


Concrete Dust Deposits
Adhesiveness of concrete dust contamination, it embeds deeply into surfaces during construction exposure. This inorganic coating forms uneven layers and thus clings to substrates like metal or stone, creating porous patterns from airborne particles settling over time. Formation occurs through mechanical abrasion and environmental settling, so contamination builds gradually and resists dislodgement. In laser cleaning applications, removal challenges arise from its dense structure, which absorbs energy unevenly and leads to incomplete ablation on rough areas. Material-specific behaviors vary; on metals, it scatters laser beams thus prolonging treatment, while on concrete bases, it merges with the host material and demands precise pulse adjustments. After irradiation, residues still persist in crevices, so post-process verification confirms surface recovery. This contamination, it demands tailored parameters for effective clearance.
Produced Compounds
Affected Materials

Aluminum
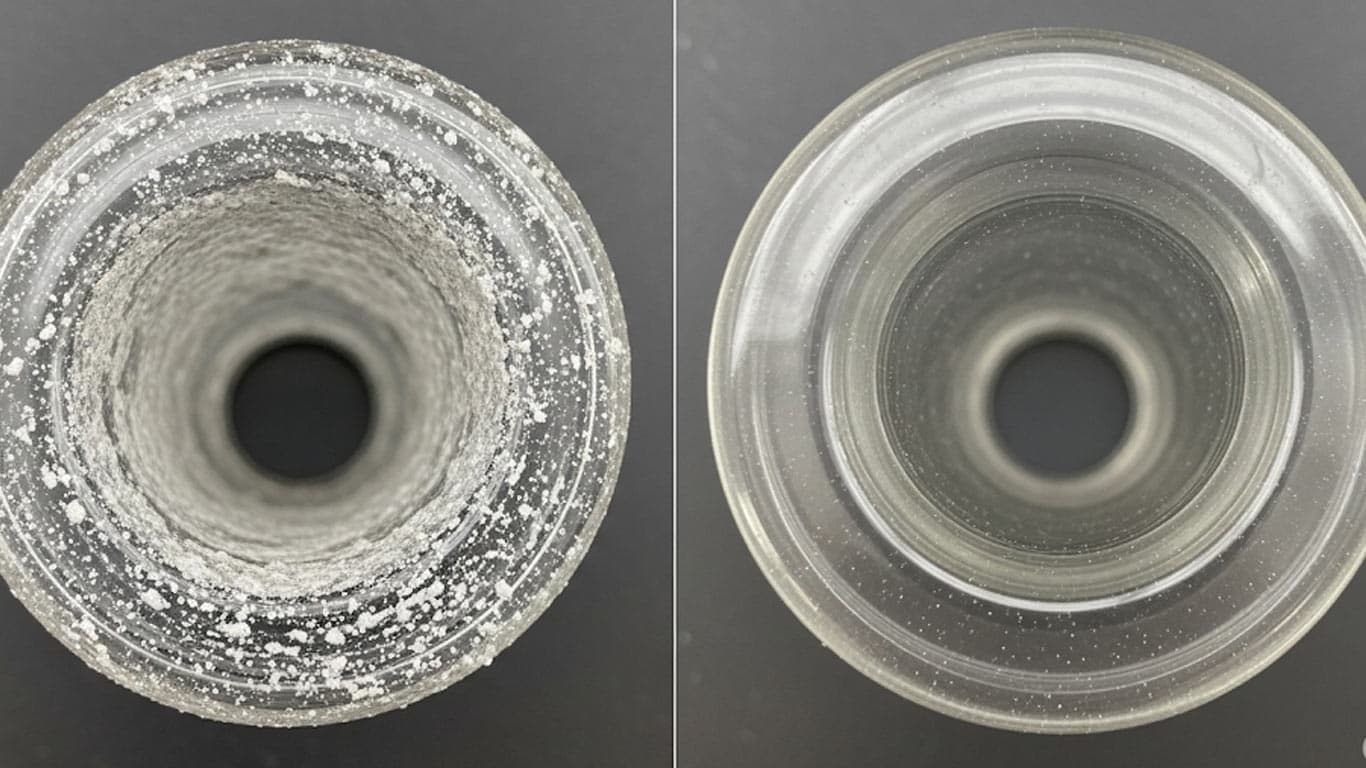

Borosilicate Glass

Brass

Brick

Bronze
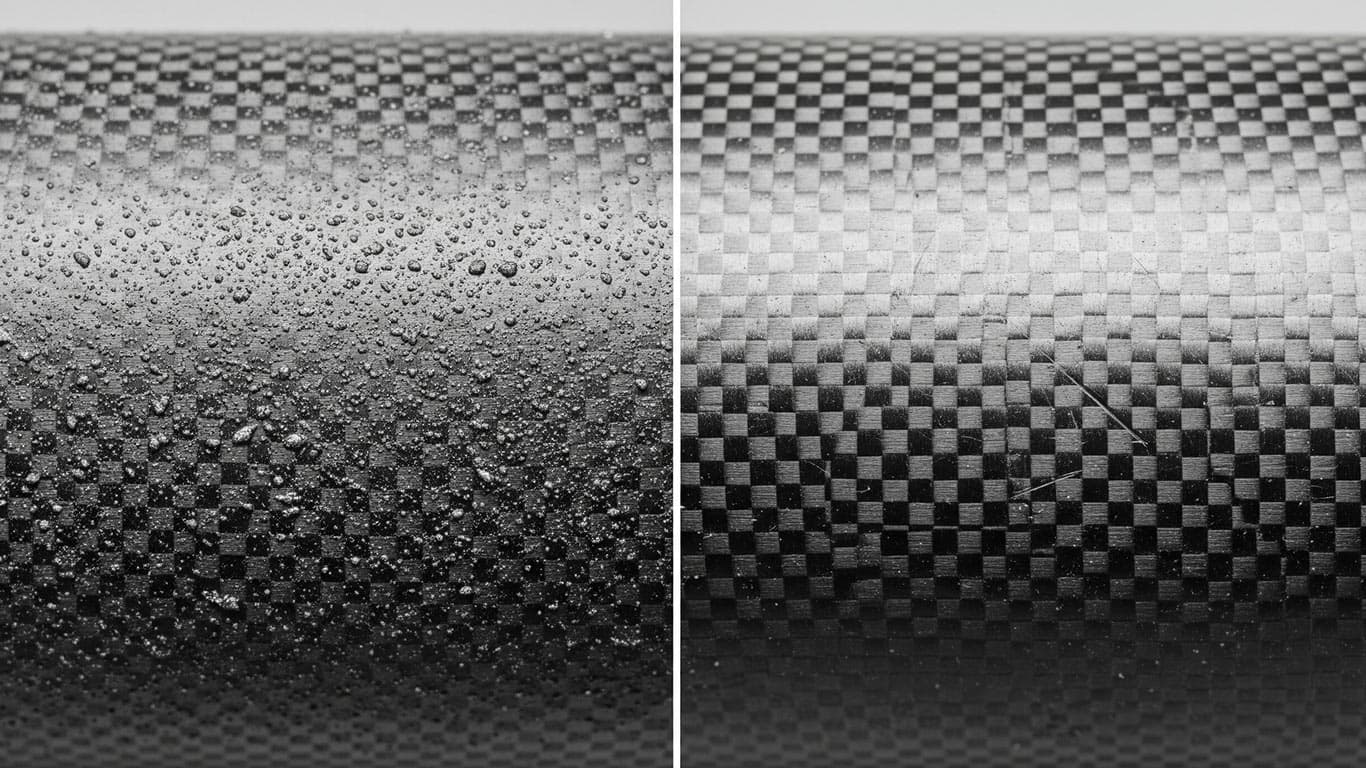
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer

Cast Iron

Ceramic Matrix Composites CMCs

Concrete

Copper
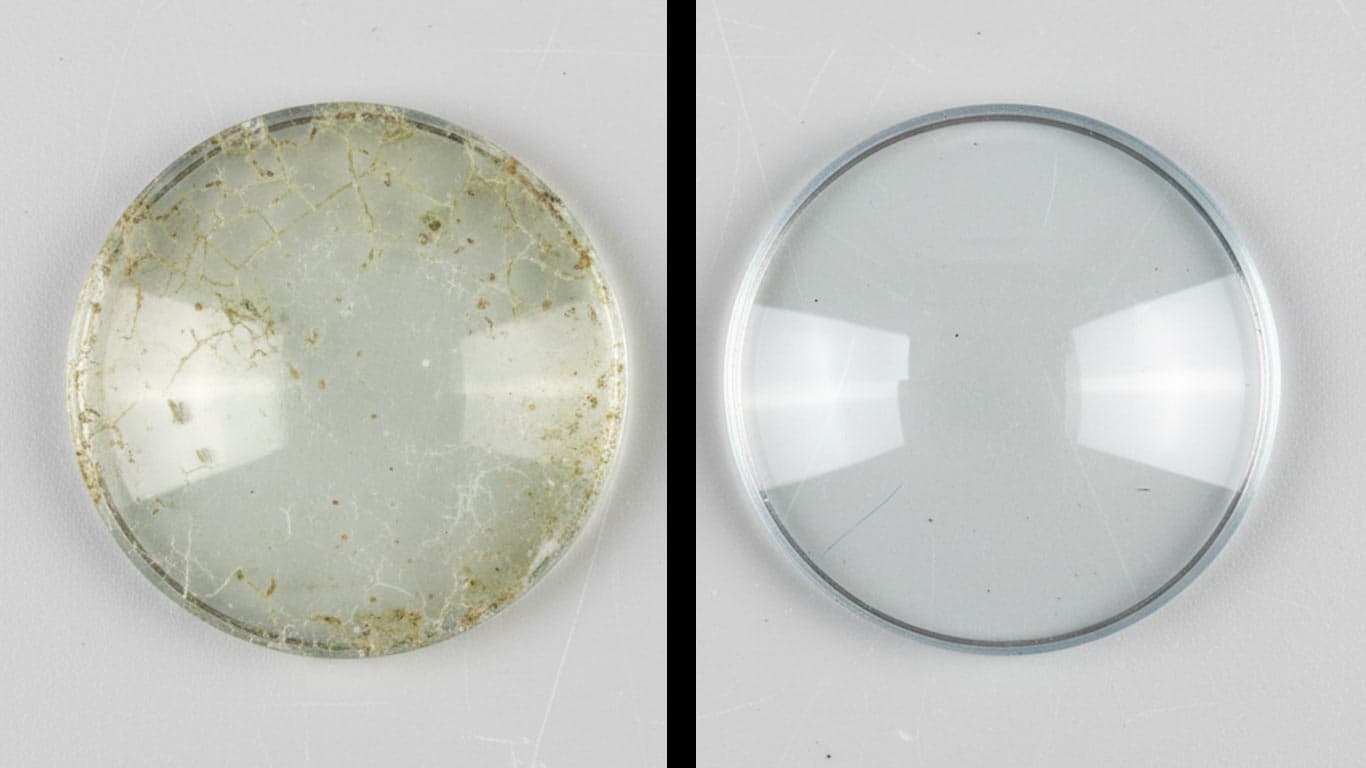

Crown Glass
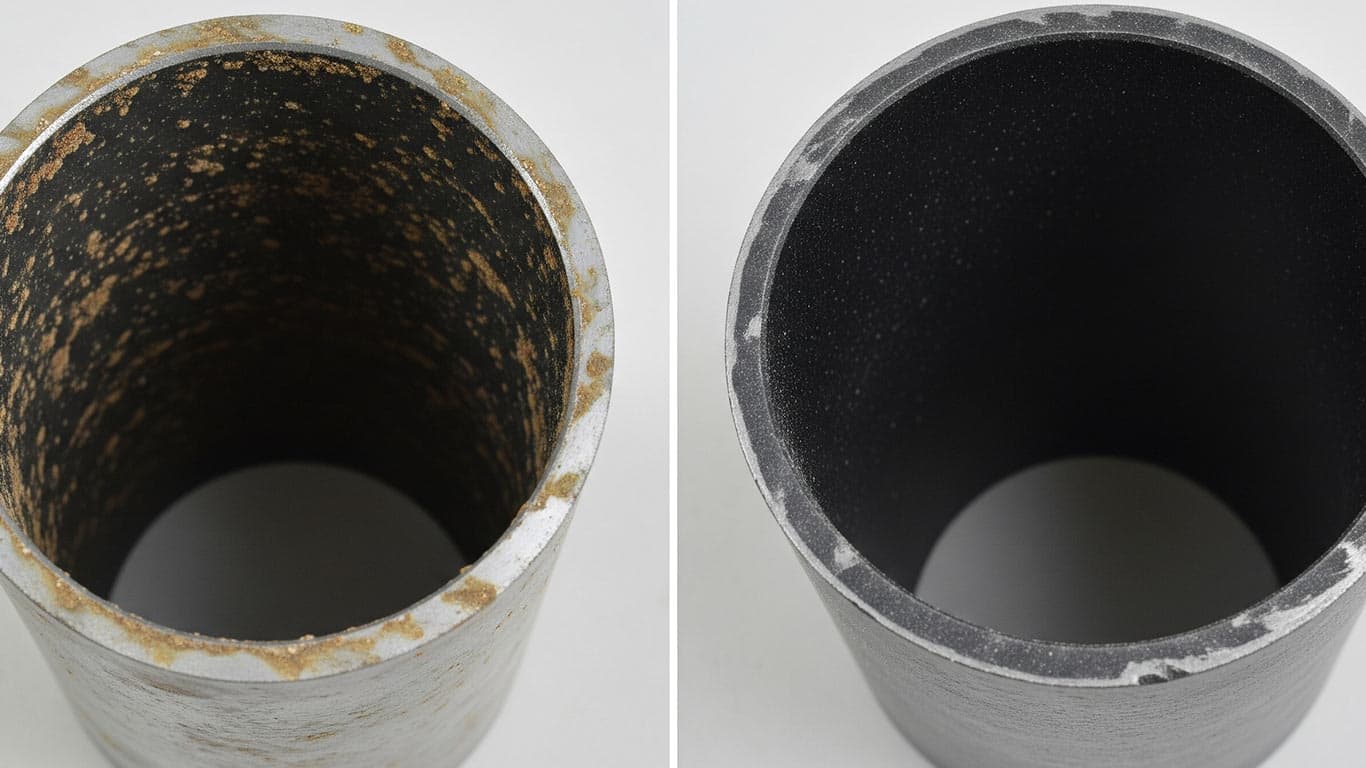

Epoxy Resin Composites
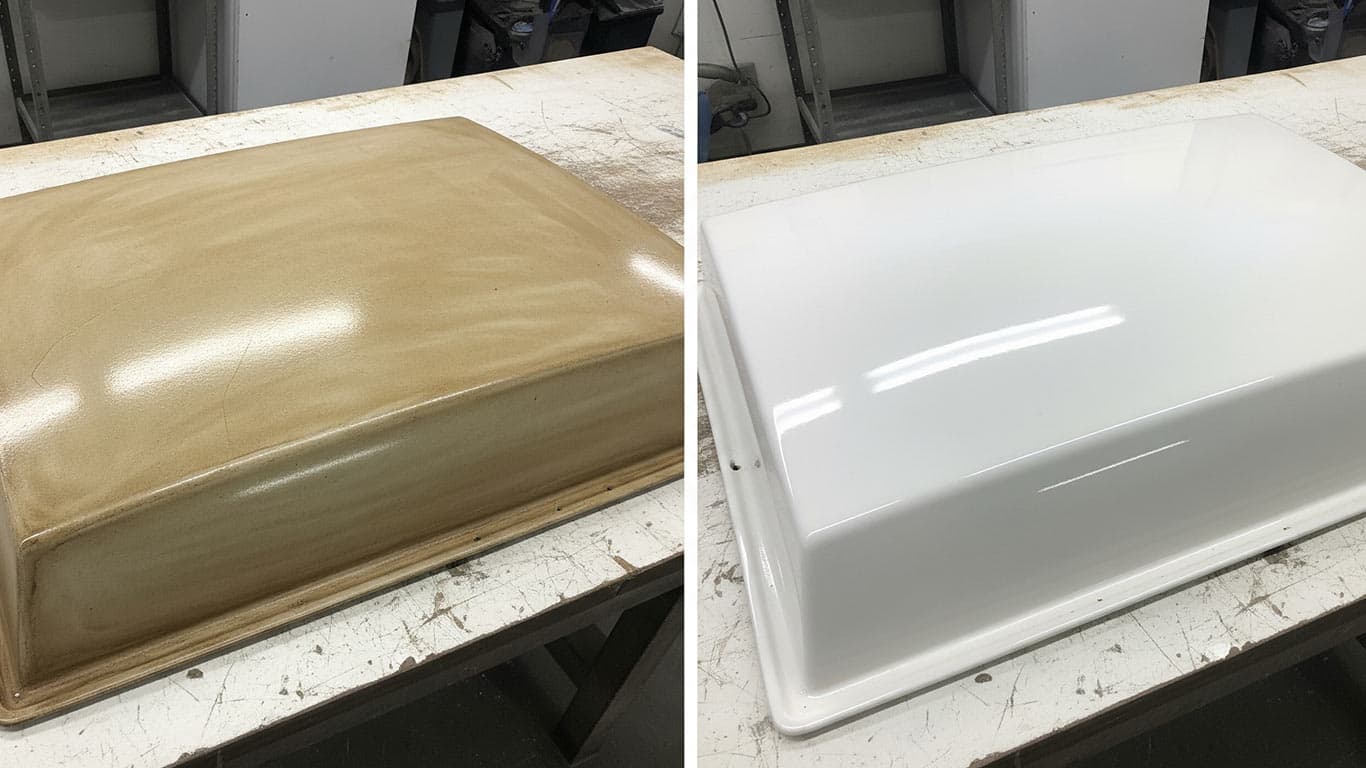

Fiberglass
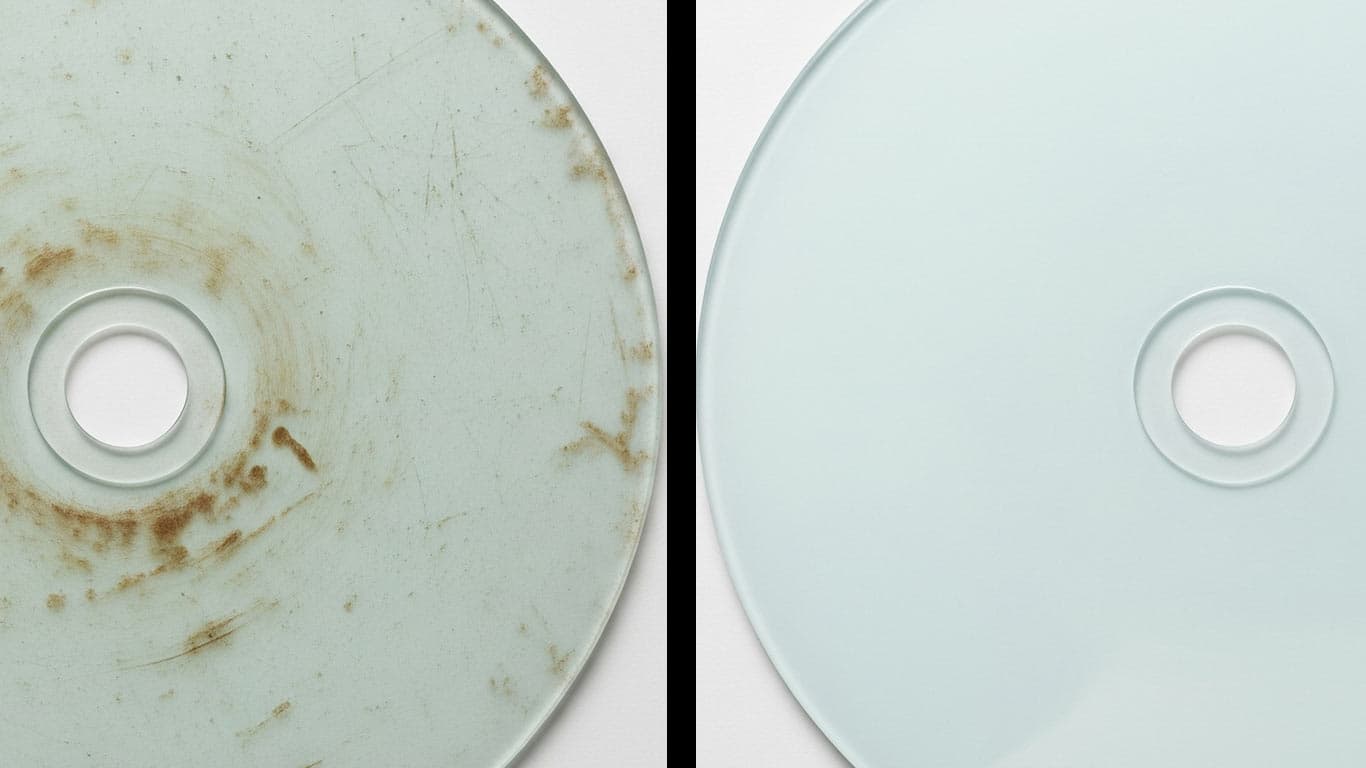

Float Glass
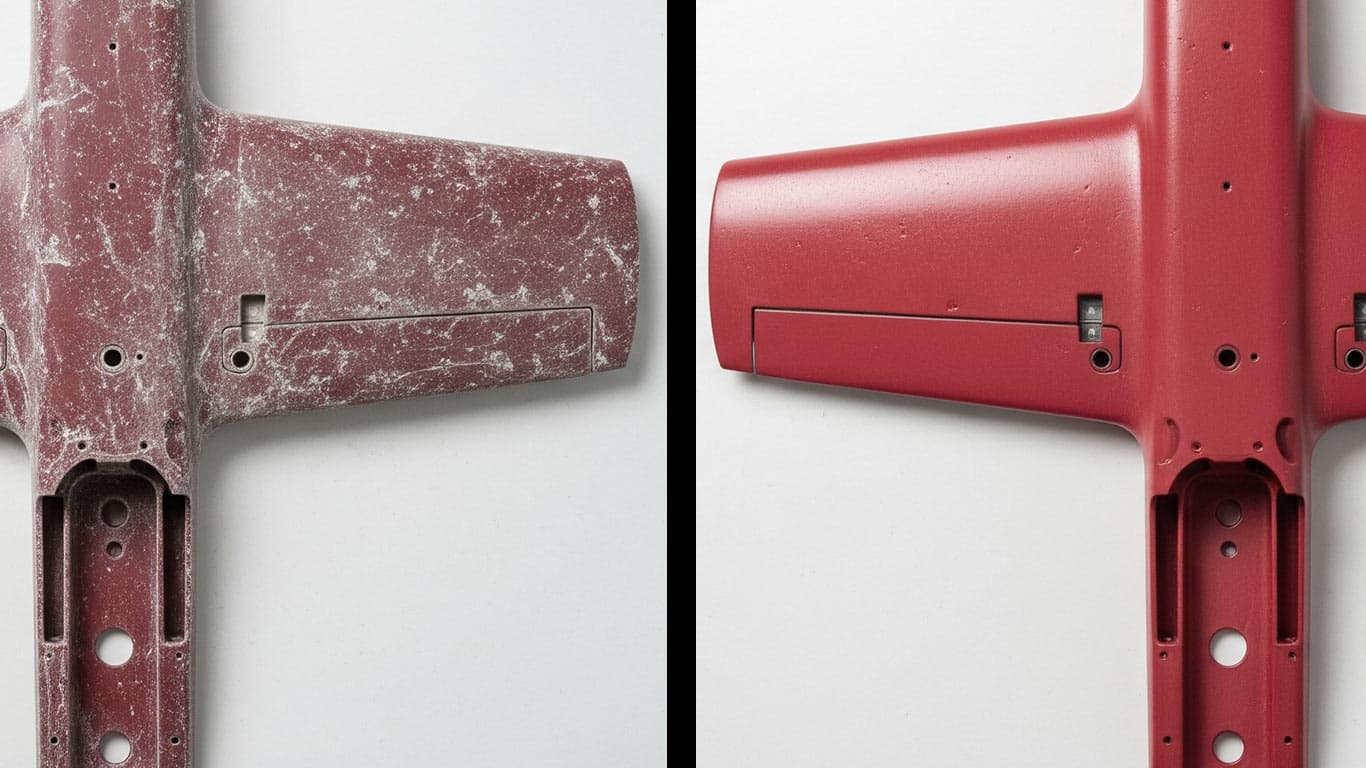

Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymers GFRP
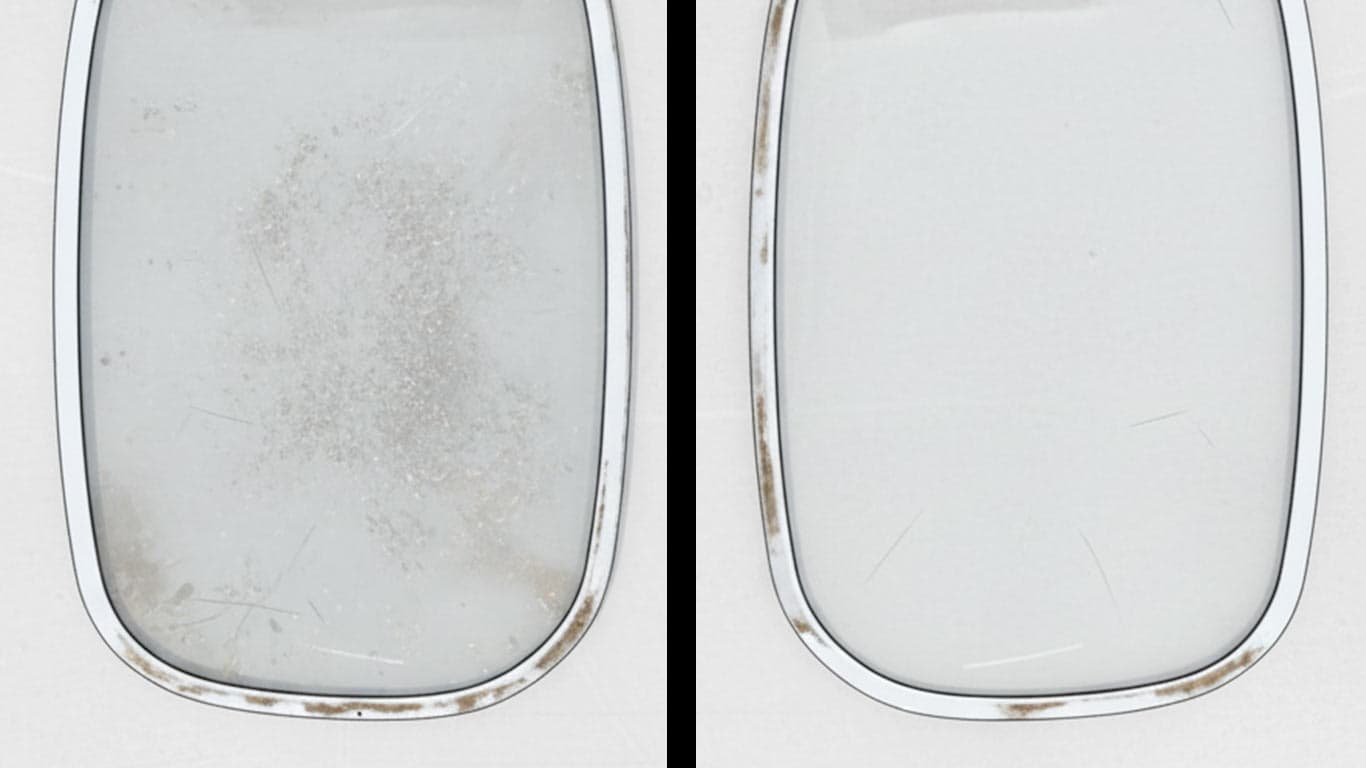
Gorilla Glass

Granite

Iron
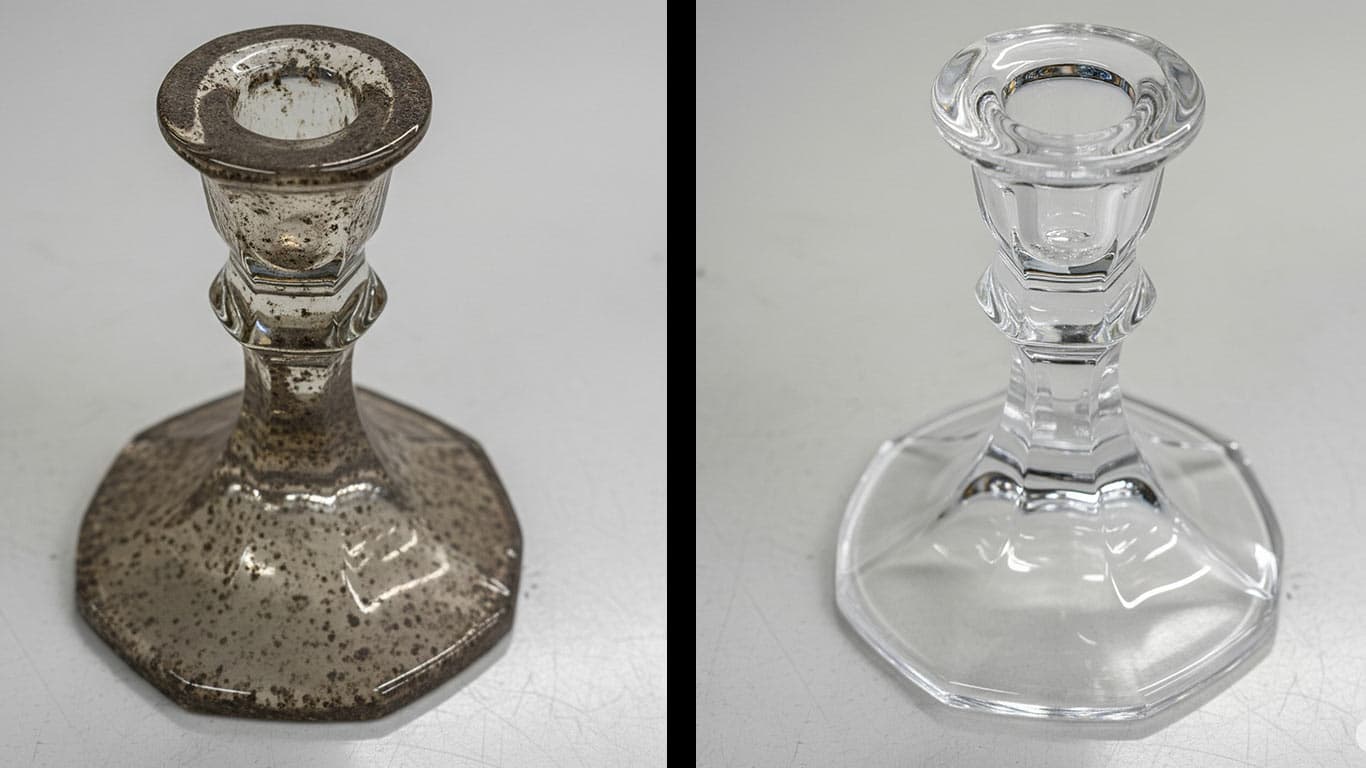

Lead Crystal

Limestone

Magnesium

Marble

Metal Matrix Composites MMCs

Nickel

Phenolic Resin Composites

Polyester Resin Composites

Porcelain

Quartz Glass

Sandstone
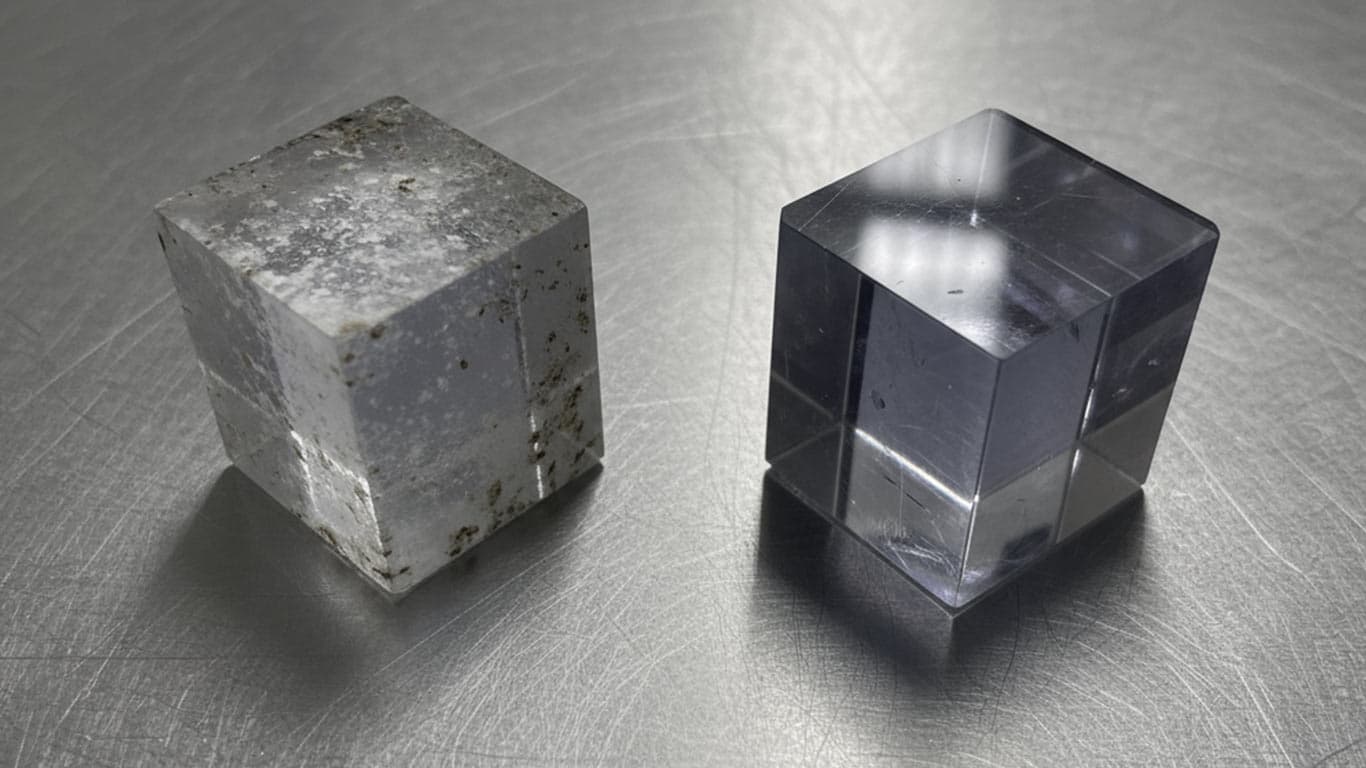

Sapphire Glass

Slate
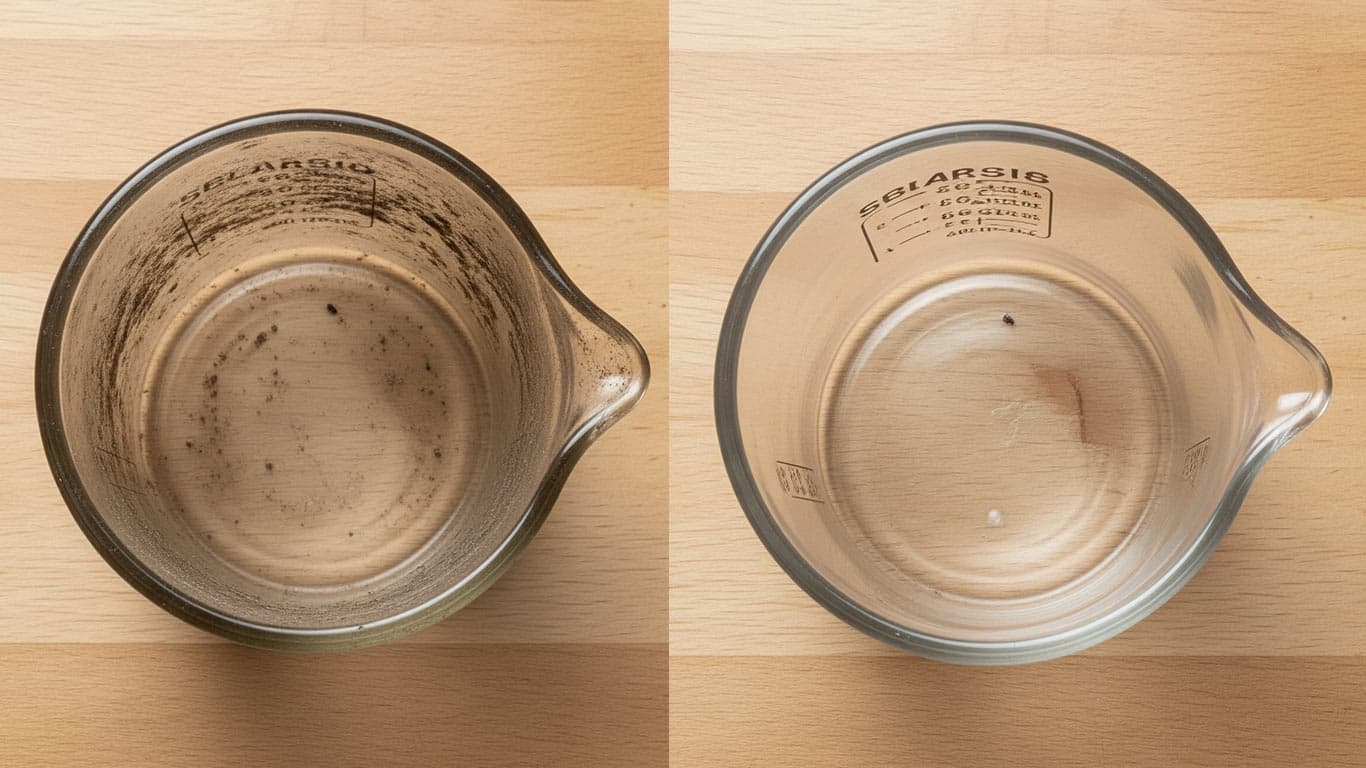

Soda-Lime Glass

Stainless Steel

Steel
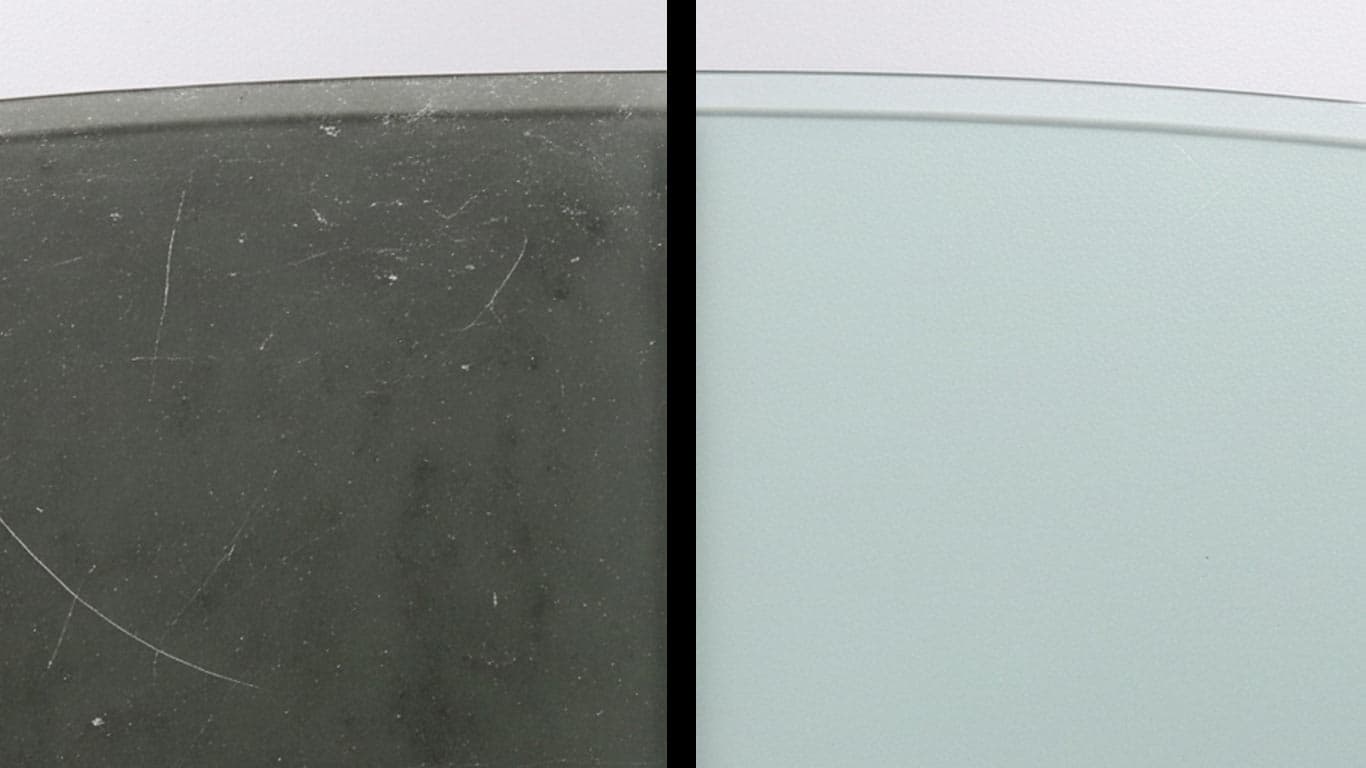

Tempered Glass

Terracotta

Titanium

Titanium Carbide

Tool Steel
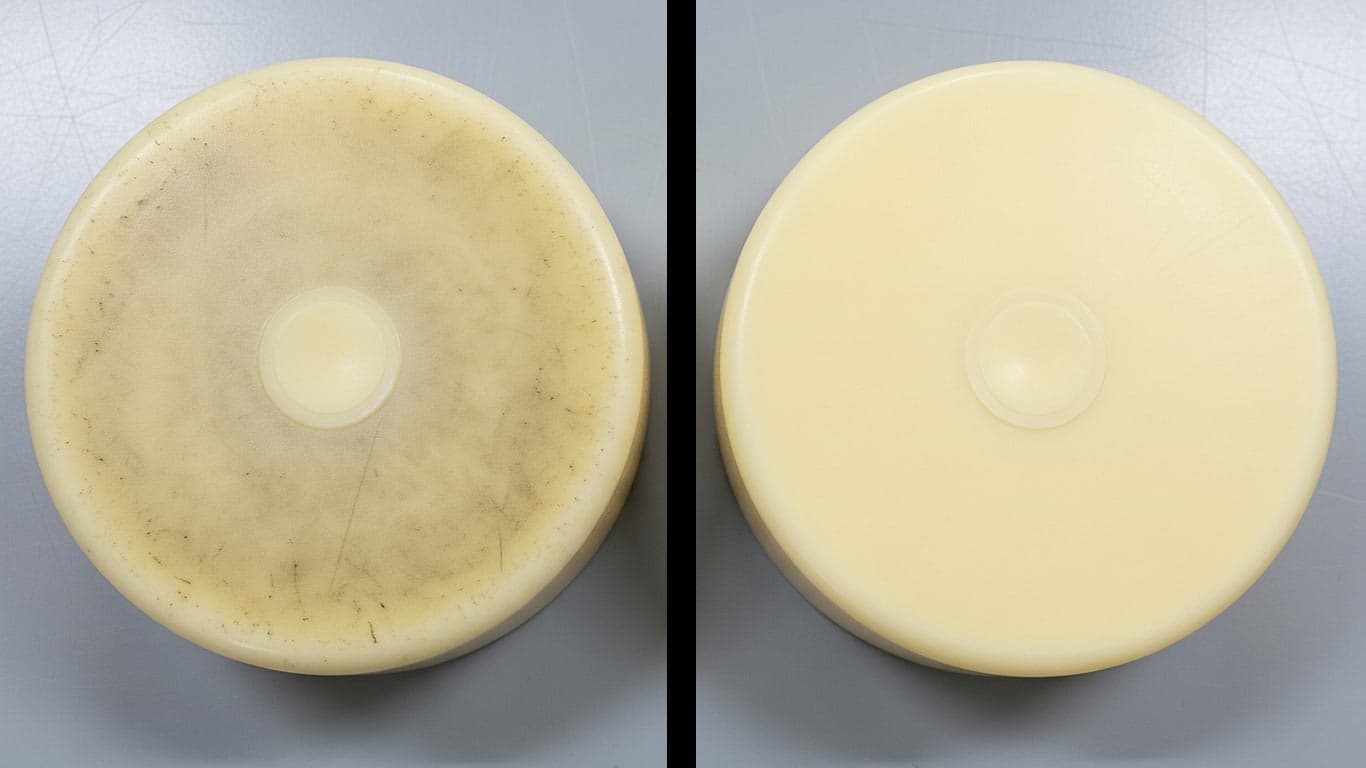

Urethane Composites

Zinc

Aluminosilicate Glass

Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)

Stainless Steel 316

Stainless Steel 304

Aluminum Bronze

Aluminum Nitride

Titanium Nitride
Concrete Dust Deposits Dataset
License: Creative Commons BY 4.0 • Free to use with attribution •Learn more



