


PTFE Coating Residue
Teflon residue contamination, it arises from polymer degradation during high-heat processes and forms irregular, patchy films on metal surfaces. This contamination, it adheres strongly due to low surface energy of Teflon, thus creating unique droplet-like patterns that spread unevenly. In laser cleaning applications, removal challenges emerge because residue exhibits high thermal stability and resists ablation. Laser pulses apply, yet organic bonds in Teflon break incompletely, so fragments scatter and redeposit nearby. Material-specific behaviors show that on stainless steel, residue softens slowly under infrared lasers and leaves behind hazy remnants. After treatment, surface still exhibits stickiness in contaminated zones, thus requiring multiple passes for partial clearance. Efficiency of cleaning, it drops with thicker films, and so hybrid methods often follow to enhance removal.
Yi-Chun Lin, Ph.D., Taiwan
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
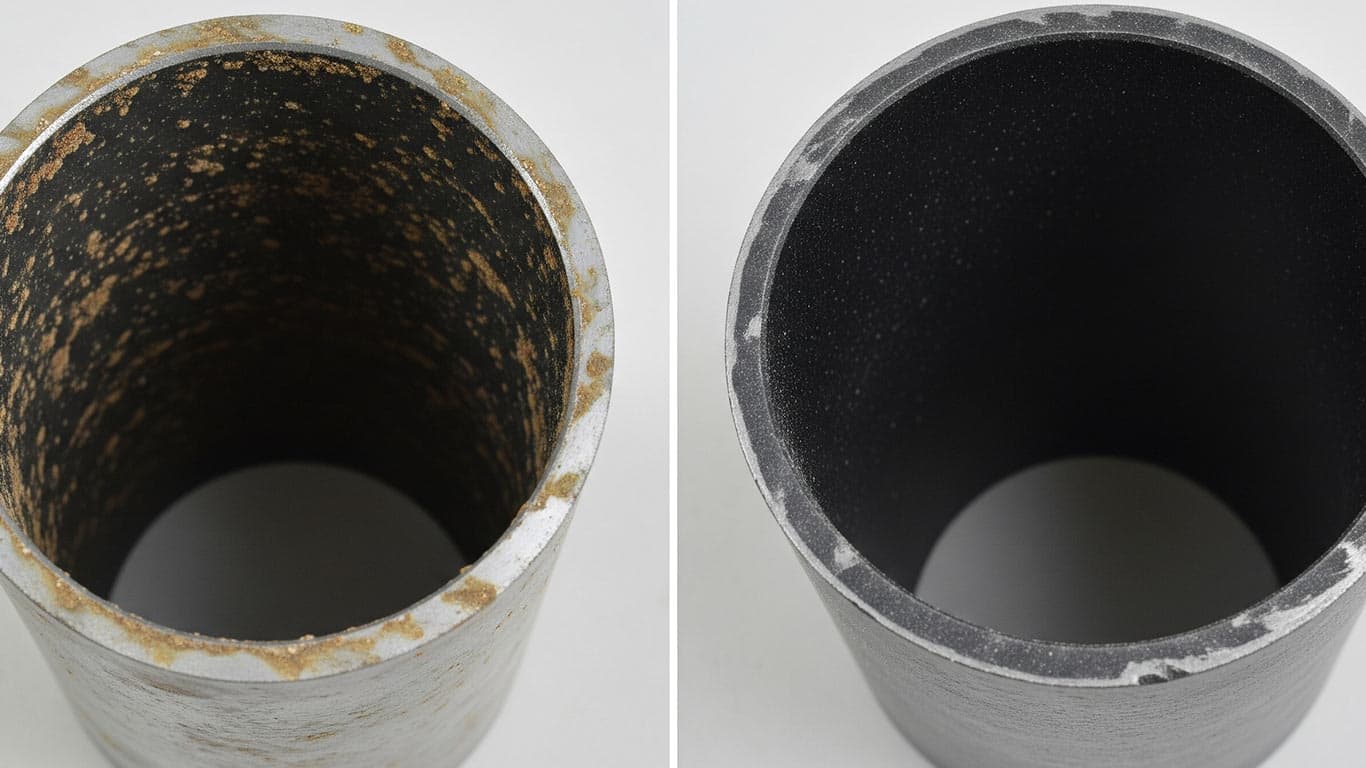

Epoxy Resin Composites
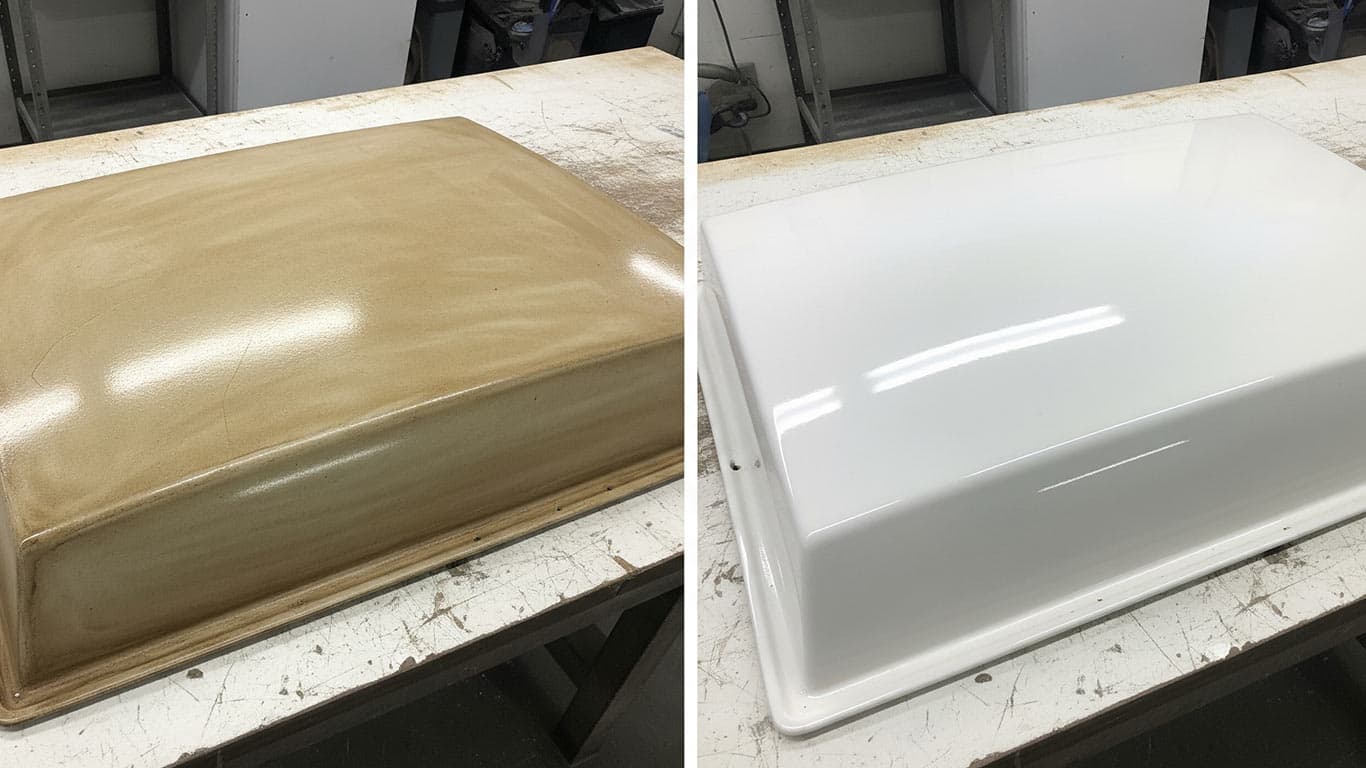

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel

Phenolic Resin Composites

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
PTFE Coating Residue Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more

