


Forging Mill Scale
Forging scale contamination, it arises from thermal damage in metal processing. This contamination forms unique patterns, like layered oxide buildup on steel surfaces and thus adheres strongly during high-heat forging. Material behaviors differ; steel shows thick, irregular scales from rapid oxidation, while aluminum develops thinner, porous ones and resists cracking less. Removal challenges emerge, especially with laser cleaning. Scale resists ablation due to its dense structure, so pulses must target precisely to avoid substrate damage. After treatment, surface smoothness improves, yet remnants persist on irregular areas. This contamination, it demands adjusted laser parameters for effective detachment and thus enhances cleaning efficiency on varied metals.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum
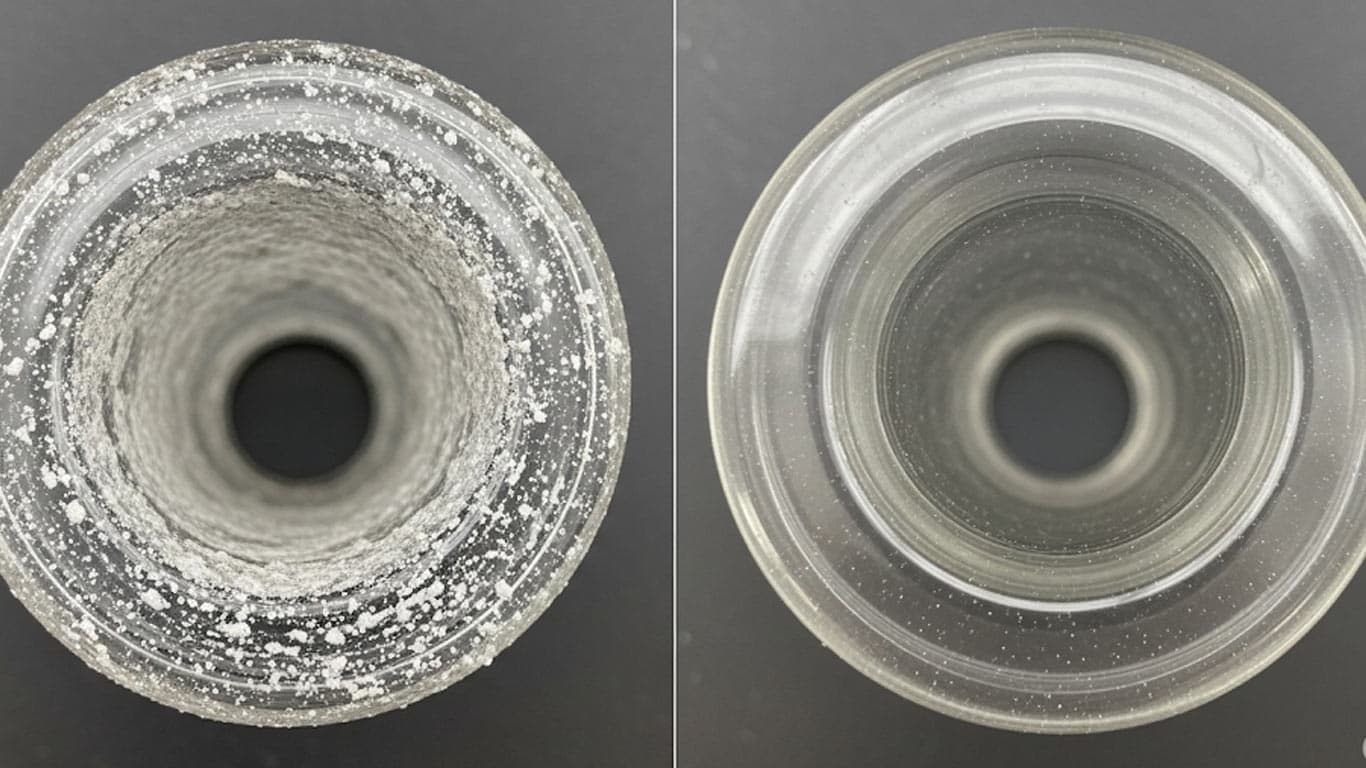

Borosilicate Glass

Brass

Bronze

Cast Iron

Concrete

Copper
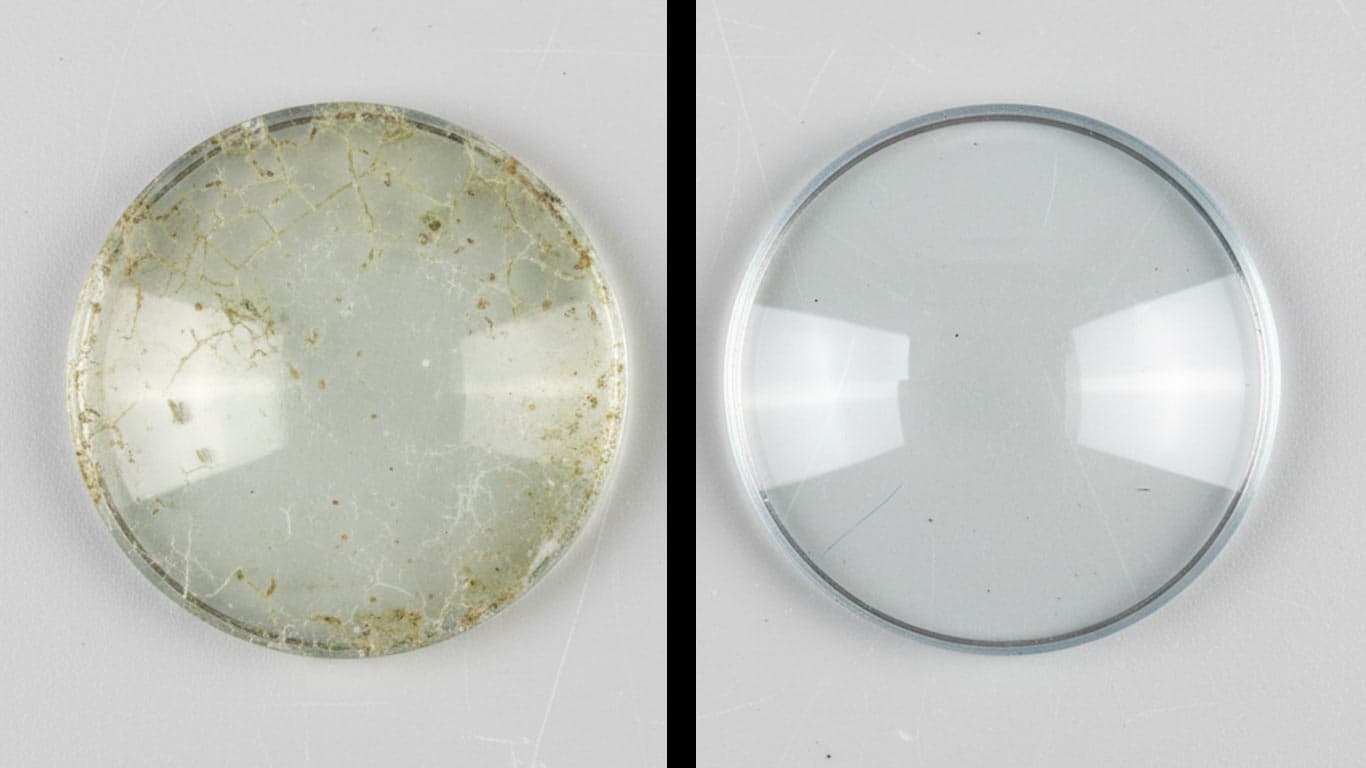

Crown Glass
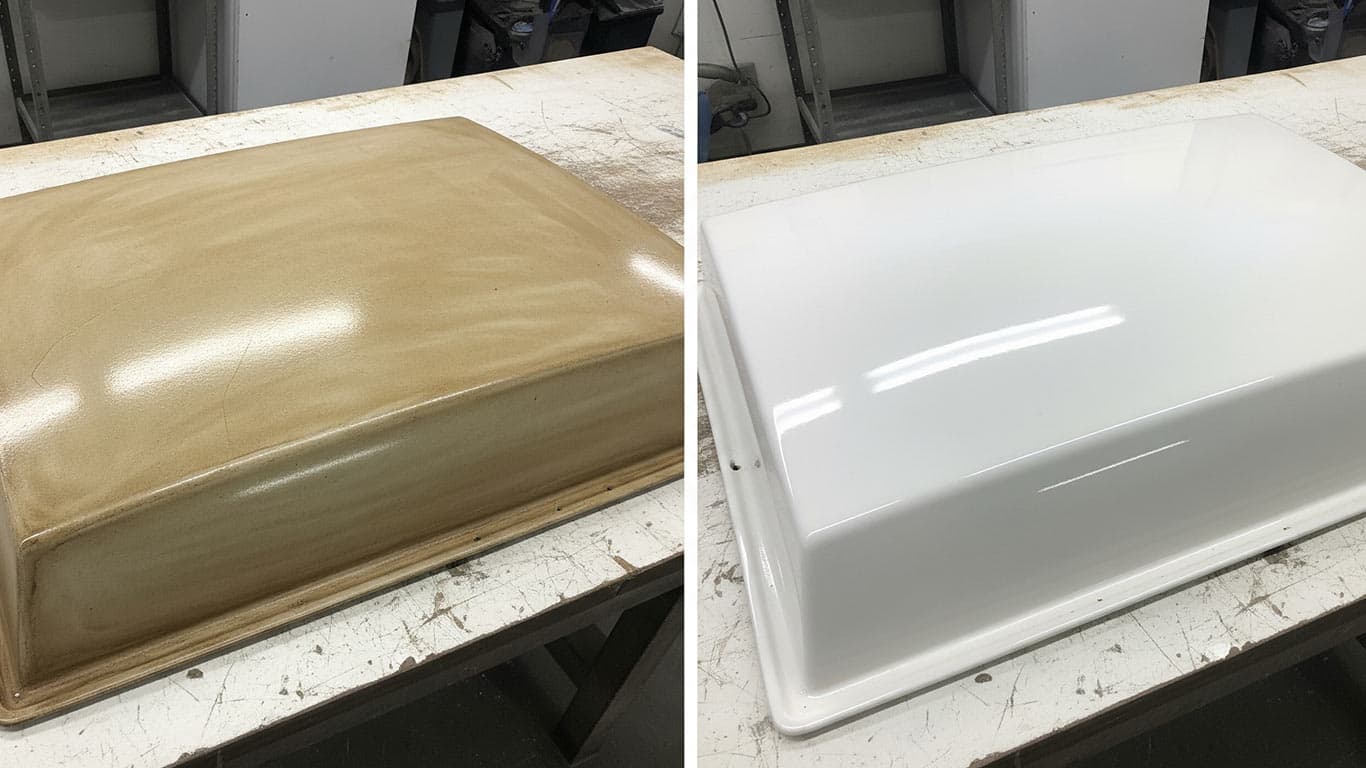

Fiberglass
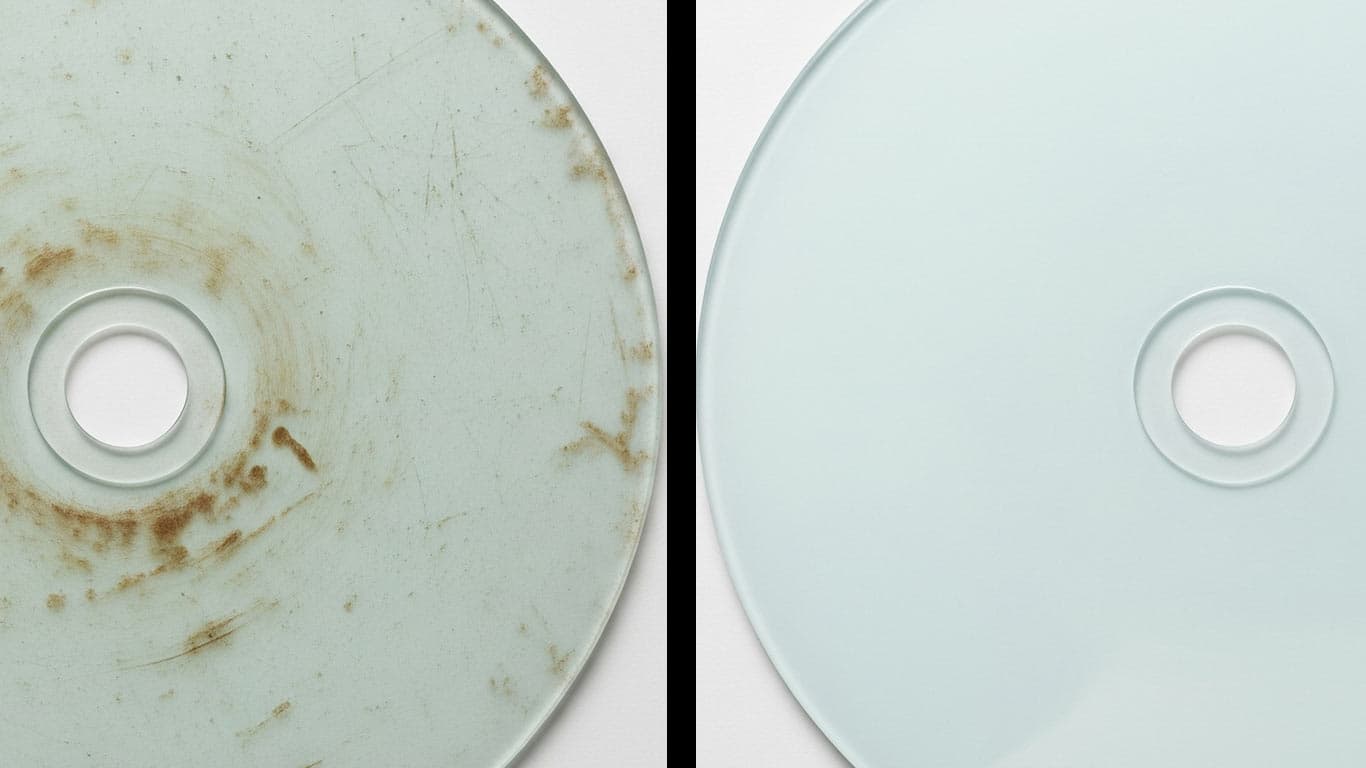

Float Glass
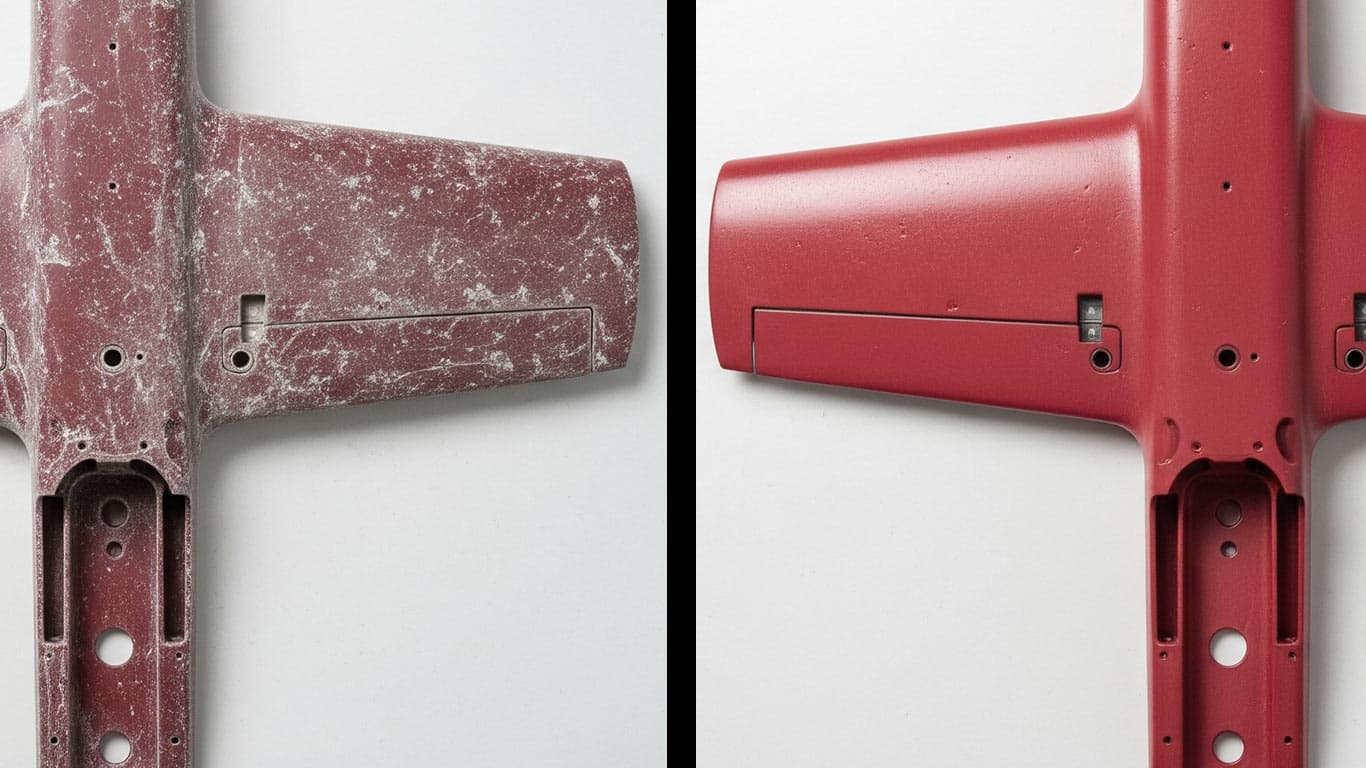

Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers GFRP
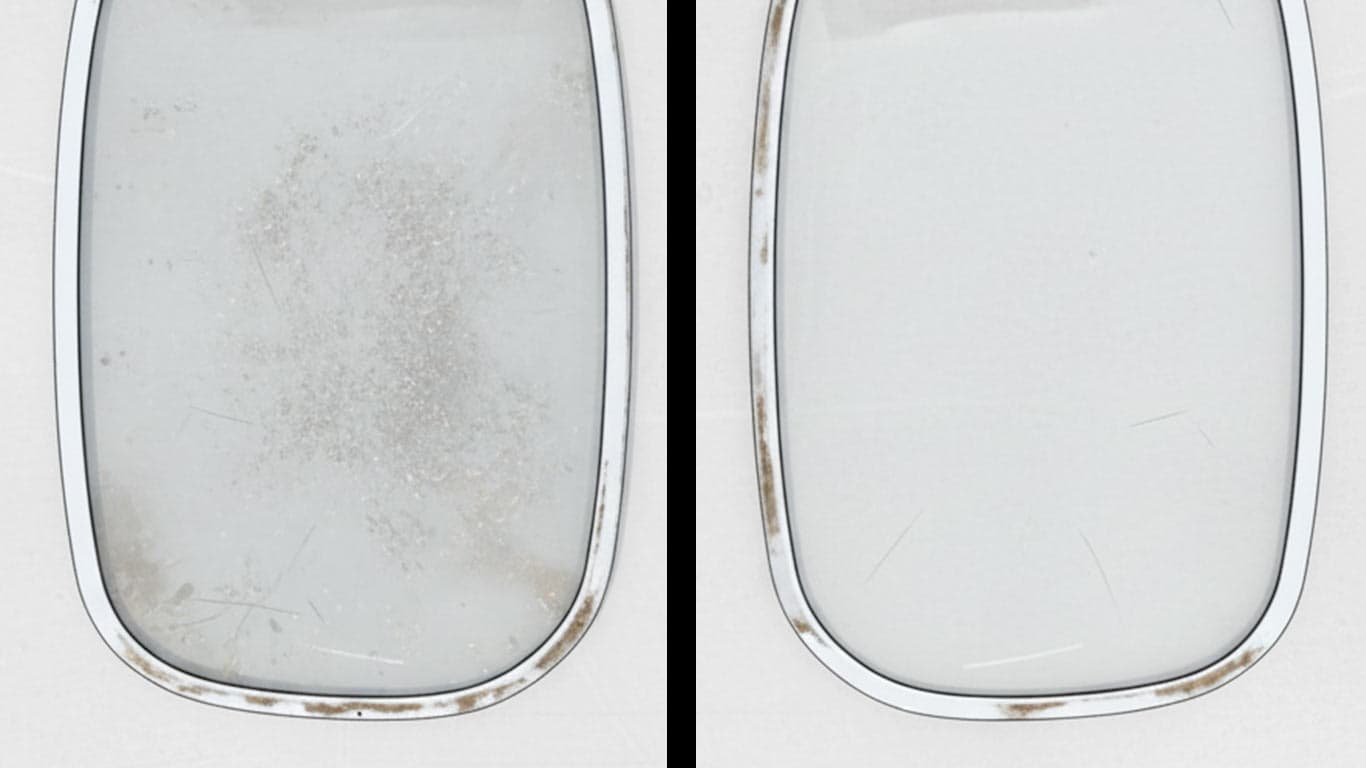
Gorilla Glass

Granite

Iron
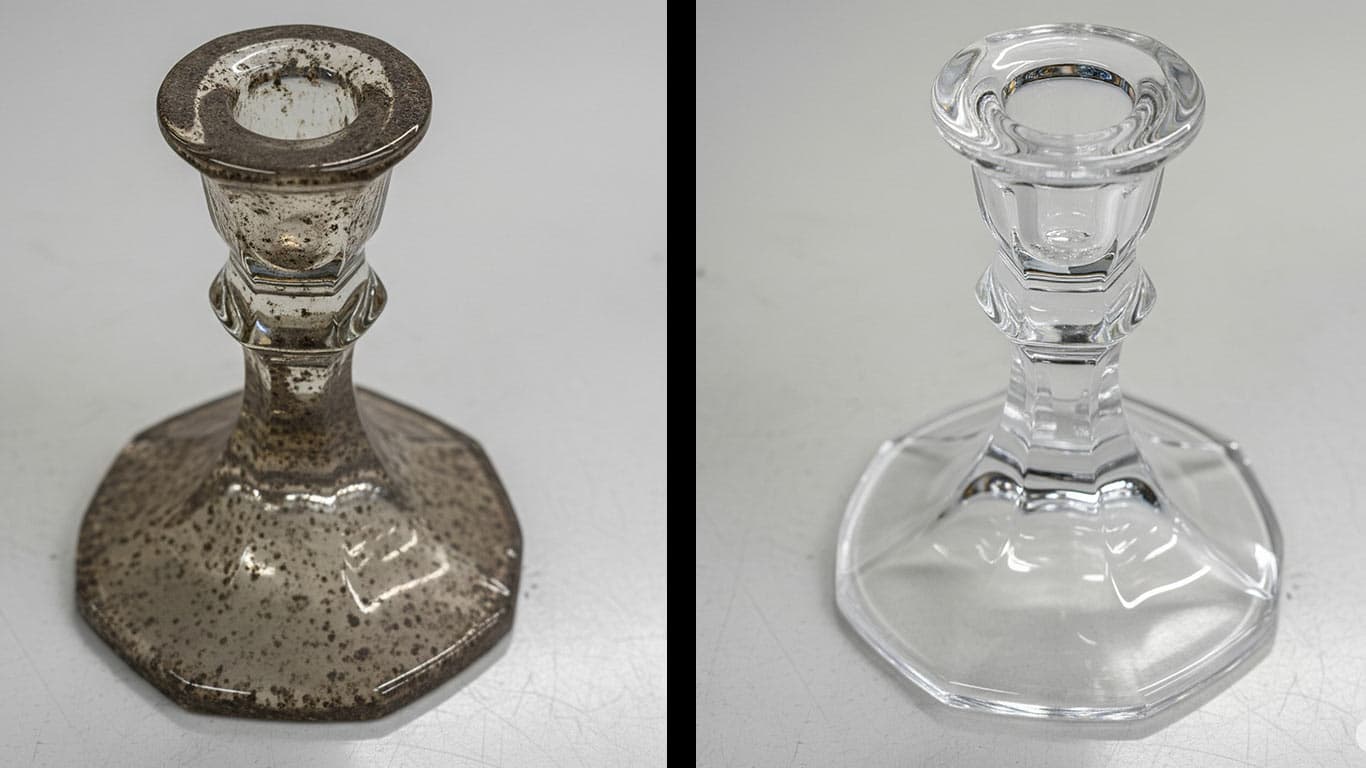

Lead Crystal

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble

Nickel
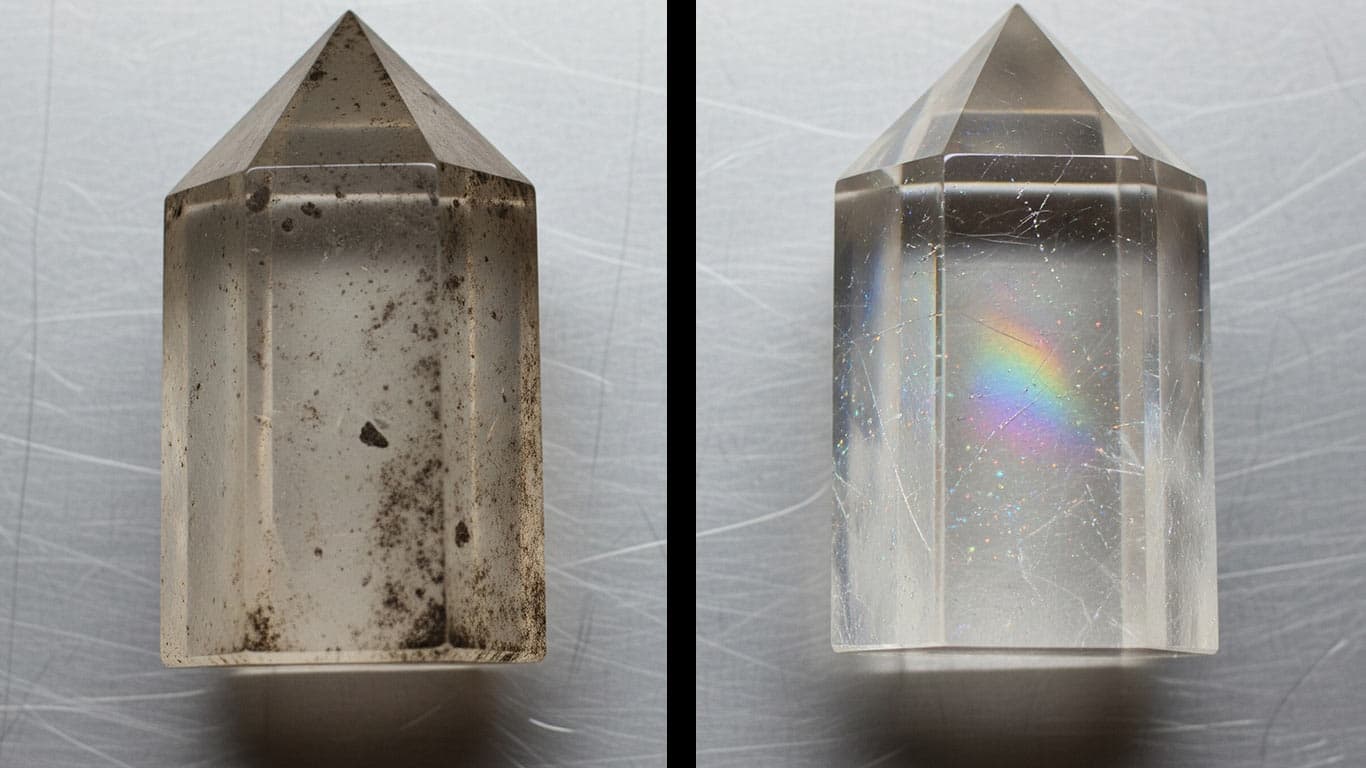

Quartz Glass

Sandstone
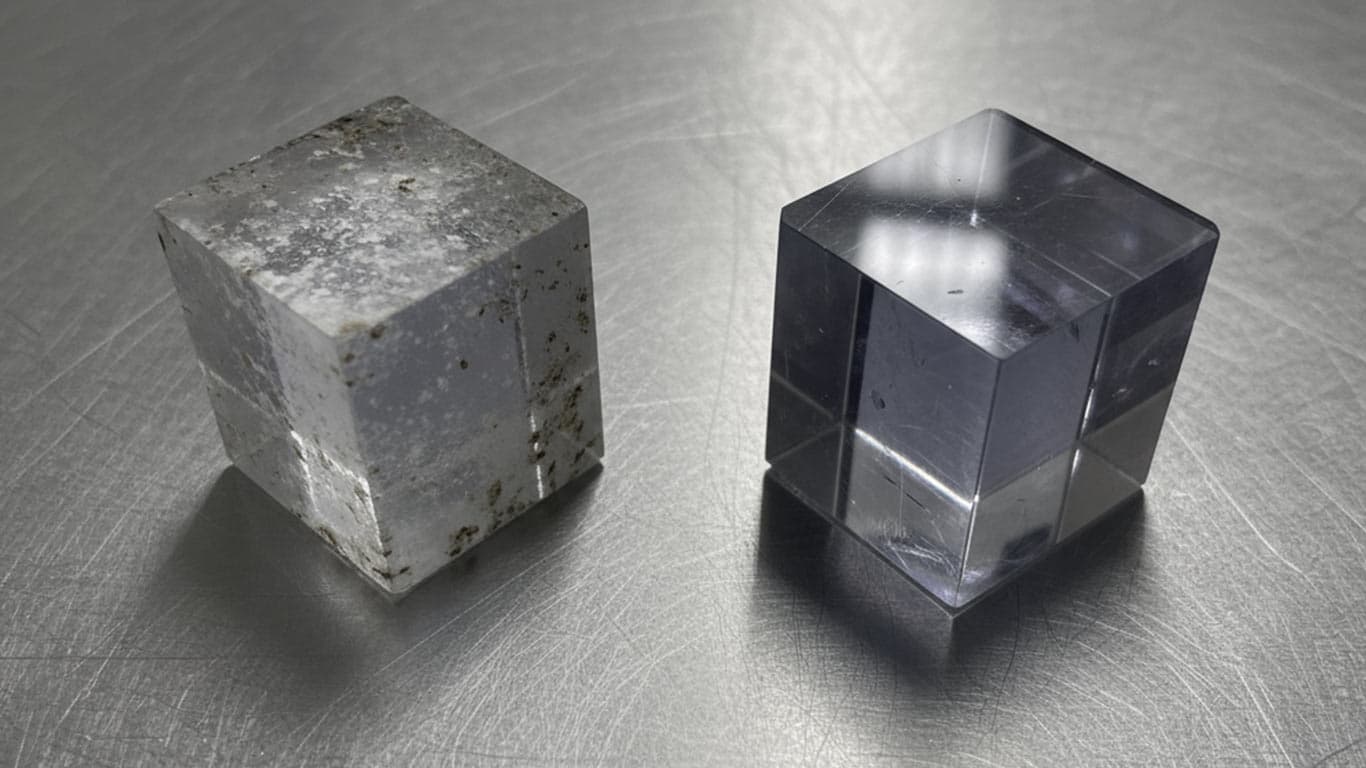

Sapphire Glass

Slate
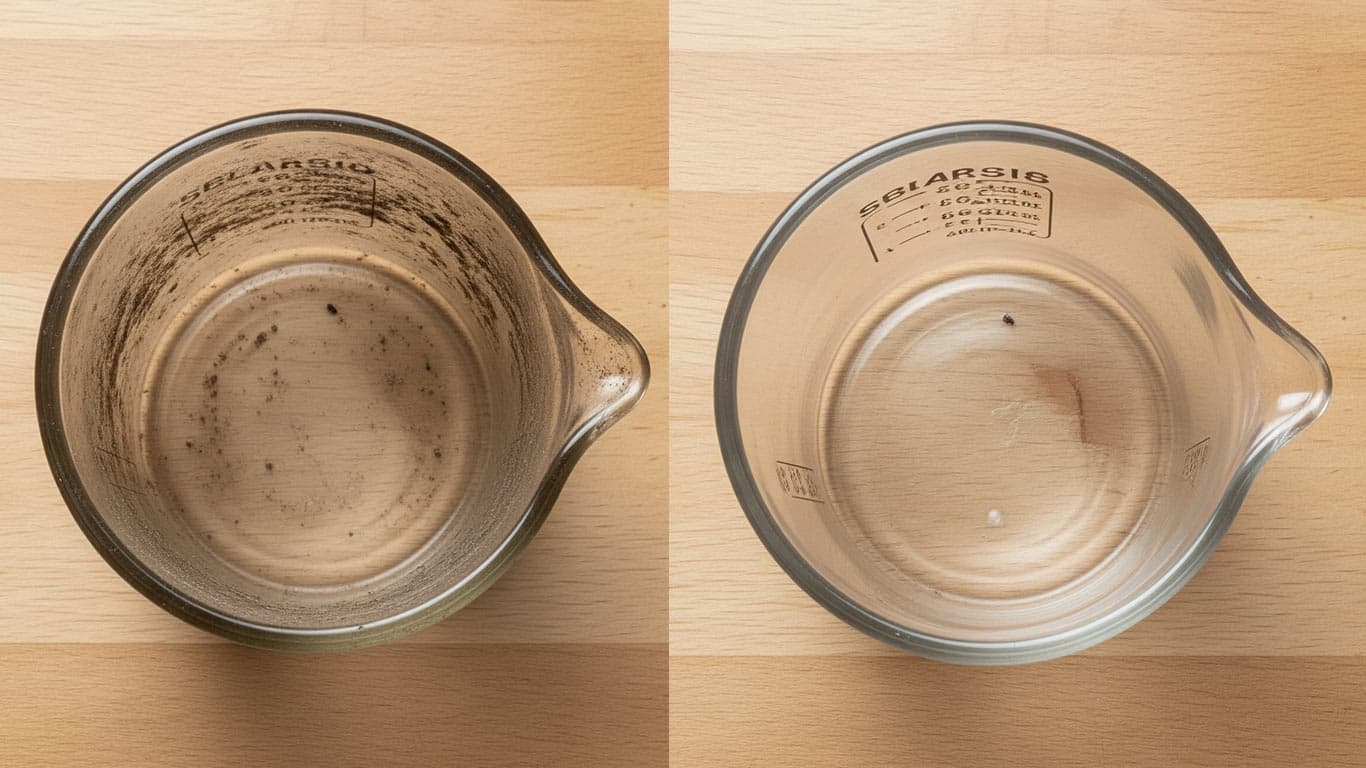

Soda-Lime Glass

Stainless Steel

Steel
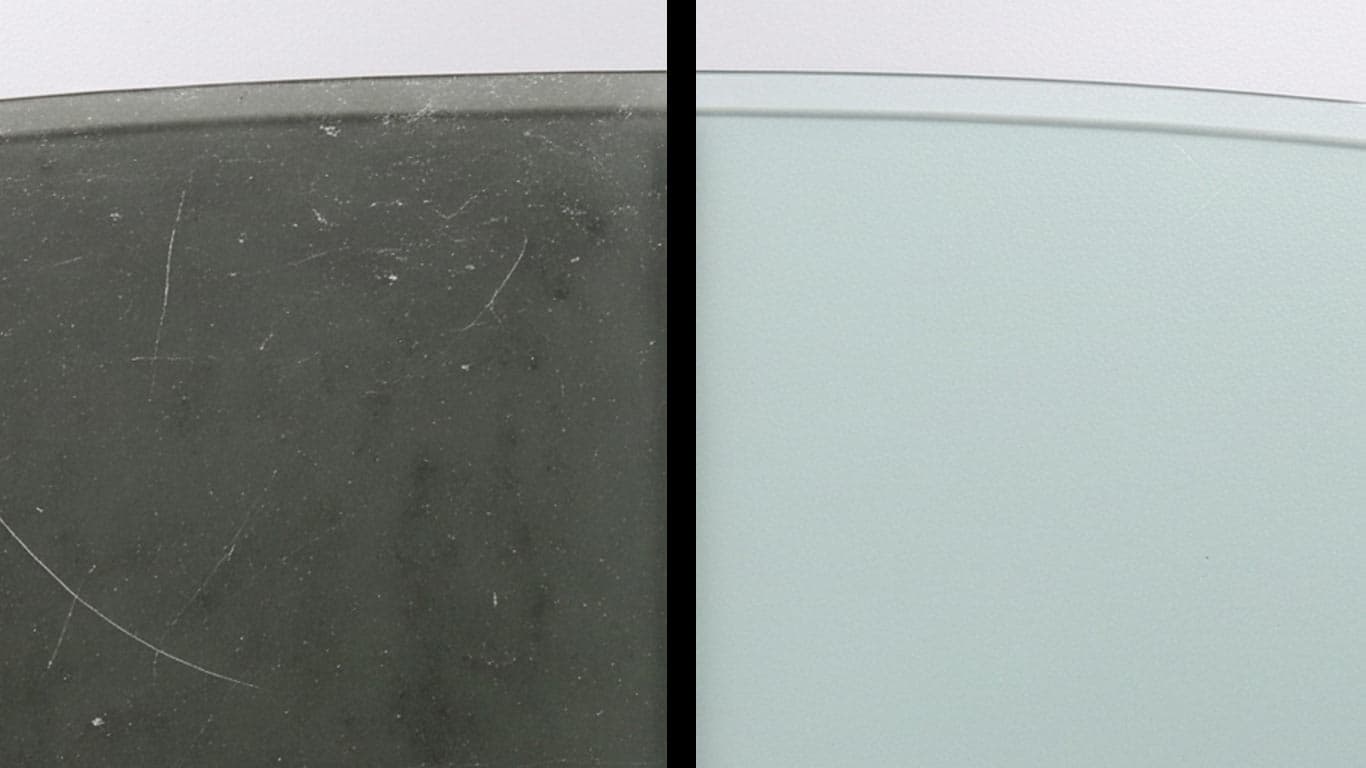

Tempered Glass

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel

Zinc

Aluminosilicate Glass

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Forging Mill Scale Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more


