


Thermal Spray Coating
Plasma-spray contamination arises during the thermal deposition process, where molten particles adhere unevenly to substrates. This contamination, it manifests as tenacious oxide layers, which exhibit regional variations influenced from substrate geometry. On metals like steel, the deposits persist densely, showing heat-resistant bonds that resist initial laser pulses. Ceramics, by contrast, display fragmented patterns, less adherent yet prone to microcracking under exposure.
Removal challenges emerge distinctly; the contamination adheres stubbornly to ferrous materials, demanding prolonged irradiation to dislodge, while on non-metallics, it disperses more readily but leaves residual roughness. It appears that laser cleaning yields incomplete results on uneven surfaces, where shadows hinder uniform ablation. These behaviors, they highlight the need for tailored wavelengths, as confirmed by surface scans. The process effectively mitigates thermal damage, though adhesion varies regionally.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum

Brass

Brick

Bronze
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
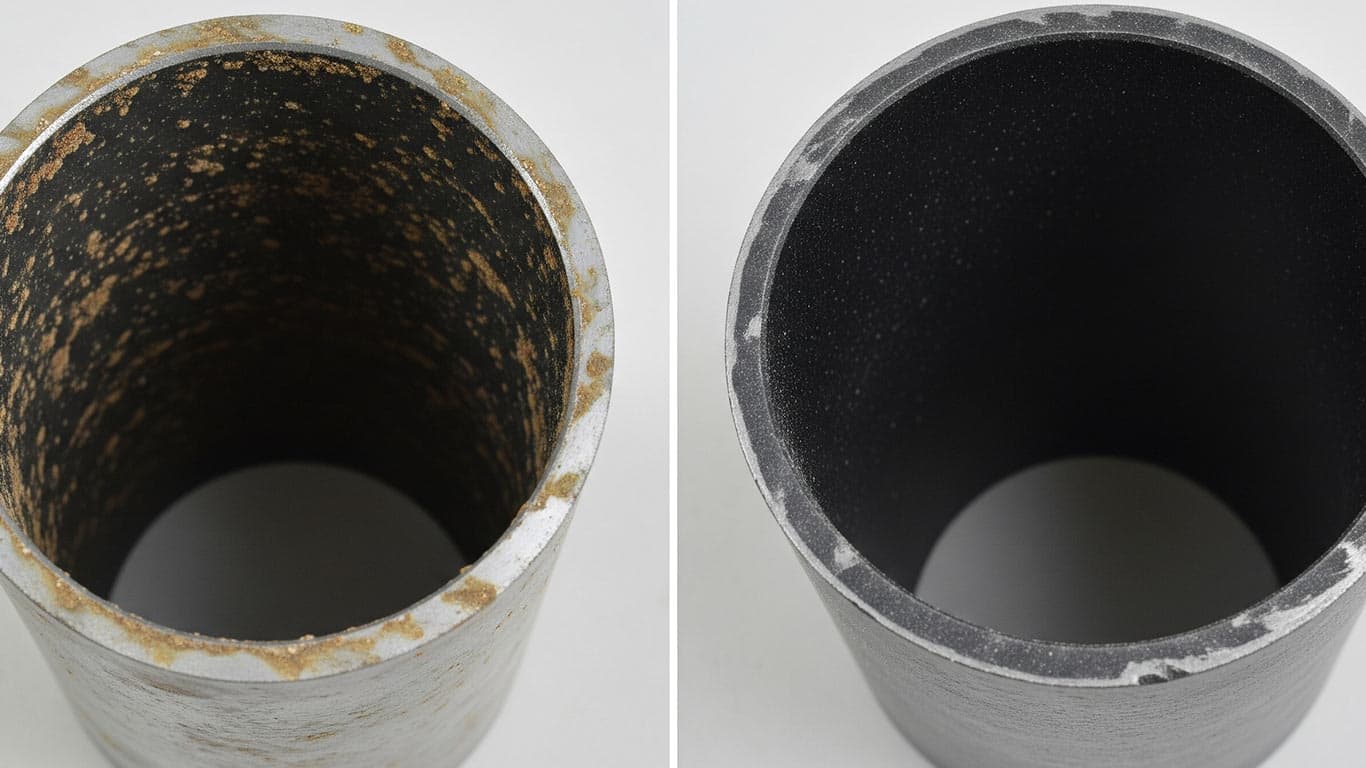

Epoxy Resin Composites
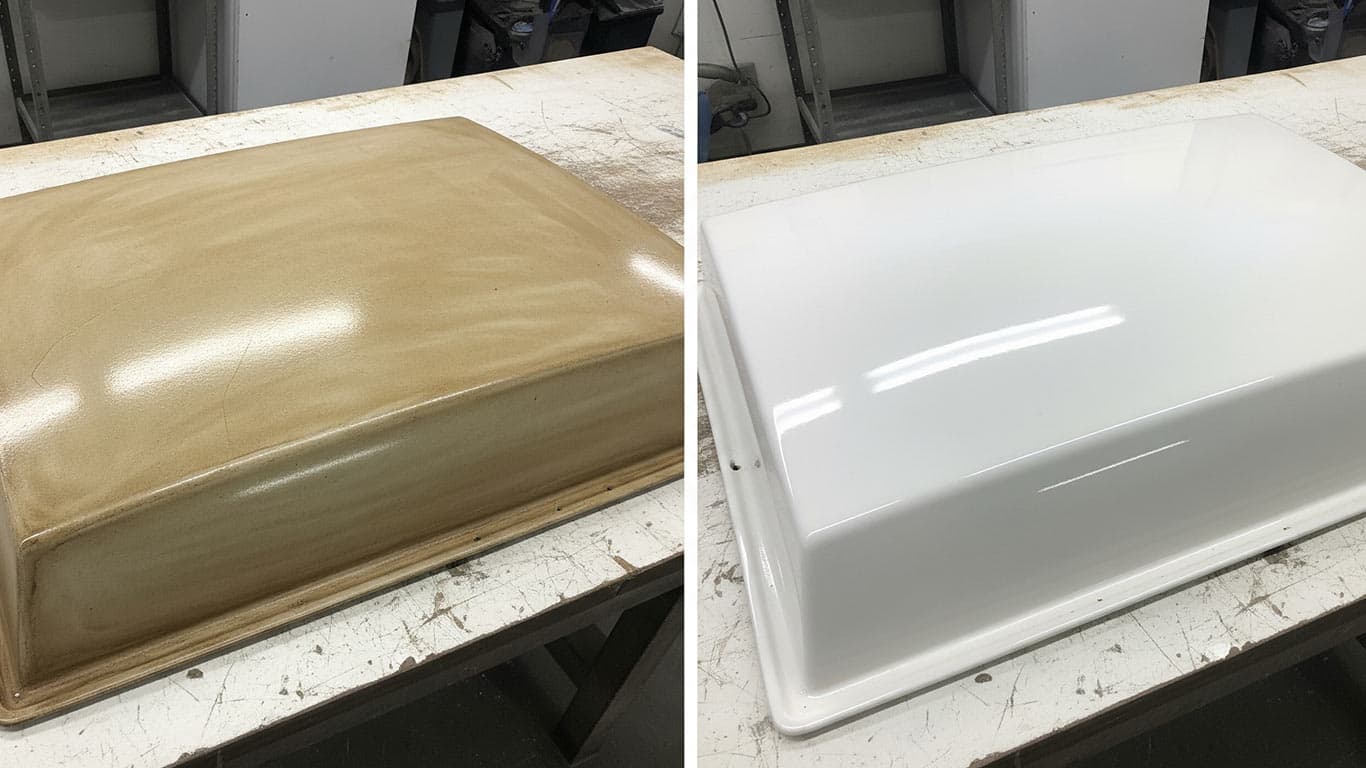

Fiberglass

Granite

Iron

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble
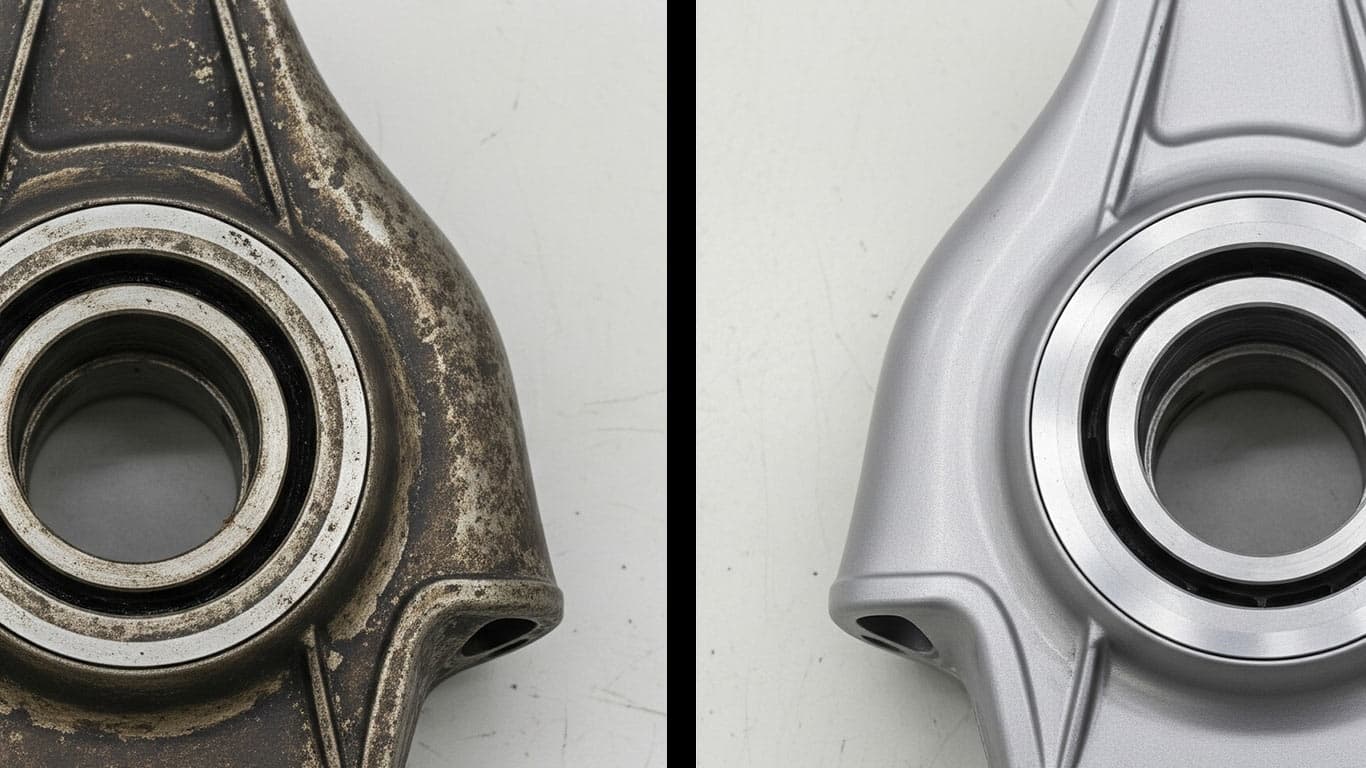

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel
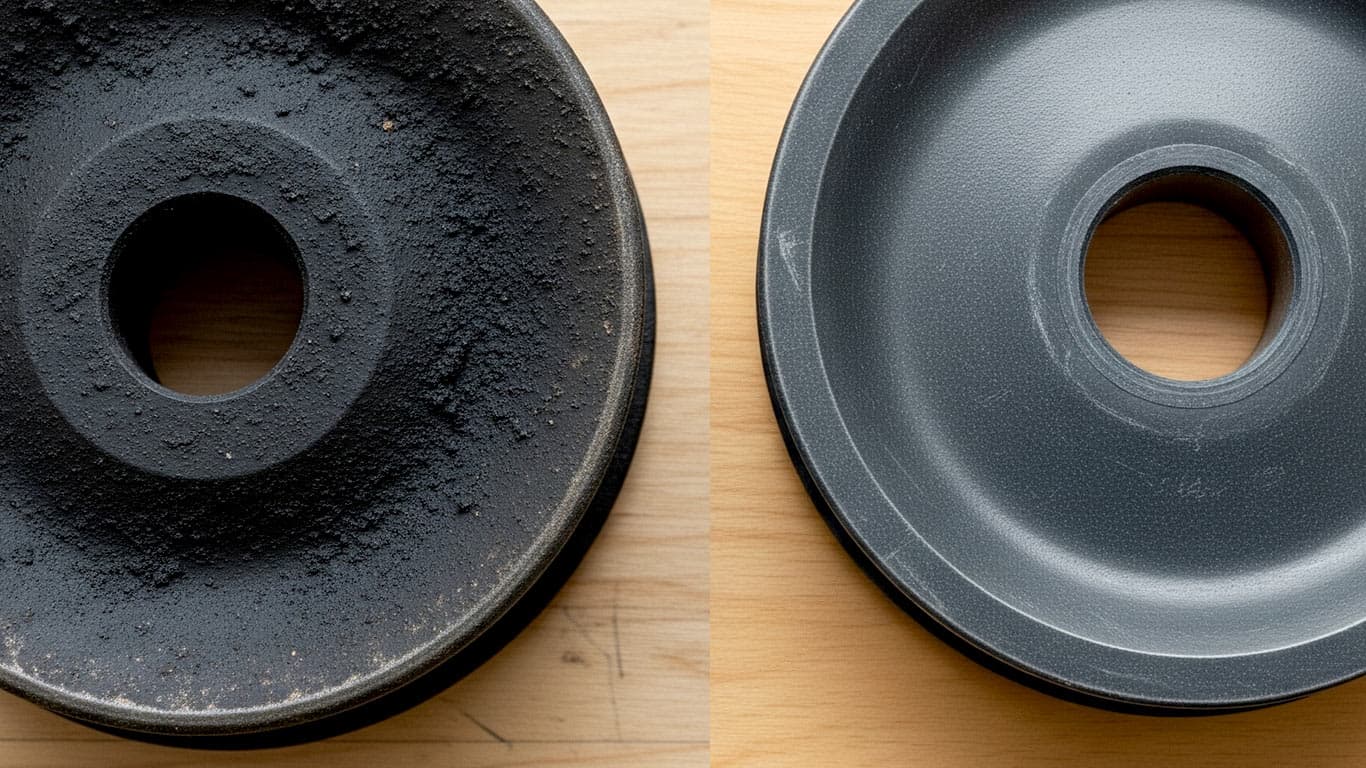

Phenolic Resin Composites
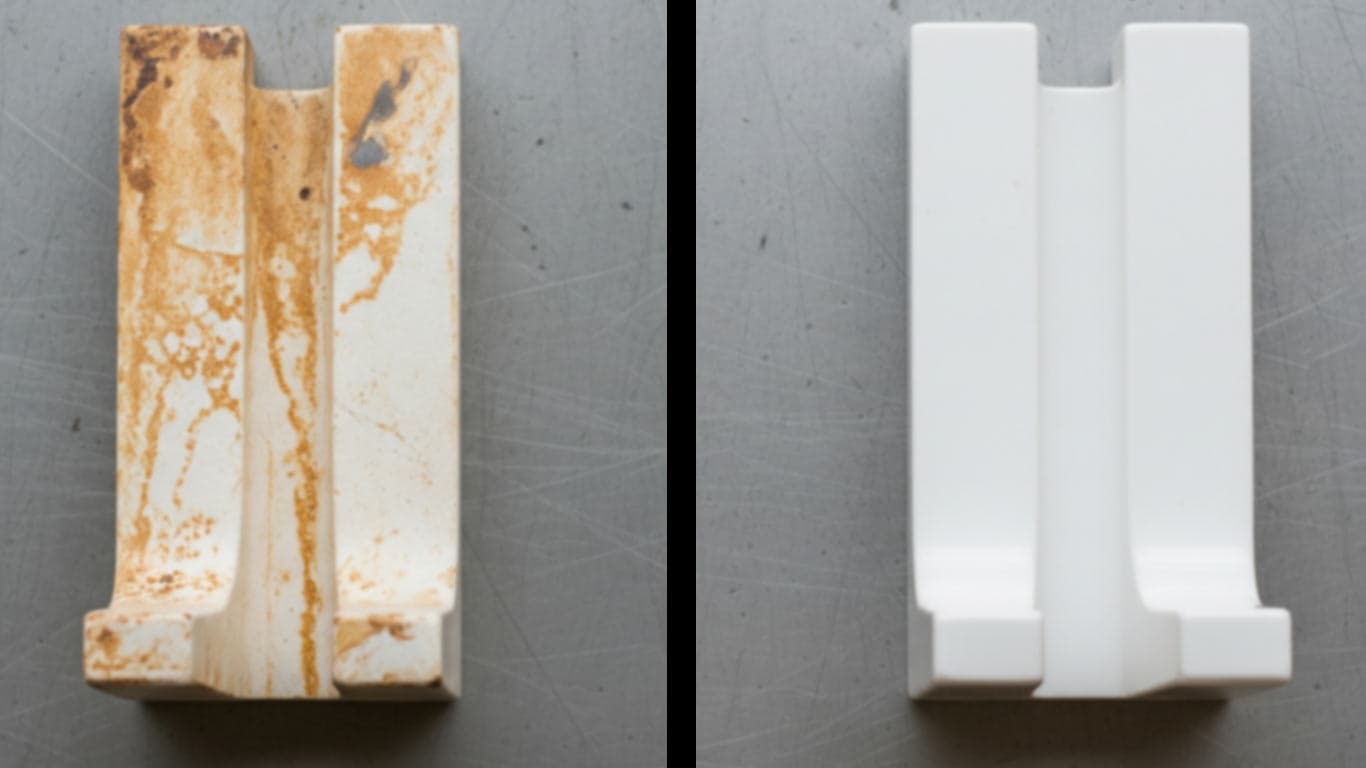

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Sandstone

Slate

Stainless Steel

Steel

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
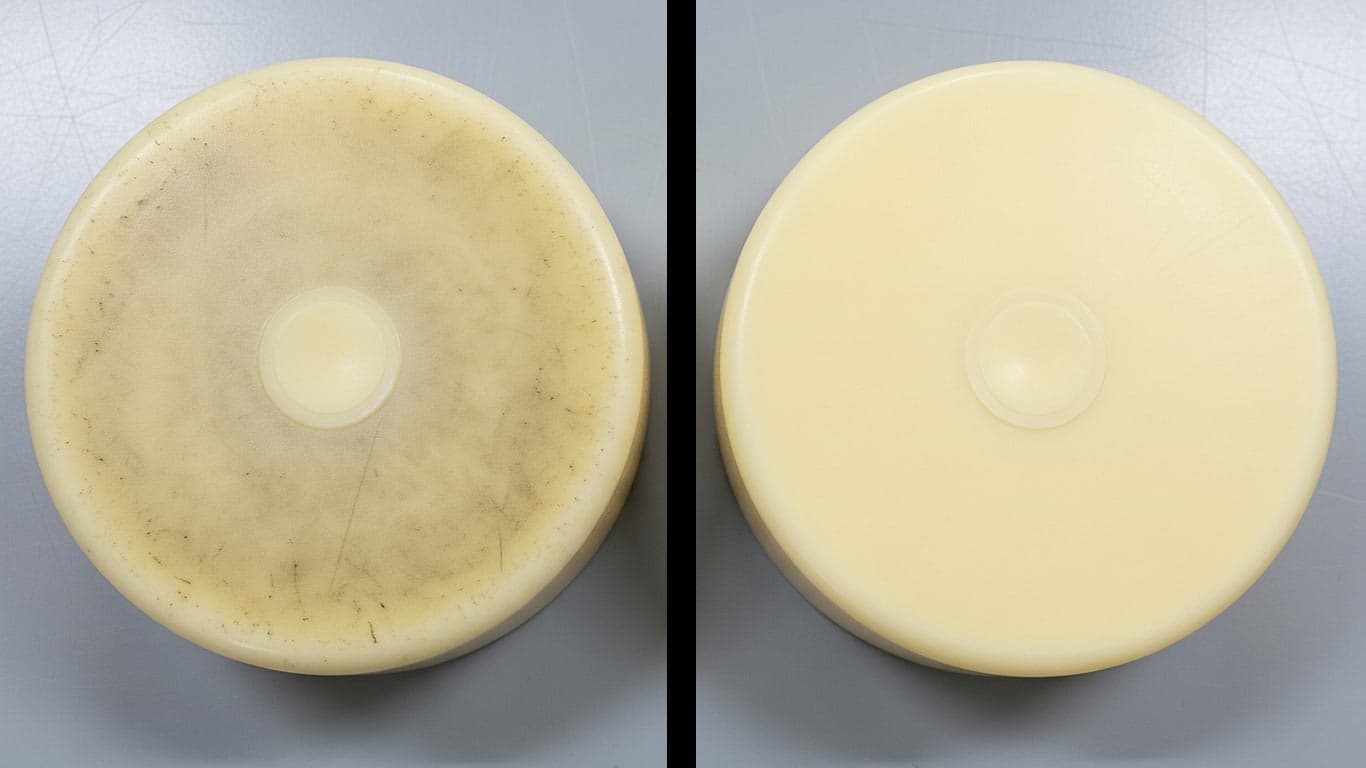

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Thermal Spray Coating Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more


