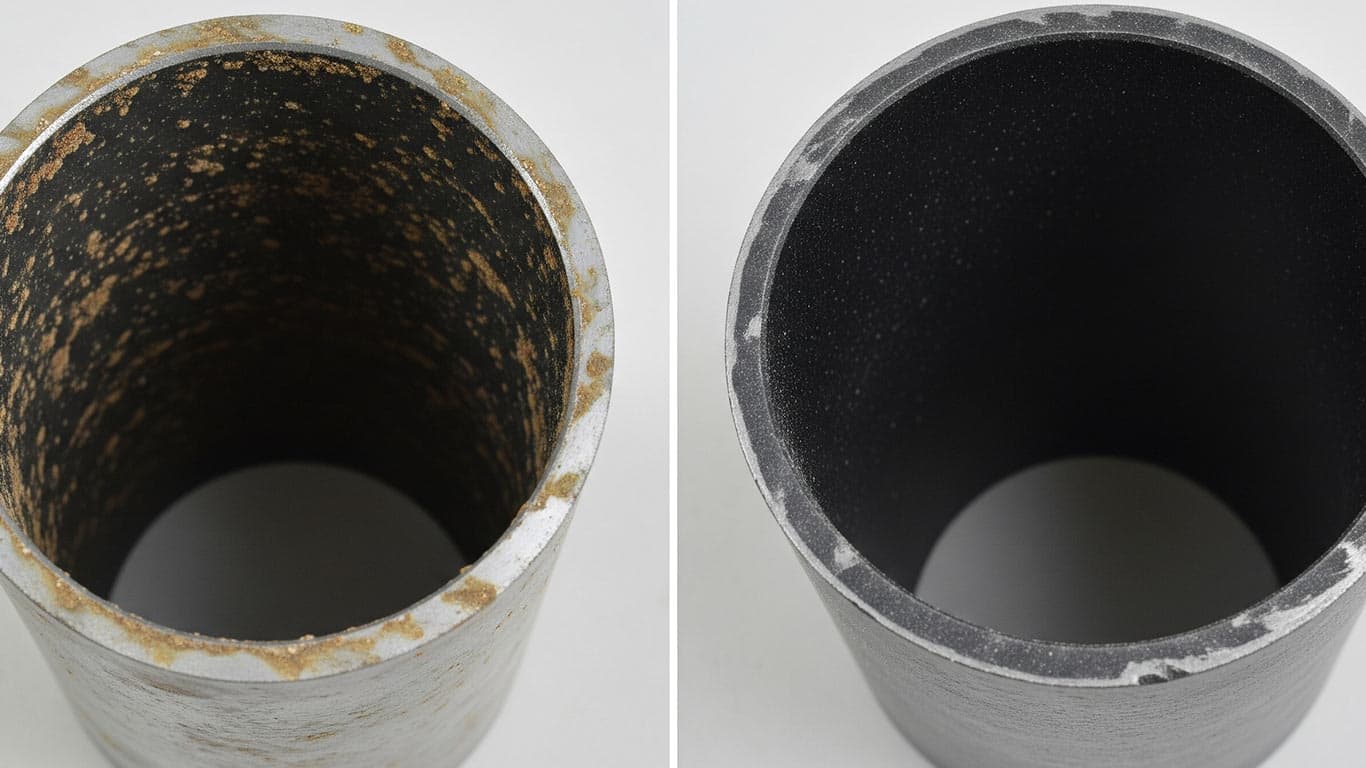
Brass-plating contamination arises during exposure to humid environments, and it forms unique patterns on the coated surface. This contamination, it develops as thin oxide layers with patchy distributions, thus creating irregular adhesion spots across brass regions. Material-specific behaviors emerge from brass's alloy composition, where zinc content accelerates corrosion and binds contaminants tightly, so removal proves challenging in laser cleaning applications. Laser pulses interact with these layers, yet the contamination still resists ablation due to its reflective nature on brass, and thus selective energy absorption leads to uneven cleaning. Following laser treatment, underlying plating often exhibits subtle discoloration, while persistent residues demand multiple passes for complete elimination. Efficiency of the process, it depends on pulse adjustments, and so optimized sequences reveal cleaner surfaces without substrate damage. Yi-Chun Lin, Ph.D.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper

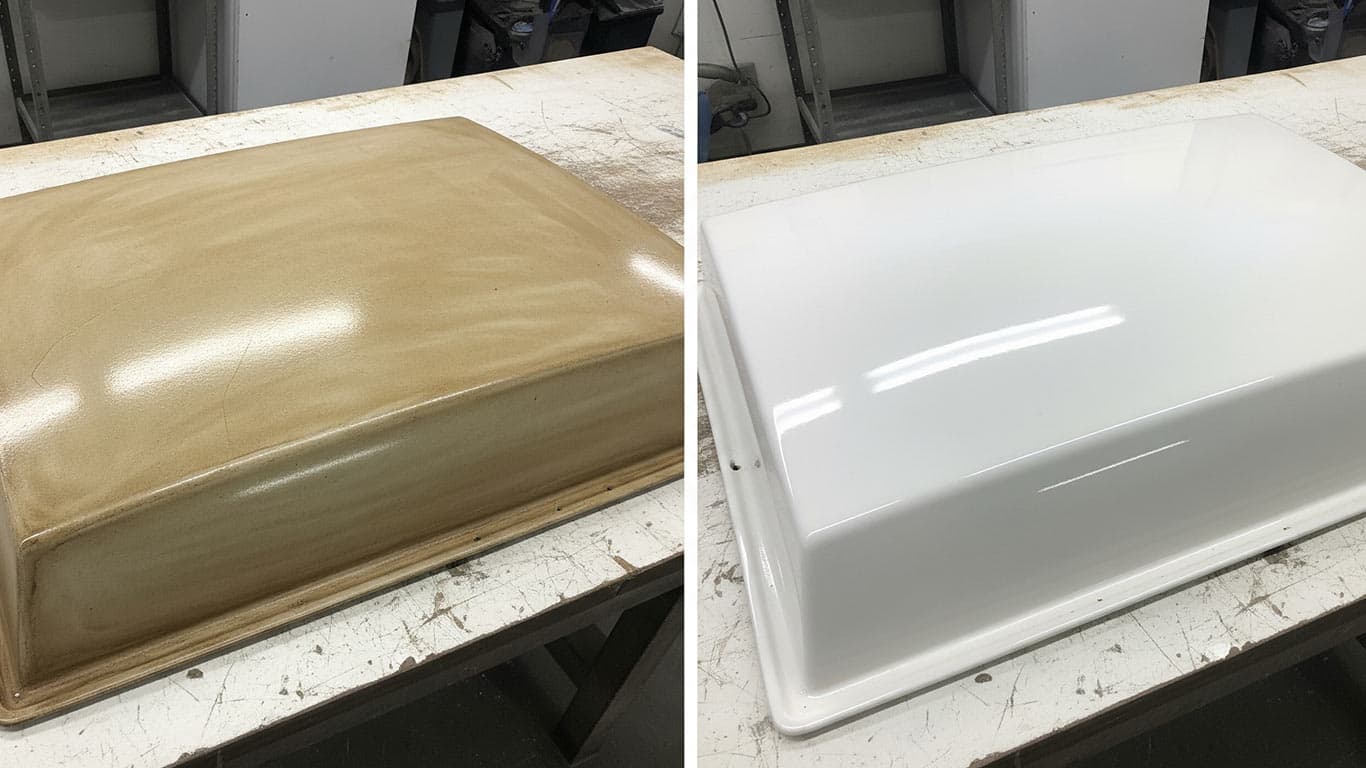
Epoxy Resin Composites

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
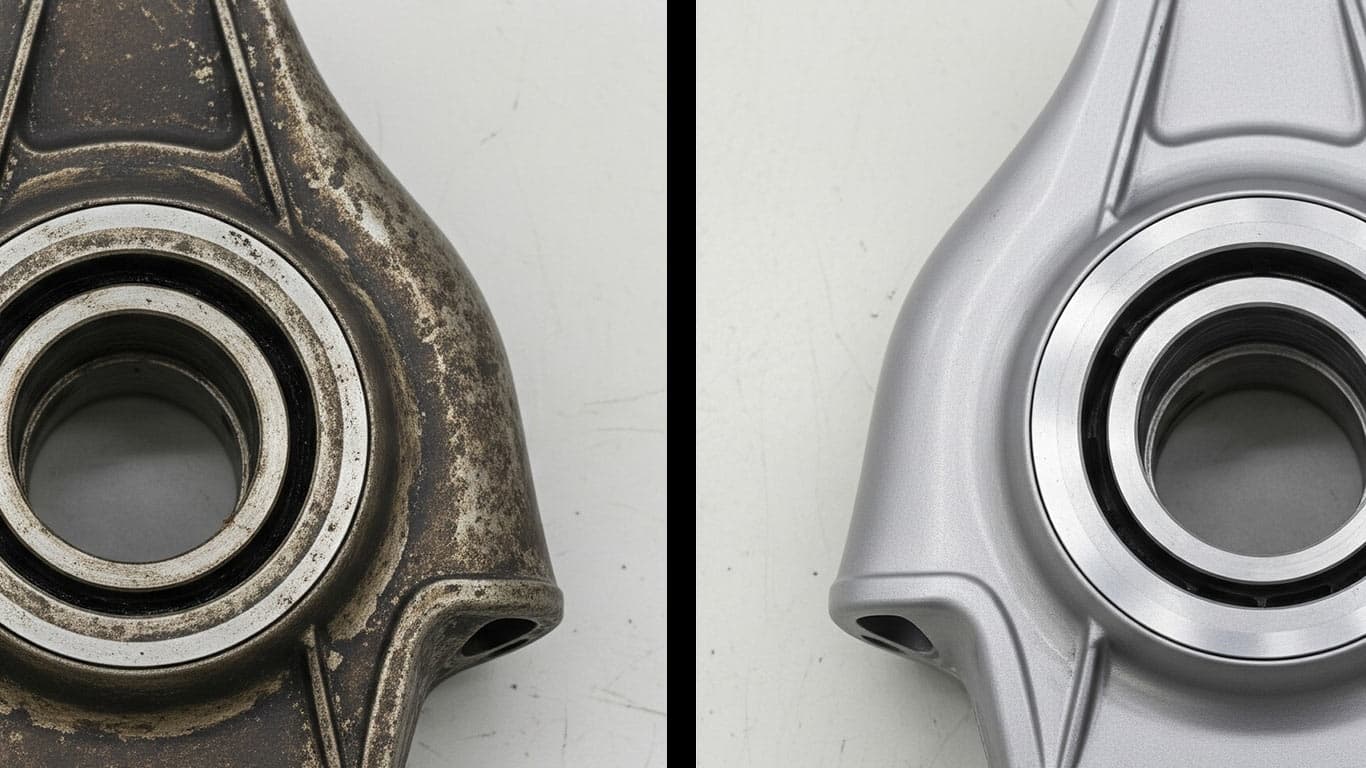

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
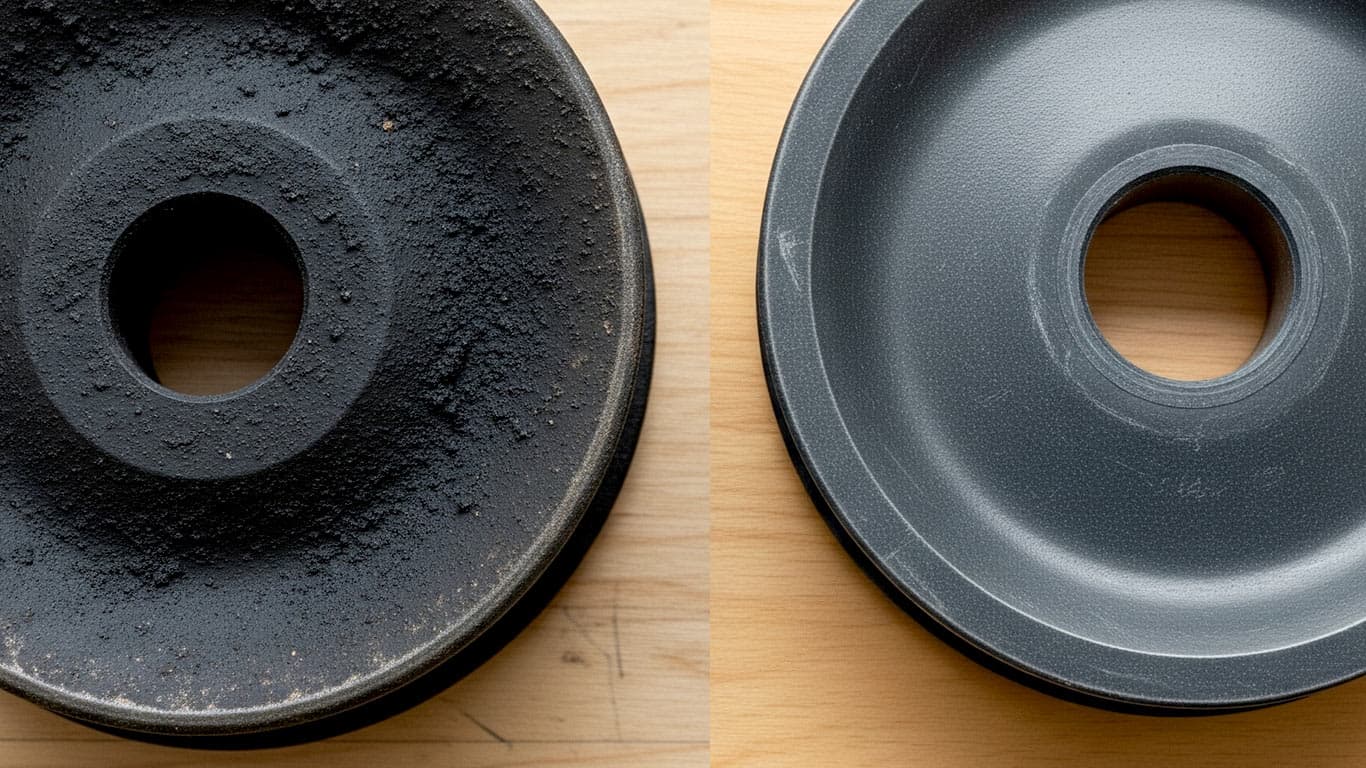

Phenolic Resin Composites
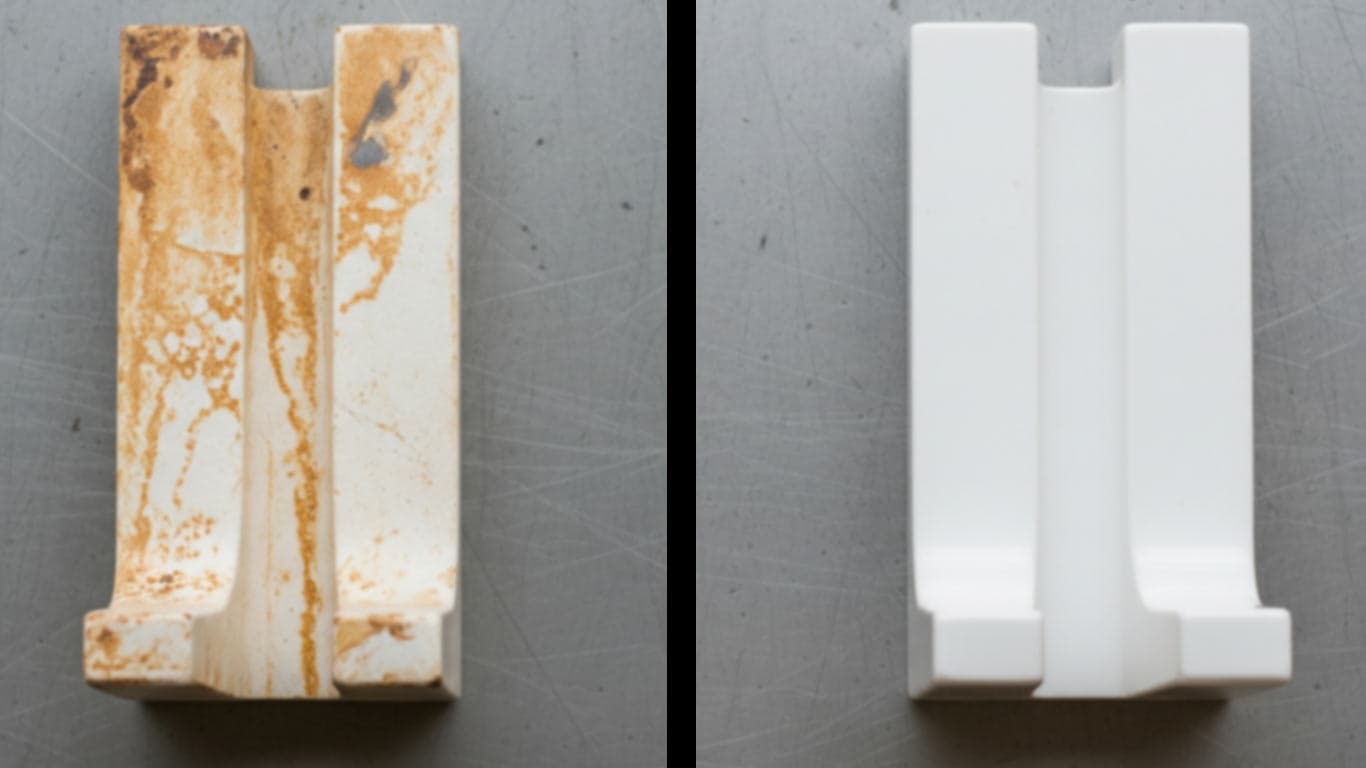

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
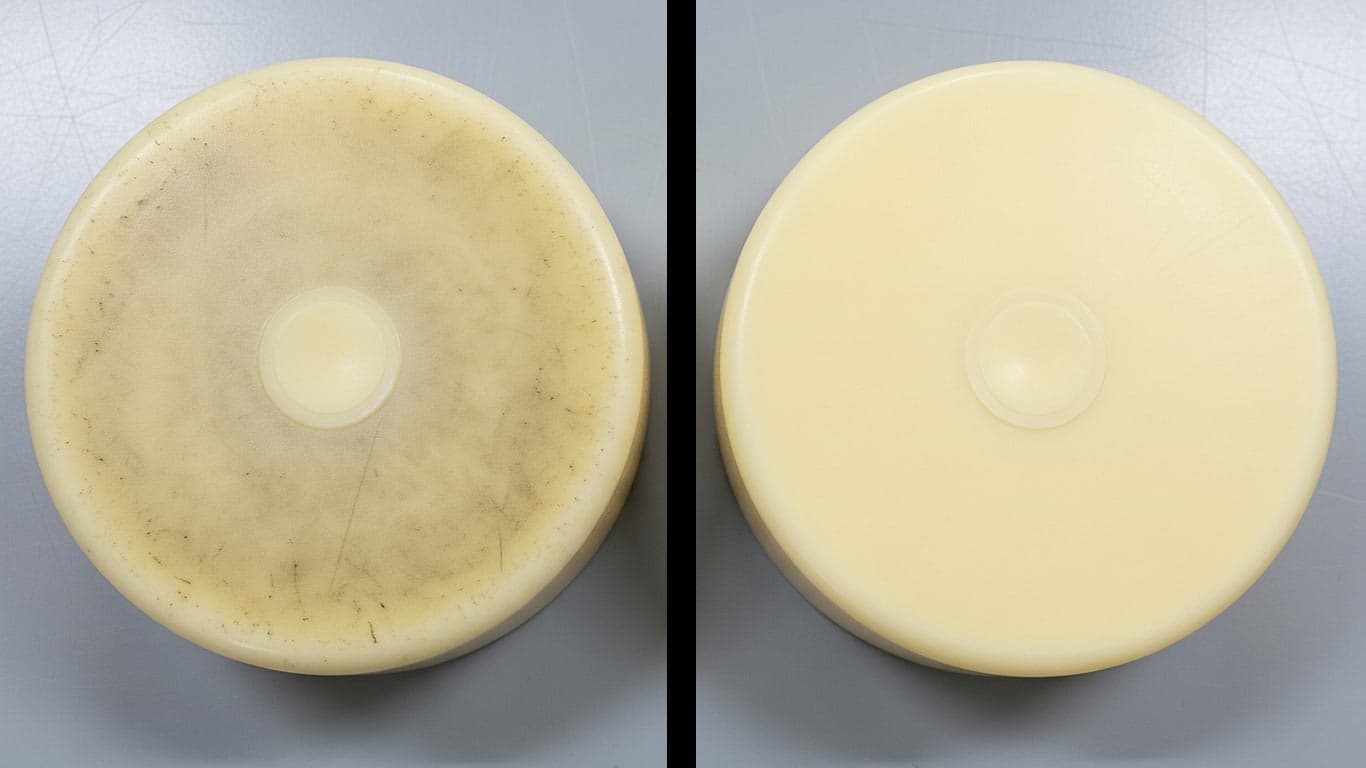

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Brass Coating Removal Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more



