


Heat Treatment Scale
Annealing scale contamination forms when metals heat up during processing. This thermal damage creates thick oxide layers that cling tightly to surfaces. Engineers run into unique patterns here—crystalline structures build up unevenly, often cracking in jagged lines. Removal poses distinct challenges; lasers must dial in precise pulses to avoid re-annealing the base material. In practice, steel shows stubborn adhesion that resists clean finishes, while aluminum flakes off more readily but leaves residue behind. Overall, addressing this demands tailored approaches to cut down on rework. Testing confirms these behaviors vary by alloy, turning potential pitfalls into manageable outcomes.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum
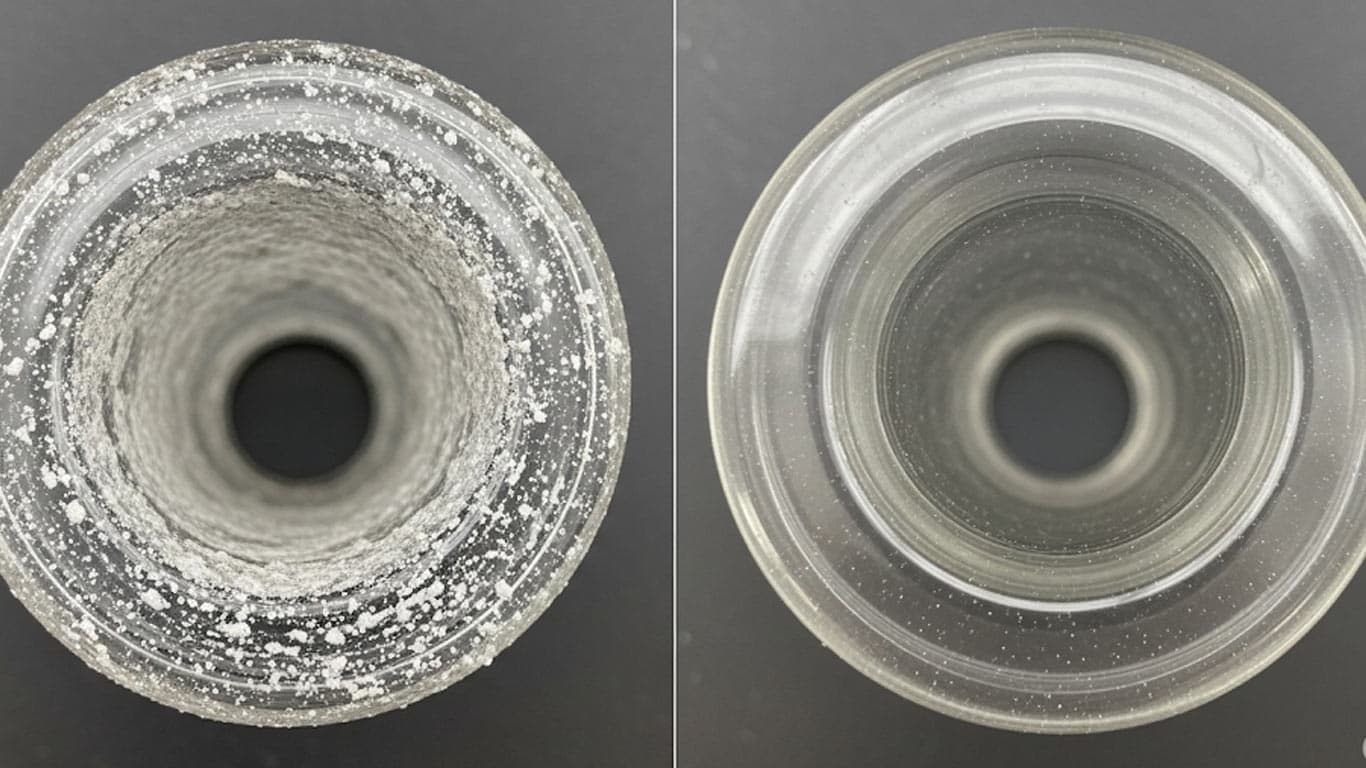

Borosilicate Glass

Brass

Bronze

Cast Iron

Concrete

Copper
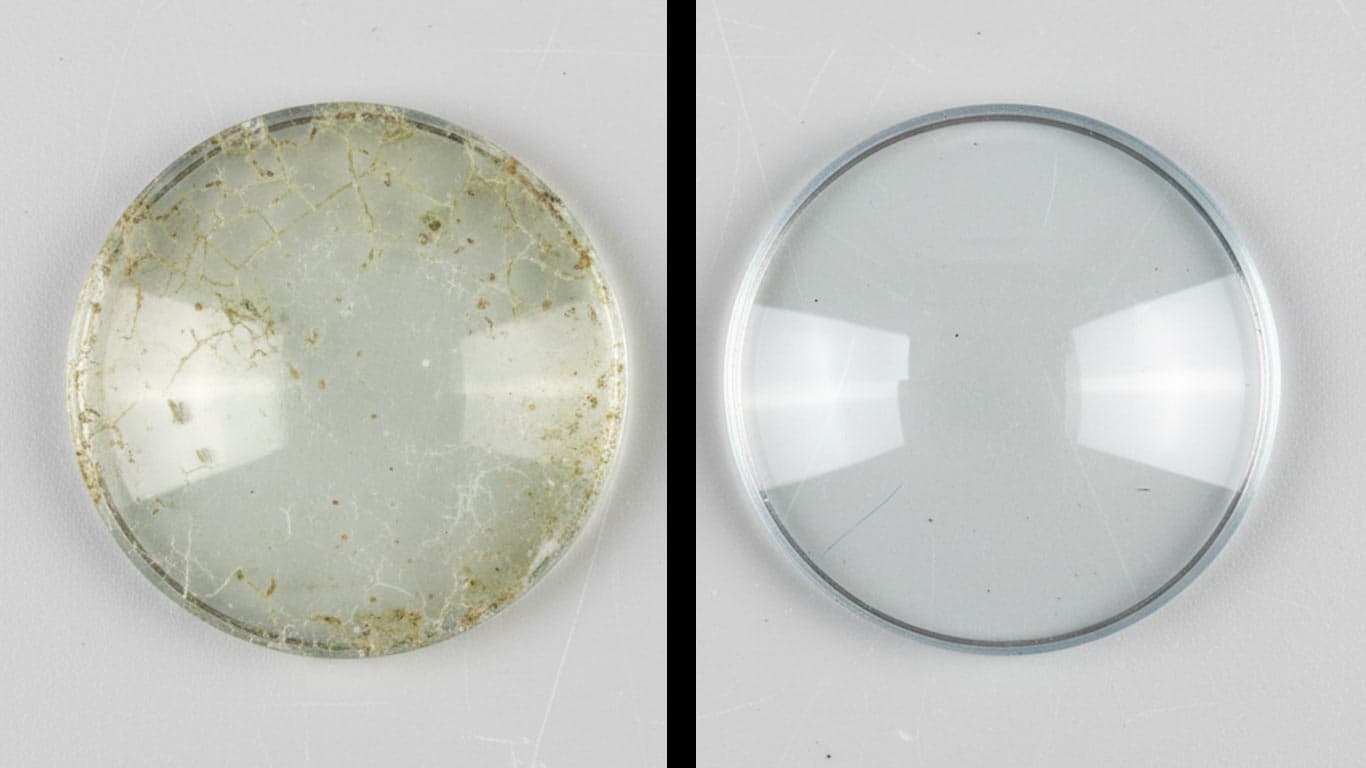

Crown Glass
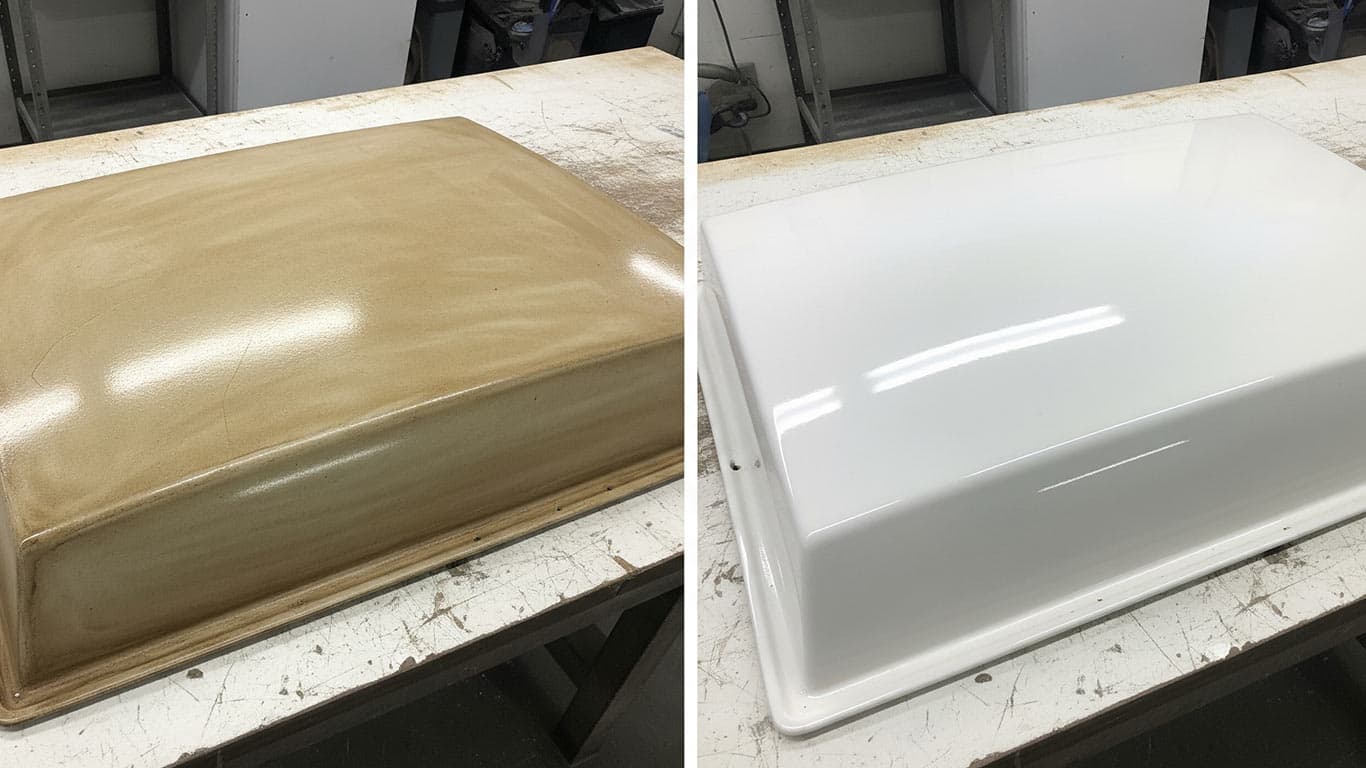

Fiberglass
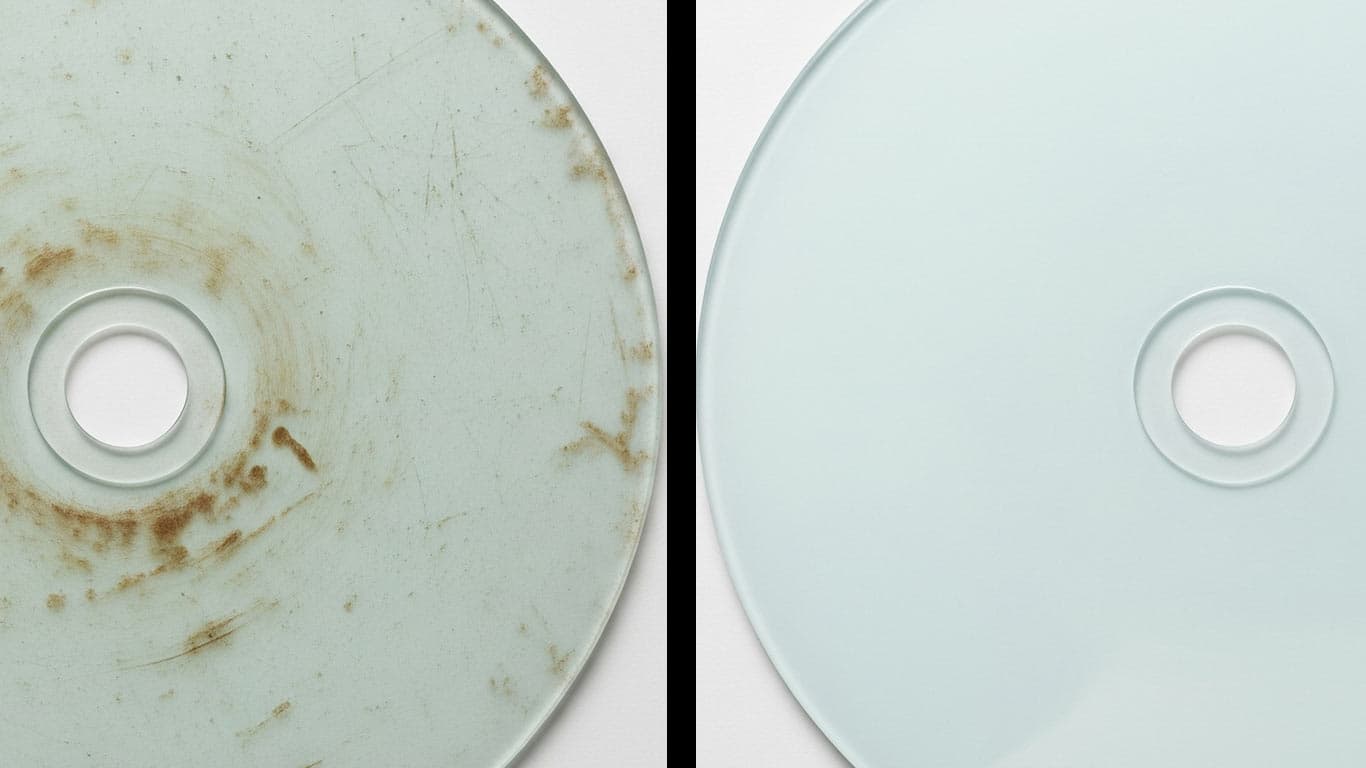

Float Glass
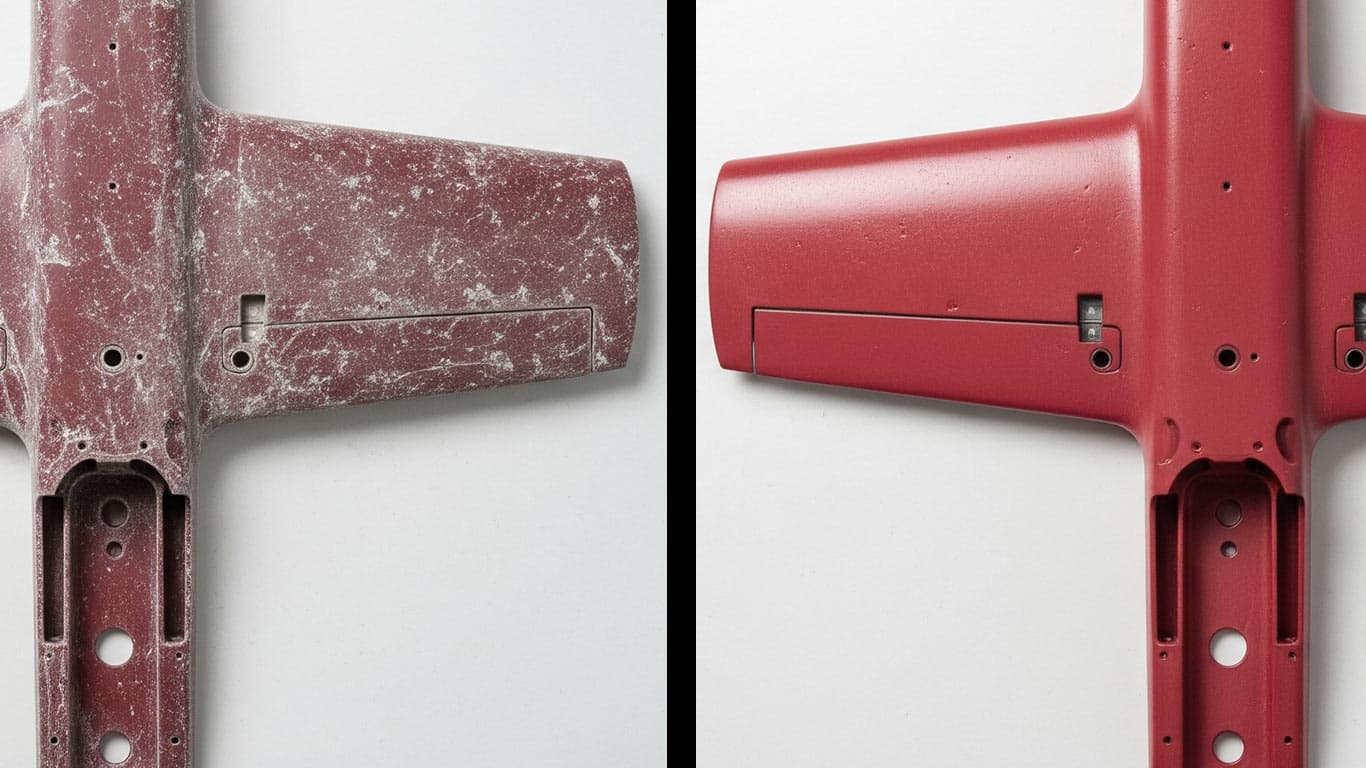

Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers GFRP
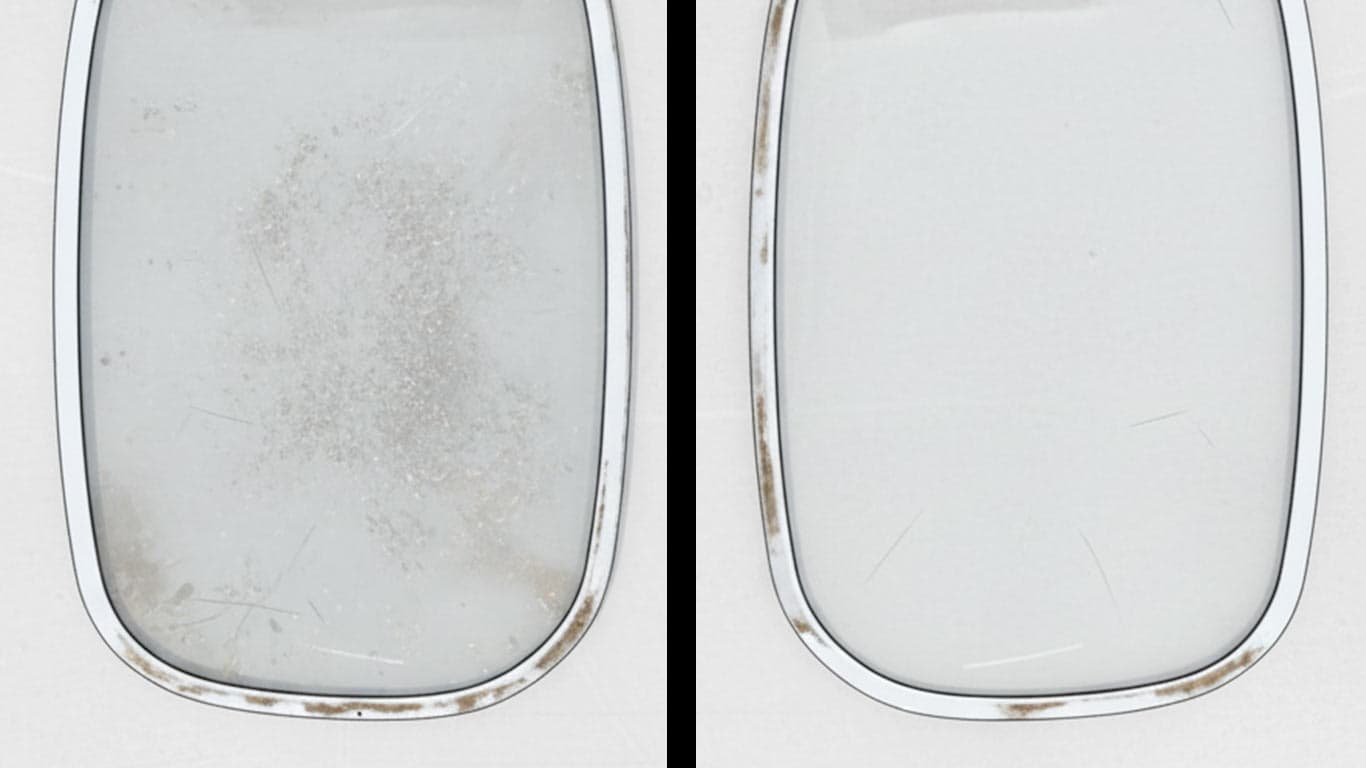
Gorilla Glass

Granite

Iron
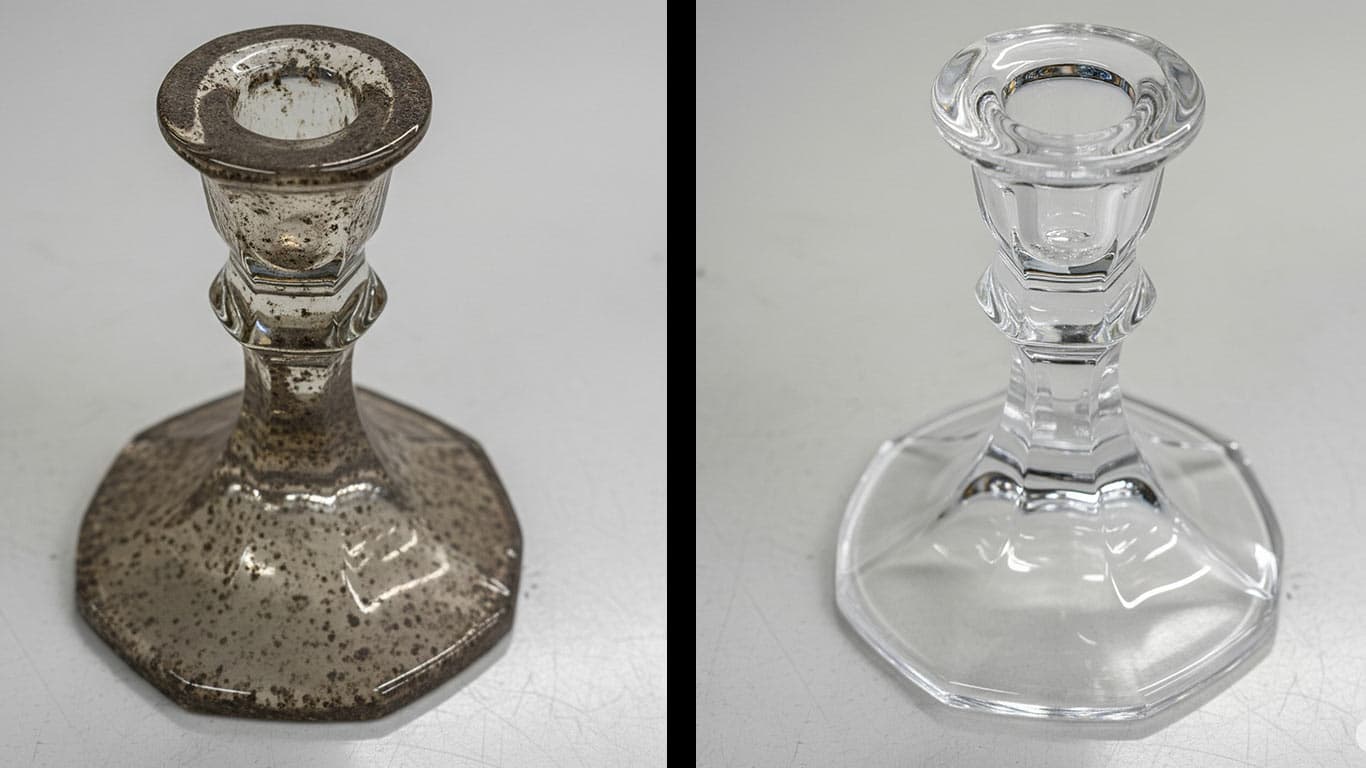

Lead Crystal

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble

Nickel
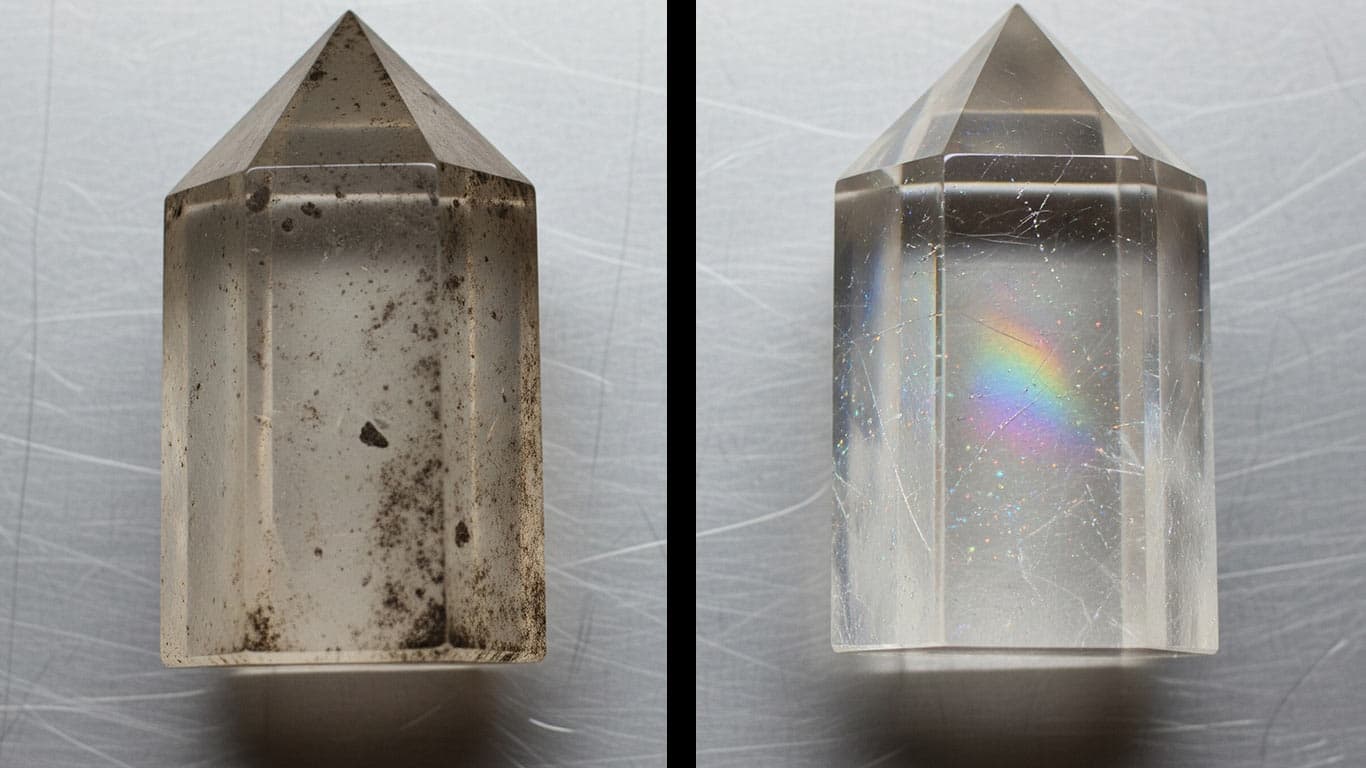

Quartz Glass

Sandstone
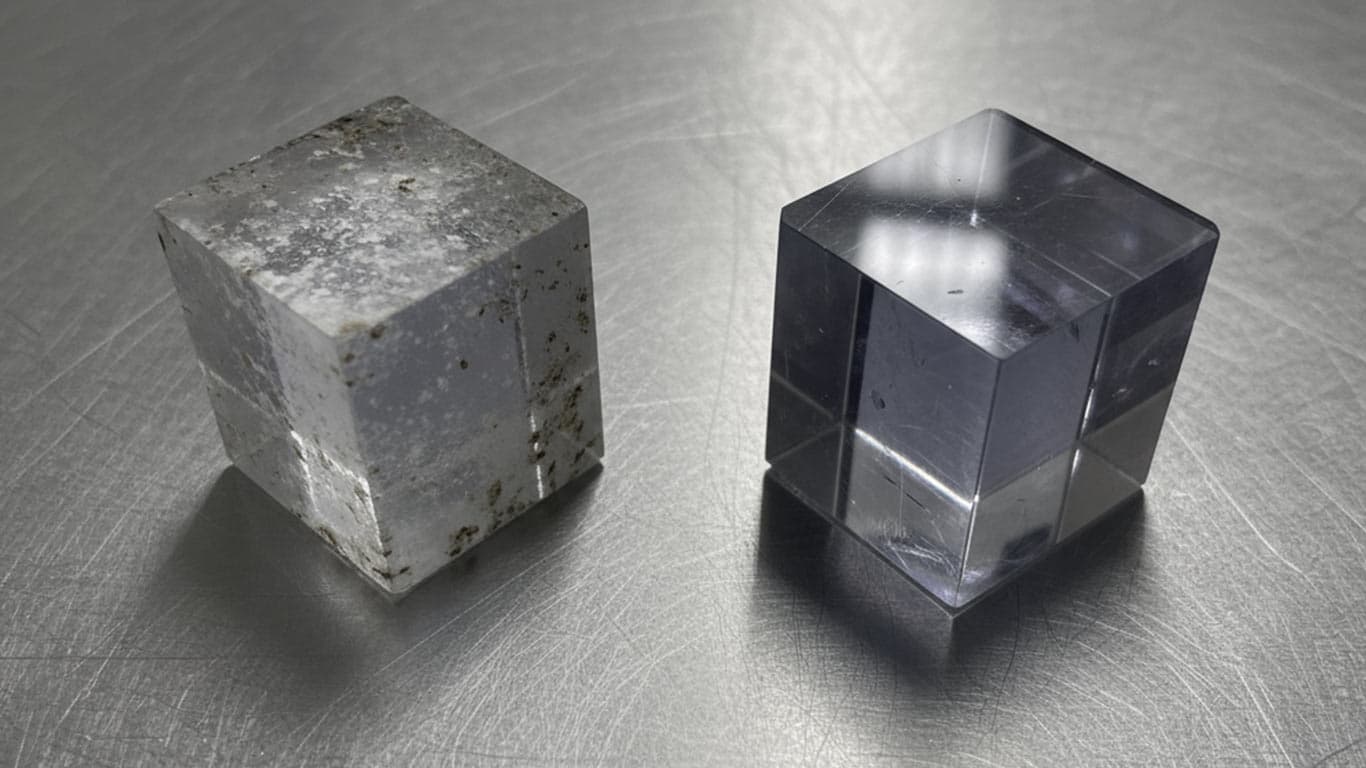

Sapphire Glass

Slate
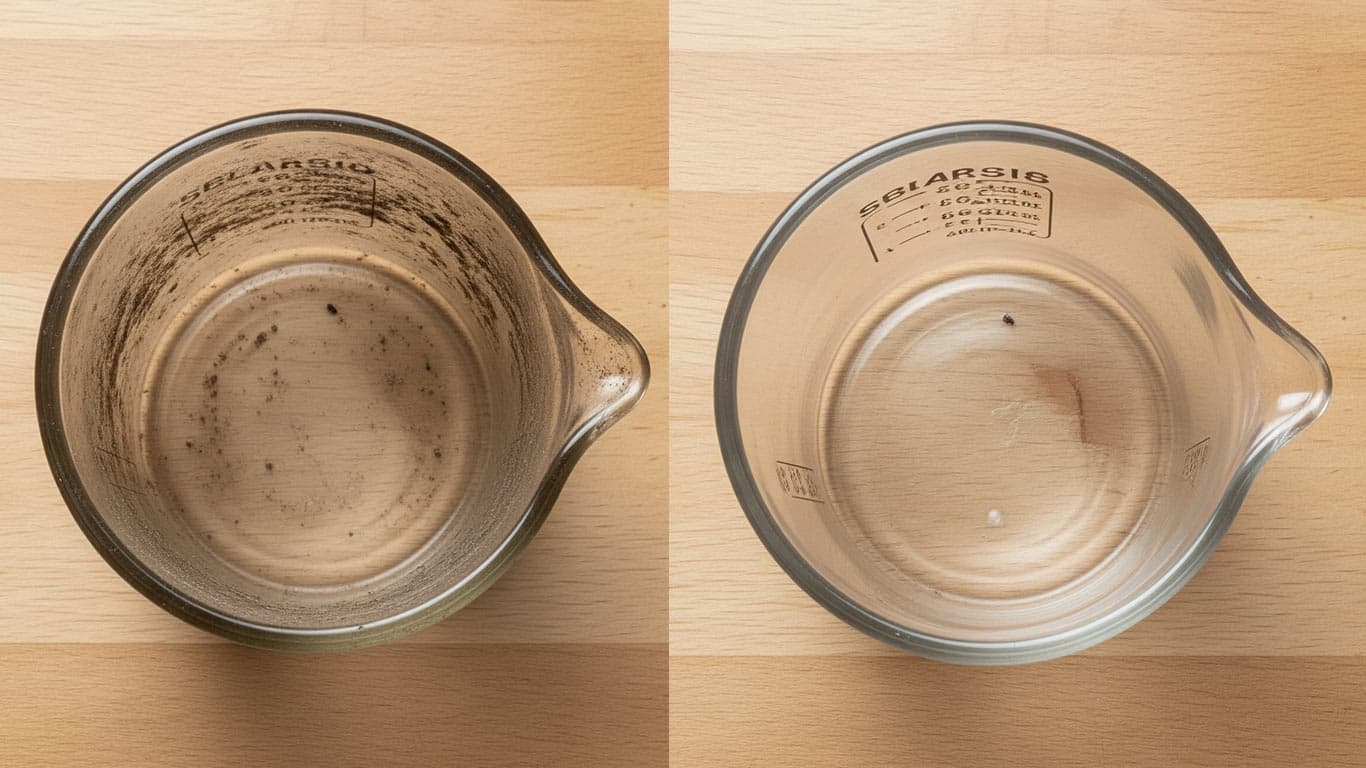

Soda-Lime Glass

Stainless Steel

Steel
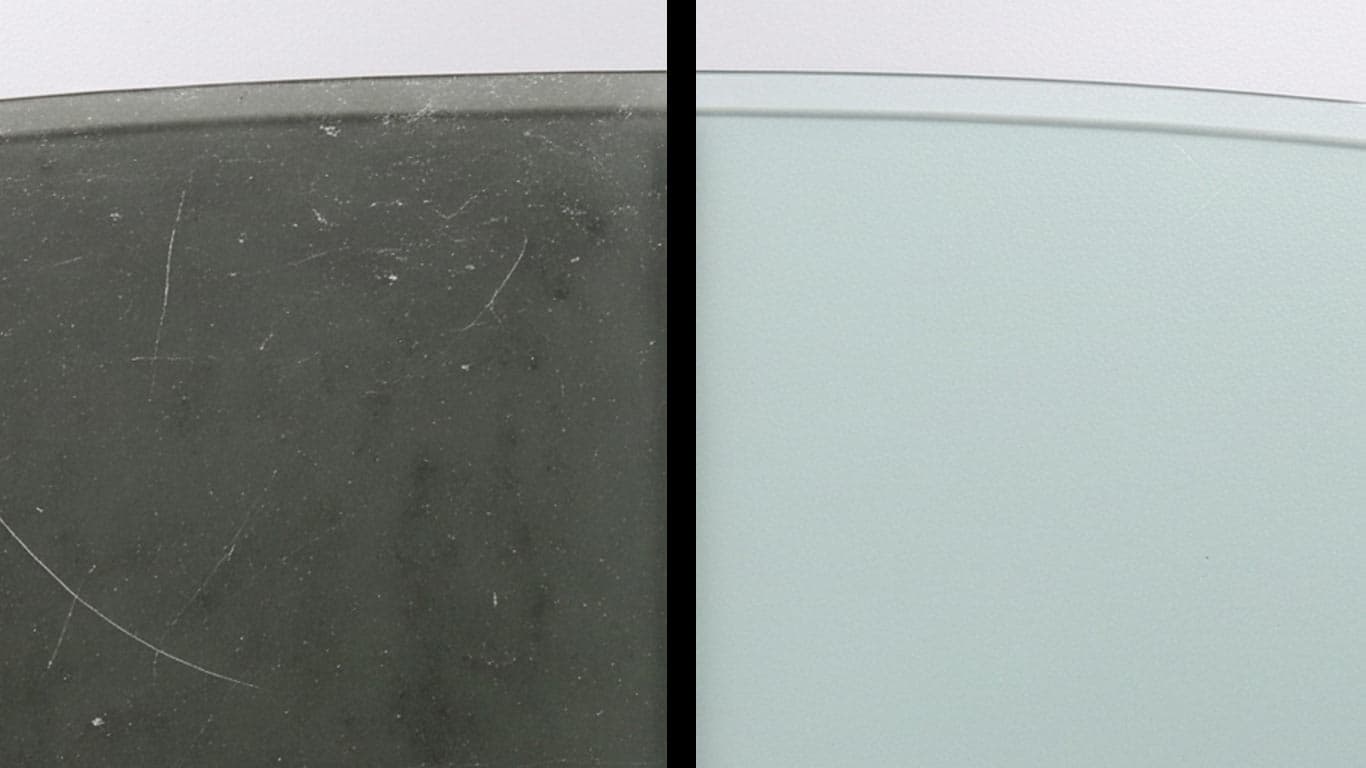

Tempered Glass

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel

Zinc

Aluminosilicate Glass

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Heat Treatment Scale Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more



